Koryna Lewandowska
LucidPPN: Unambiguous Prototypical Parts Network for User-centric Interpretable Computer Vision
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Prototypical parts networks combine the power of deep learning with the explainability of case-based reasoning to make accurate, interpretable decisions. They follow the this looks like that reasoning, representing each prototypical part with patches from training images. However, a single image patch comprises multiple visual features, such as color, shape, and texture, making it difficult for users to identify which feature is important to the model. To reduce this ambiguity, we introduce the Lucid Prototypical Parts Network (LucidPPN), a novel prototypical parts network that separates color prototypes from other visual features. Our method employs two reasoning branches: one for non-color visual features, processing grayscale images, and another focusing solely on color information. This separation allows us to clarify whether the model's decisions are based on color, shape, or texture. Additionally, LucidPPN identifies prototypical parts corresponding to semantic parts of classified objects, making comparisons between data classes more intuitive, e.g., when two bird species might differ primarily in belly color. Our experiments demonstrate that the two branches are complementary and together achieve results comparable to baseline methods. More importantly, LucidPPN generates less ambiguous prototypical parts, enhancing user understanding.
Interpretable Image Classification with Differentiable Prototypes Assignment
Dec 06, 2021



Abstract:We introduce ProtoPool, an interpretable image classification model with a pool of prototypes shared by the classes. The training is more straightforward than in the existing methods because it does not require the pruning stage. It is obtained by introducing a fully differentiable assignment of prototypes to particular classes. Moreover, we introduce a novel focal similarity function to focus the model on the rare foreground features. We show that ProtoPool obtains state-of-the-art accuracy on the CUB-200-2011 and the Stanford Cars datasets, substantially reducing the number of prototypes. We provide a theoretical analysis of the method and a user study to show that our prototypes are more distinctive than those obtained with competitive methods.
Visual Probing: Cognitive Framework for Explaining Self-Supervised Image Representations
Jun 21, 2021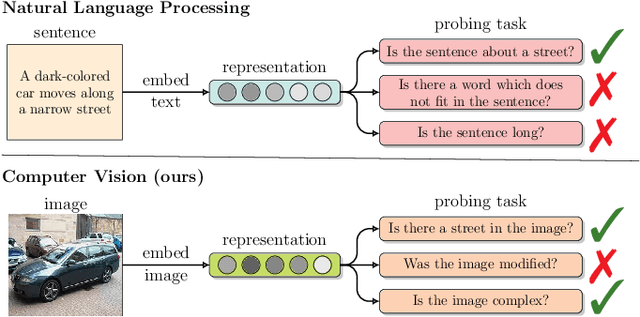
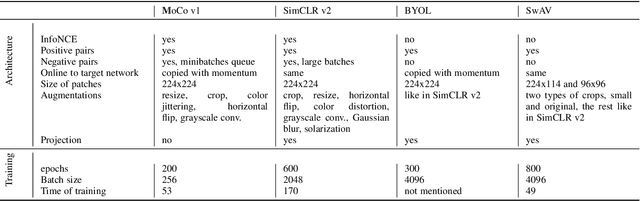
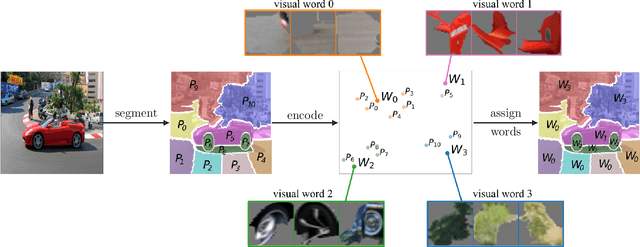
Abstract:Recently introduced self-supervised methods for image representation learning provide on par or superior results to their fully supervised competitors, yet the corresponding efforts to explain the self-supervised approaches lag behind. Motivated by this observation, we introduce a novel visual probing framework for explaining the self-supervised models by leveraging probing tasks employed previously in natural language processing. The probing tasks require knowledge about semantic relationships between image parts. Hence, we propose a systematic approach to obtain analogs of natural language in vision, such as visual words, context, and taxonomy. Our proposal is grounded in Marr's computational theory of vision and concerns features like textures, shapes, and lines. We show the effectiveness and applicability of those analogs in the context of explaining self-supervised representations. Our key findings emphasize that relations between language and vision can serve as an effective yet intuitive tool for discovering how machine learning models work, independently of data modality. Our work opens a plethora of research pathways towards more explainable and transparent AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge