Kyuwon Kim
GSta: Efficient Training Scheme with Siestaed Gaussians for Monocular 3D Scene Reconstruction
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:Gaussian Splatting (GS) is a popular approach for 3D reconstruction, mostly due to its ability to converge reasonably fast, faithfully represent the scene and render (novel) views in a fast fashion. However, it suffers from large storage and memory requirements, and its training speed still lags behind the hash-grid based radiance field approaches (e.g. Instant-NGP), which makes it especially difficult to deploy them in robotics scenarios, where 3D reconstruction is crucial for accurate operation. In this paper, we propose GSta that dynamically identifies Gaussians that have converged well during training, based on their positional and color gradient norms. By forcing such Gaussians into a siesta and stopping their updates (freezing) during training, we improve training speed with competitive accuracy compared to state of the art. We also propose an early stopping mechanism based on the PSNR values computed on a subset of training images. Combined with other improvements, such as integrating a learning rate scheduler, GSta achieves an improved Pareto front in convergence speed, memory and storage requirements, while preserving quality. We also show that GSta can improve other methods and complement orthogonal approaches in efficiency improvement; once combined with Trick-GS, GSta achieves up to 5x faster training, 16x smaller disk size compared to vanilla GS, while having comparable accuracy and consuming only half the peak memory. More visualisations are available at https://anilarmagan.github.io/SRUK-GSta.
Enhancing Korean Dependency Parsing with Morphosyntactic Features
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces UniDive for Korean, an integrated framework that bridges Universal Dependencies (UD) and Universal Morphology (UniMorph) to enhance the representation and processing of Korean {morphosyntax}. Korean's rich inflectional morphology and flexible word order pose challenges for existing frameworks, which often treat morphology and syntax separately, leading to inconsistencies in linguistic analysis. UniDive unifies syntactic and morphological annotations by preserving syntactic dependencies while incorporating UniMorph-derived features, improving consistency in annotation. We construct an integrated dataset and apply it to dependency parsing, demonstrating that enriched morphosyntactic features enhance parsing accuracy, particularly in distinguishing grammatical relations influenced by morphology. Our experiments, conducted with both encoder-only and decoder-only models, confirm that explicit morphological information contributes to more accurate syntactic analysis.
K-UD: Revising Korean Universal Dependencies Guidelines
Dec 01, 2024

Abstract:Critique has surfaced concerning the existing linguistic annotation framework for Korean Universal Dependencies (UDs), particularly in relation to syntactic relationships. In this paper, our primary objective is to refine the definition of syntactic dependency of UDs within the context of analyzing the Korean language. Our aim is not only to achieve a consensus within UDs but also to garner agreement beyond the UD framework for analyzing Korean sentences using dependency structure, by establishing a linguistic consensus model.
Unlocking Korean Verbs: A User-Friendly Exploration into the Verb Lexicon
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:The Sejong dictionary dataset offers a valuable resource, providing extensive coverage of morphology, syntax, and semantic representation. This dataset can be utilized to explore linguistic information in greater depth. The labeled linguistic structures within this dataset form the basis for uncovering relationships between words and phrases and their associations with target verbs. This paper introduces a user-friendly web interface designed for the collection and consolidation of verb-related information, with a particular focus on subcategorization frames. Additionally, it outlines our efforts in mapping this information by aligning subcategorization frames with corresponding illustrative sentence examples. Furthermore, we provide a Python library that would simplify syntactic parsing and semantic role labeling. These tools are intended to assist individuals interested in harnessing the Sejong dictionary dataset to develop applications for Korean language processing.
Two-timescale Extragradient for Finding Local Minimax Points
May 25, 2023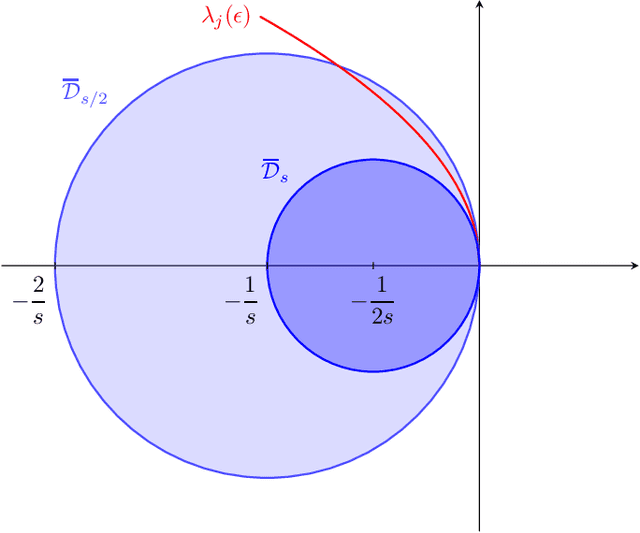
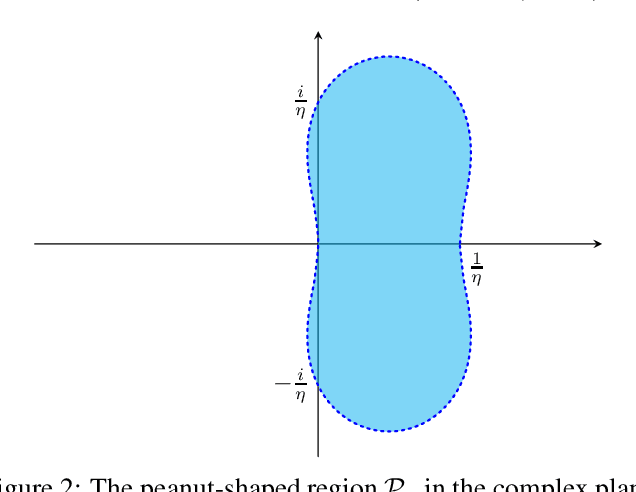
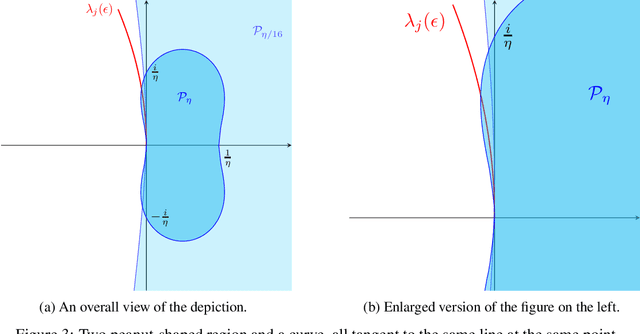
Abstract:Minimax problems are notoriously challenging to optimize. However, we demonstrate that the two-timescale extragradient can be a viable solution. By utilizing dynamical systems theory, we show that it converges to points that satisfy the second-order necessary condition of local minimax points, under a mild condition. This work surpasses all previous results as we eliminate a crucial assumption that the Hessian, with respect to the maximization variable, is nondegenerate.
K-UniMorph: Korean Universal Morphology and its Feature Schema
May 17, 2023Abstract:We present in this work a new Universal Morphology dataset for Korean. Previously, the Korean language has been underrepresented in the field of morphological paradigms amongst hundreds of diverse world languages. Hence, we propose this Universal Morphological paradigms for the Korean language that preserve its distinct characteristics. For our K-UniMorph dataset, we outline each grammatical criterion in detail for the verbal endings, clarify how to extract inflected forms, and demonstrate how we generate the morphological schemata. This dataset adopts morphological feature schema from Sylak-Glassman et al. (2015) and Sylak-Glassman (2016) for the Korean language as we extract inflected verb forms from the Sejong morphologically analyzed corpus that is one of the largest annotated corpora for Korean. During the data creation, our methodology also includes investigating the correctness of the conversion from the Sejong corpus. Furthermore, we carry out the inflection task using three different Korean word forms: letters, syllables and morphemes. Finally, we discuss and describe future perspectives on Korean morphological paradigms and the dataset.
Tunnel Facility-based Vehicle Localization in Highway Tunnel using 3D LIDAR
Dec 24, 2020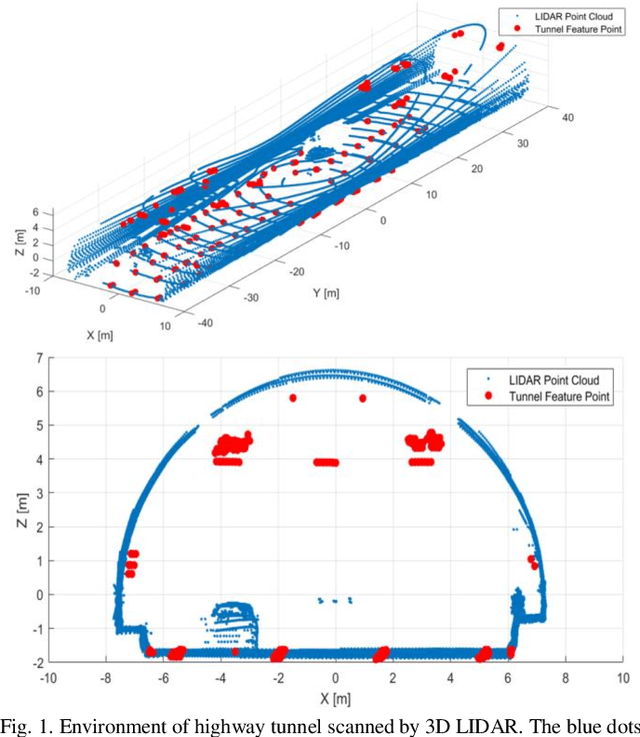
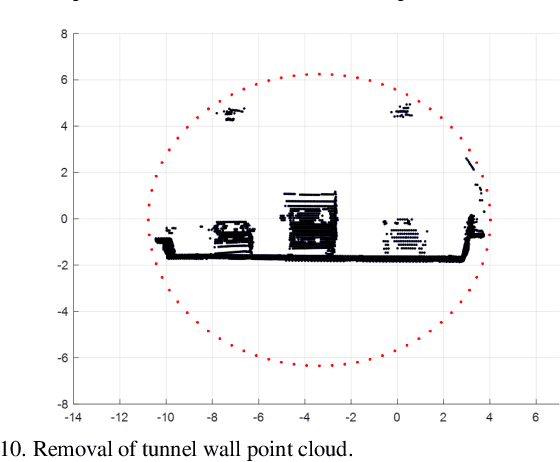
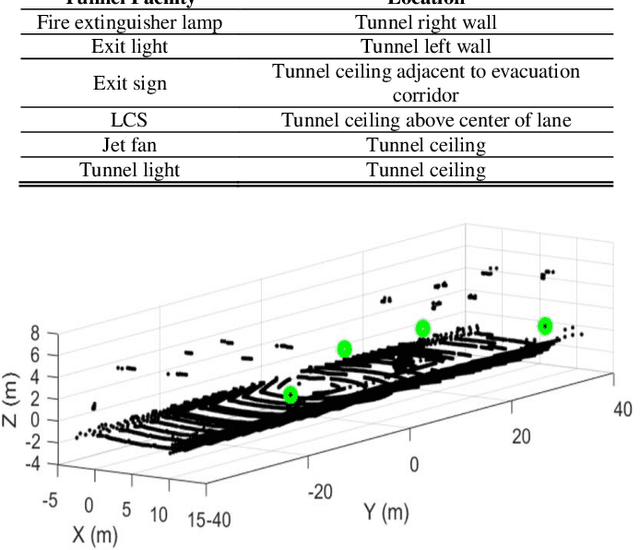
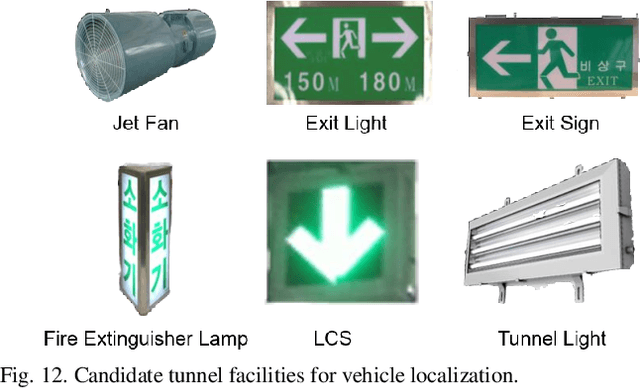
Abstract:Vehicle localization in highway tunnels is a challenging issue for autonomous vehicle navigation. Since GPS signals from satellites cannot be received inside a highway tunnel, map-aided localization is essential. However, the environment around the tunnel is composed mostly of an elliptical wall. Thereby, the unique feature points for map matching are few unlike the case outdoors. As a result, it is a very difficult condition to perform vehicle navigation in the tunnel with existing map-aided localization. In this paper, we propose tunnel facility-based precise vehicle localization in highway tunnels using 3D LIDAR. For vehicle localization in a highway tunnel, a point landmark map that stores the center points of tunnel facilities and a probability distribution map that stores the probability distributions of the lane markings are used. Point landmark-based localization is possible regardless of the number of feature points, if only representative points of an object can be extracted. Therefore, it is a suitable localization method for highway tunnels where the feature points are few. The tunnel facility points were extracted using 3D LIDAR. Position estimation is conducted using an EKF-based navigation filter. The proposed localization algorithm is verified through experiments using actual highway driving data. The experimental results verify that the tunnel facility-based vehicle localization yields precise results in real time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge