Konstantinos Drossos
Beyond Omnidirectional: Neural Ambisonics Encoding for Arbitrary Microphone Directivity Patterns using Cross-Attention
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We present a deep neural network approach for encoding microphone array signals into Ambisonics that generalizes to arbitrary microphone array configurations with fixed microphone count but varying locations and frequency-dependent directional characteristics. Unlike previous methods that rely only on array geometry as metadata, our approach uses directional array transfer functions, enabling accurate characterization of real-world arrays. The proposed architecture employs separate encoders for audio and directional responses, combining them through cross-attention mechanisms to generate array-independent spatial audio representations. We evaluate the method on simulated data in two settings: a mobile phone with complex body scattering, and a free-field condition, both with varying numbers of sound sources in reverberant environments. Evaluations demonstrate that our approach outperforms both conventional digital signal processing-based methods and existing deep neural network solutions. Furthermore, using array transfer functions instead of geometry as metadata input improves accuracy on realistic arrays.
Discriminating real and synthetic super-resolved audio samples using embedding-based classifiers
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models have recently achieved state-of-the-art performance in audio super-resolution (ADSR), producing perceptually convincing wideband audio from narrowband inputs. However, existing evaluations primarily rely on signal-level or perceptual metrics, leaving open the question of how closely the distributions of synthetic super-resolved and real wideband audio match. Here we address this problem by analyzing the separability of real and super-resolved audio in various embedding spaces. We consider both middle-band ($4\to 16$~kHz) and full-band ($16\to 48$~kHz) upsampling tasks for speech and music, training linear classifiers to distinguish real from synthetic samples based on multiple types of audio embeddings. Comparisons with objective metrics and subjective listening tests reveal that embedding-based classifiers achieve near-perfect separation, even when the generated audio attains high perceptual quality and state-of-the-art metric scores. This behavior is consistent across datasets and models, including recent diffusion-based approaches, highlighting a persistent gap between perceptual quality and true distributional fidelity in ADSR models.
Lightweight DNN for Full-Band Speech Denoising on Mobile Devices: Exploiting Long and Short Temporal Patterns
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Speech denoising (SD) is an important task of many, if not all, modern signal processing chains used in devices and for everyday-life applications. While there are many published and powerful deep neural network (DNN)-based methods for SD, few are optimized for resource-constrained platforms such as mobile devices. Additionally, most DNN-based methods for SD are not focusing on full-band (FB) signals, i.e. having 48 kHz sampling rate, and/or low latency cases. In this paper we present a causal, low latency, and lightweight DNN-based method for full-band SD, leveraging both short and long temporal patterns. The method is based on a modified UNet architecture employing look-back frames, temporal spanning of convolutional kernels, and recurrent neural networks for exploiting short and long temporal patterns in the signal and estimated denoising mask. The DNN operates on a causal frame-by-frame basis taking as an input the STFT magnitude, utilizes inverted bottlenecks inspired by MobileNet, employs causal instance normalization for channel-wise normalization, and achieves a real-time factor below 0.02 when deployed on a modern mobile phone. The proposed method is evaluated using established speech denoising metrics and publicly available datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in achieving an (SI-)SDR value that outperforms existing FB and low latency SD methods.
Multi-Utterance Speech Separation and Association Trained on Short Segments
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Current deep neural network (DNN) based speech separation faces a fundamental challenge -- while the models need to be trained on short segments due to computational constraints, real-world applications typically require processing significantly longer recordings with multiple utterances per speaker than seen during training. In this paper, we investigate how existing approaches perform in this challenging scenario and propose a frequency-temporal recurrent neural network (FTRNN) that effectively bridges this gap. Our FTRNN employs a full-band module to model frequency dependencies within each time frame and a sub-band module that models temporal patterns in each frequency band. Despite being trained on short fixed-length segments of 10 s, our model demonstrates robust separation when processing signals significantly longer than training segments (21-121 s) and preserves speaker association across utterance gaps exceeding those seen during training. Unlike the conventional segment-separation-stitch paradigm, our lightweight approach (0.9 M parameters) performs inference on long audio without segmentation, eliminating segment boundary distortions while simplifying deployment. Experimental results demonstrate the generalization ability of FTRNN for multi-utterance speech separation and speaker association.
Attractor-Based Speech Separation of Multiple Utterances by Unknown Number of Speakers
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of single-channel speech separation, where the number of speakers is unknown, and each speaker may speak multiple utterances. We propose a speech separation model that simultaneously performs separation, dynamically estimates the number of speakers, and detects individual speaker activities by integrating an attractor module. The proposed system outperforms existing methods by introducing an attractor-based architecture that effectively combines local and global temporal modeling for multi-utterance scenarios. To evaluate the method in reverberant and noisy conditions, a multi-speaker multi-utterance dataset was synthesized by combining Librispeech speech signals with WHAM! noise signals. The results demonstrate that the proposed system accurately estimates the number of sources. The system effectively detects source activities and separates the corresponding utterances into correct outputs in both known and unknown source count scenarios.
Knowledge Distillation for Speech Denoising by Latent Representation Alignment with Cosine Distance
May 06, 2025



Abstract:Speech denoising is a generally adopted and impactful task, appearing in many common and everyday-life use cases. Although there are very powerful methods published, most of those are too complex for deployment in everyday and low-resources computational environments, like hand-held devices, intelligent glasses, hearing aids, etc. Knowledge distillation (KD) is a prominent way for alleviating this complexity mismatch and is based on the transferring/distilling of knowledge from a pre-trained complex model, the teacher, to another less complex one, the student. Existing KD methods for speech denoising are based on processes that potentially hamper the KD by bounding the learning of the student to the distribution, information ordering, and feature dimensionality learned by the teacher. In this paper, we present and assess a method that tries to treat this issue, by exploiting the well-known denoising-autoencoder framework, the linear inverted bottlenecks, and the properties of the cosine similarity. We use a public dataset and conduct repeated experiments with different mismatching scenarios between the teacher and the student, reporting the mean and standard deviation of the metrics of our method and another, state-of-the-art method that is used as a baseline. Our results show that with the proposed method, the student can perform better and can also retain greater mismatching conditions compared to the teacher.
Gen-A: Generalizing Ambisonics Neural Encoding to Unseen Microphone Arrays
Jan 14, 2025


Abstract:Using deep neural networks (DNNs) for encoding of microphone array (MA) signals to the Ambisonics spatial audio format can surpass certain limitations of established conventional methods, but existing DNN-based methods need to be trained separately for each MA. This paper proposes a DNN-based method for Ambisonics encoding that can generalize to arbitrary MA geometries unseen during training. The method takes as inputs the MA geometry and MA signals and uses a multi-level encoder consisting of separate paths for geometry and signal data, where geometry features inform the signal encoder at each level. The method is validated in simulated anechoic and reverberant conditions with one and two sources. The results indicate improvement over conventional encoding across the whole frequency range for dry scenes, while for reverberant scenes the improvement is frequency-dependent.
Representation Learning for Audio Privacy Preservation using Source Separation and Robust Adversarial Learning
Aug 09, 2023



Abstract:Privacy preservation has long been a concern in smart acoustic monitoring systems, where speech can be passively recorded along with a target signal in the system's operating environment. In this study, we propose the integration of two commonly used approaches in privacy preservation: source separation and adversarial representation learning. The proposed system learns the latent representation of audio recordings such that it prevents differentiating between speech and non-speech recordings. Initially, the source separation network filters out some of the privacy-sensitive data, and during the adversarial learning process, the system will learn privacy-preserving representation on the filtered signal. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method by comparing our method against systems without source separation, without adversarial learning, and without both. Overall, our results suggest that the proposed system can significantly improve speech privacy preservation compared to that of using source separation or adversarial learning solely while maintaining good performance in the acoustic monitoring task.
Adversarial Representation Learning for Robust Privacy Preservation in Audio
Apr 29, 2023Abstract:Sound event detection systems are widely used in various applications such as surveillance and environmental monitoring where data is automatically collected, processed, and sent to a cloud for sound recognition. However, this process may inadvertently reveal sensitive information about users or their surroundings, hence raising privacy concerns. In this study, we propose a novel adversarial training method for learning representations of audio recordings that effectively prevents the detection of speech activity from the latent features of the recordings. The proposed method trains a model to generate invariant latent representations of speech-containing audio recordings that cannot be distinguished from non-speech recordings by a speech classifier. The novelty of our work is in the optimization algorithm, where the speech classifier's weights are regularly replaced with the weights of classifiers trained in a supervised manner. This increases the discrimination power of the speech classifier constantly during the adversarial training, motivating the model to generate latent representations in which speech is not distinguishable, even using new speech classifiers trained outside the adversarial training loop. The proposed method is evaluated against a baseline approach with no privacy measures and a prior adversarial training method, demonstrating a significant reduction in privacy violations compared to the baseline approach. Additionally, we show that the prior adversarial method is practically ineffective for this purpose.
Domestic Activity Clustering from Audio via Depthwise Separable Convolutional Autoencoder Network
Aug 04, 2022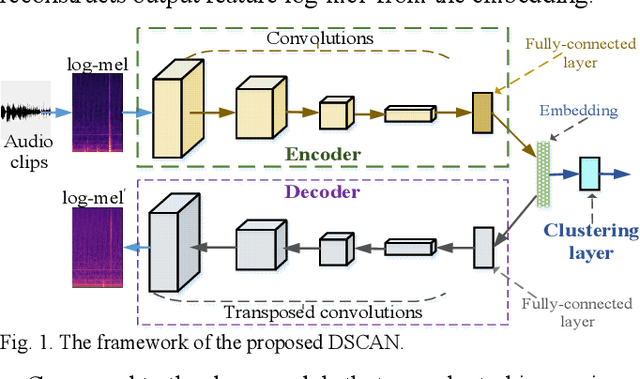
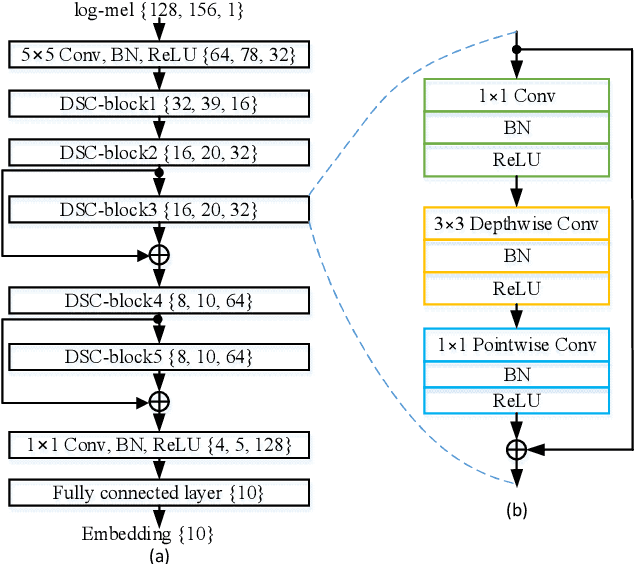
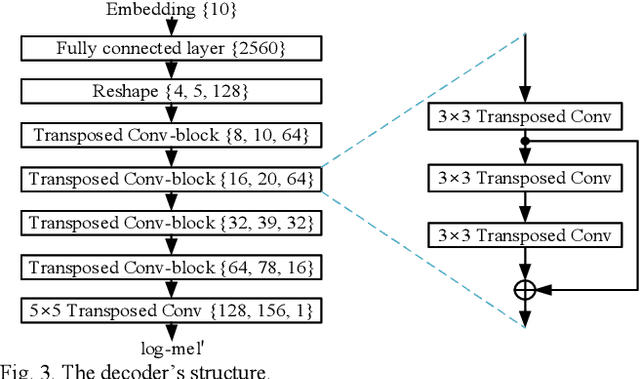
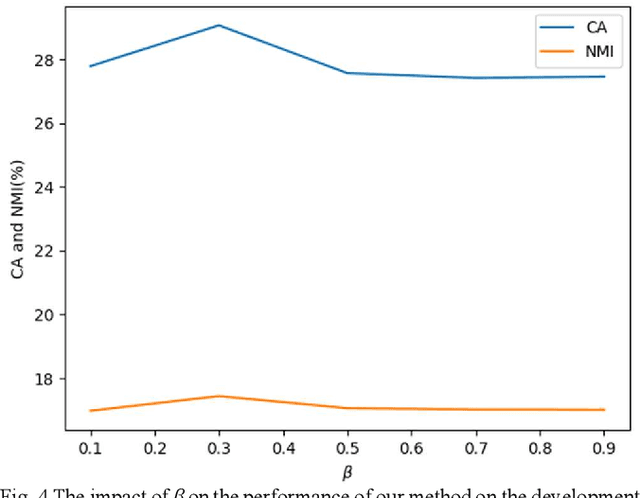
Abstract:Automatic estimation of domestic activities from audio can be used to solve many problems, such as reducing the labor cost for nursing the elderly people. This study focuses on solving the problem of domestic activity clustering from audio. The target of domestic activity clustering is to cluster audio clips which belong to the same category of domestic activity into one cluster in an unsupervised way. In this paper, we propose a method of domestic activity clustering using a depthwise separable convolutional autoencoder network. In the proposed method, initial embeddings are learned by the depthwise separable convolutional autoencoder, and a clustering-oriented loss is designed to jointly optimize embedding refinement and cluster assignment. Different methods are evaluated on a public dataset (a derivative of the SINS dataset) used in the challenge on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) in 2018. Our method obtains the normalized mutual information (NMI) score of 54.46%, and the clustering accuracy (CA) score of 63.64%, and outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of NMI and CA. In addition, both computational complexity and memory requirement of our method is lower than that of previous deep-model-based methods. Codes: https://github.com/vinceasvp/domestic-activity-clustering-from-audio
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge