Eunkyul Leah Jo
K-UD: Revising Korean Universal Dependencies Guidelines
Dec 01, 2024

Abstract:Critique has surfaced concerning the existing linguistic annotation framework for Korean Universal Dependencies (UDs), particularly in relation to syntactic relationships. In this paper, our primary objective is to refine the definition of syntactic dependency of UDs within the context of analyzing the Korean language. Our aim is not only to achieve a consensus within UDs but also to garner agreement beyond the UD framework for analyzing Korean sentences using dependency structure, by establishing a linguistic consensus model.
Unlocking Korean Verbs: A User-Friendly Exploration into the Verb Lexicon
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:The Sejong dictionary dataset offers a valuable resource, providing extensive coverage of morphology, syntax, and semantic representation. This dataset can be utilized to explore linguistic information in greater depth. The labeled linguistic structures within this dataset form the basis for uncovering relationships between words and phrases and their associations with target verbs. This paper introduces a user-friendly web interface designed for the collection and consolidation of verb-related information, with a particular focus on subcategorization frames. Additionally, it outlines our efforts in mapping this information by aligning subcategorization frames with corresponding illustrative sentence examples. Furthermore, we provide a Python library that would simplify syntactic parsing and semantic role labeling. These tools are intended to assist individuals interested in harnessing the Sejong dictionary dataset to develop applications for Korean language processing.
jp-evalb: Robust Alignment-based PARSEVAL Measures
May 23, 2024Abstract:We introduce an evaluation system designed to compute PARSEVAL measures, offering a viable alternative to \texttt{evalb} commonly used for constituency parsing evaluation. The widely used \texttt{evalb} script has traditionally been employed for evaluating the accuracy of constituency parsing results, albeit with the requirement for consistent tokenization and sentence boundaries. In contrast, our approach, named \texttt{jp-evalb}, is founded on an alignment method. This method aligns sentences and words when discrepancies arise. It aims to overcome several known issues associated with \texttt{evalb} by utilizing the `jointly preprocessed (JP)' alignment-based method. We introduce a more flexible and adaptive framework, ultimately contributing to a more accurate assessment of constituency parsing performance.
K-UniMorph: Korean Universal Morphology and its Feature Schema
May 17, 2023Abstract:We present in this work a new Universal Morphology dataset for Korean. Previously, the Korean language has been underrepresented in the field of morphological paradigms amongst hundreds of diverse world languages. Hence, we propose this Universal Morphological paradigms for the Korean language that preserve its distinct characteristics. For our K-UniMorph dataset, we outline each grammatical criterion in detail for the verbal endings, clarify how to extract inflected forms, and demonstrate how we generate the morphological schemata. This dataset adopts morphological feature schema from Sylak-Glassman et al. (2015) and Sylak-Glassman (2016) for the Korean language as we extract inflected verb forms from the Sejong morphologically analyzed corpus that is one of the largest annotated corpora for Korean. During the data creation, our methodology also includes investigating the correctness of the conversion from the Sejong corpus. Furthermore, we carry out the inflection task using three different Korean word forms: letters, syllables and morphemes. Finally, we discuss and describe future perspectives on Korean morphological paradigms and the dataset.
Yet Another Format of Universal Dependencies for Korean
Sep 20, 2022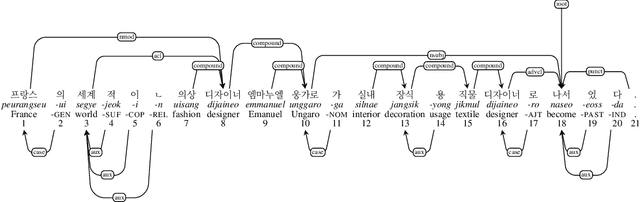

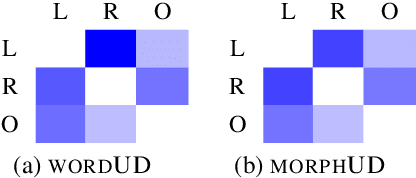
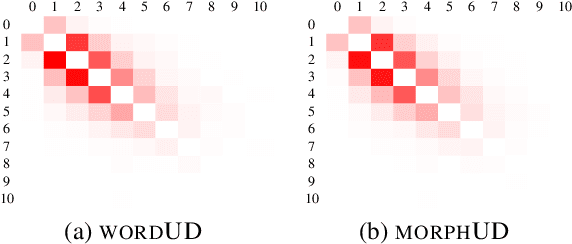
Abstract:In this study, we propose a morpheme-based scheme for Korean dependency parsing and adopt the proposed scheme to Universal Dependencies. We present the linguistic rationale that illustrates the motivation and the necessity of adopting the morpheme-based format, and develop scripts that convert between the original format used by Universal Dependencies and the proposed morpheme-based format automatically. The effectiveness of the proposed format for Korean dependency parsing is then testified by both statistical and neural models, including UDPipe and Stanza, with our carefully constructed morpheme-based word embedding for Korean. morphUD outperforms parsing results for all Korean UD treebanks, and we also present detailed error analyses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge