Koki Tsubota
Comprehensive Comparisons of Uniform Quantization in Deep Image Compression
Mar 01, 2023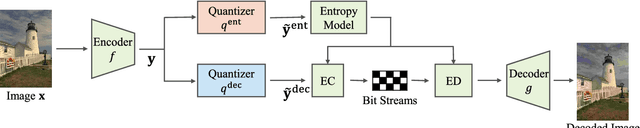

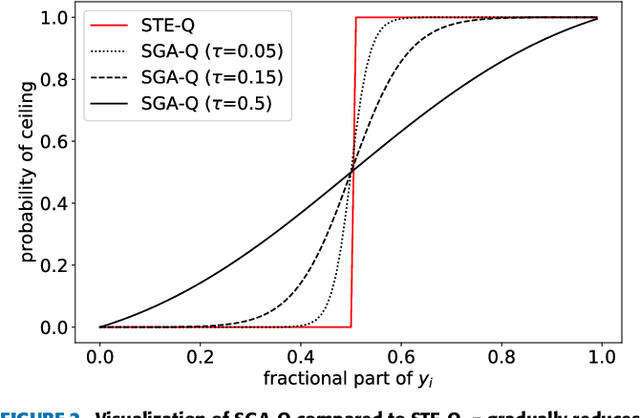
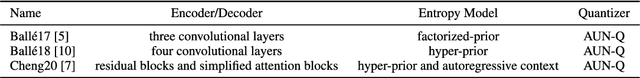
Abstract:In deep image compression, uniform quantization is applied to latent representations obtained by using an auto-encoder architecture for reducing bits and entropy coding. Quantization is a problem encountered in the end-to-end training of deep image compression. Quantization's gradient is zero, and it cannot backpropagate meaningful gradients. Many methods have been proposed to address the approximations of quantization to obtain gradients. However, there have not been equitable comparisons among them. In this study, we comprehensively compare the existing approximations of uniform quantization. Furthermore, we evaluate possible combinations of quantizers for the decoder and the entropy model, as the approximated quantizers can be different for them. We conduct experiments using three network architectures on two test datasets. The experimental results reveal that the best approximated quantization differs by the network architectures, and the best approximations of the three are different from the original ones used for the architectures. We also show that the combination of quantizers that uses universal quantization for the entropy model and differentiable soft quantization for the decoder is a comparatively good choice for different architectures and datasets.
Universal Deep Image Compression via Content-Adaptive Optimization with Adapters
Nov 02, 2022
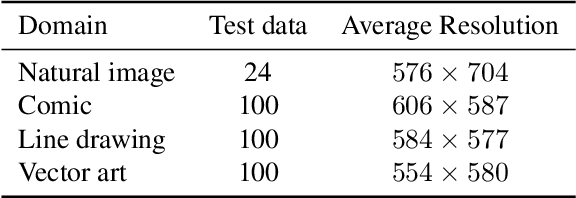
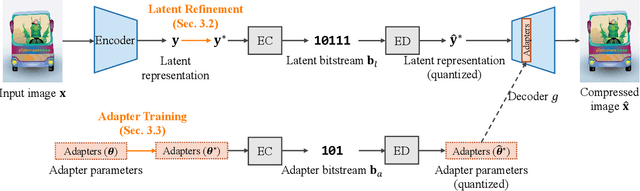
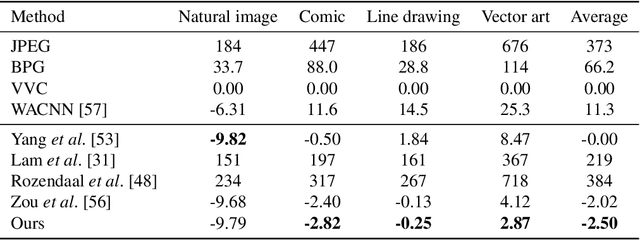
Abstract:Deep image compression performs better than conventional codecs, such as JPEG, on natural images. However, deep image compression is learning-based and encounters a problem: the compression performance deteriorates significantly for out-of-domain images. In this study, we highlight this problem and address a novel task: universal deep image compression. This task aims to compress images belonging to arbitrary domains, such as natural images, line drawings, and comics. To address this problem, we propose a content-adaptive optimization framework; this framework uses a pre-trained compression model and adapts the model to a target image during compression. Adapters are inserted into the decoder of the model. For each input image, our framework optimizes the latent representation extracted by the encoder and the adapter parameters in terms of rate-distortion. The adapter parameters are additionally transmitted per image. For the experiments, a benchmark dataset containing uncompressed images of four domains (natural images, line drawings, comics, and vector arts) is constructed and the proposed universal deep compression is evaluated. Finally, the proposed model is compared with non-adaptive and existing adaptive compression models. The comparison reveals that the proposed model outperforms these. The code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/kktsubota/universal-dic.
Evaluating the Stability of Deep Image Quality Assessment With Respect to Image Scaling
Jul 20, 2022


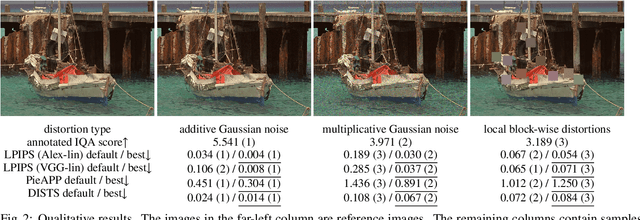
Abstract:Image quality assessment (IQA) is a fundamental metric for image processing tasks (e.g., compression). With full-reference IQAs, traditional IQAs, such as PSNR and SSIM, have been used. Recently, IQAs based on deep neural networks (deep IQAs), such as LPIPS and DISTS, have also been used. It is known that image scaling is inconsistent among deep IQAs, as some perform down-scaling as pre-processing, whereas others instead use the original image size. In this paper, we show that the image scale is an influential factor that affects deep IQA performance. We comprehensively evaluate four deep IQAs on the same five datasets, and the experimental results show that image scale significantly influences IQA performance. We found that the most appropriate image scale is often neither the default nor the original size, and the choice differs depending on the methods and datasets used. We visualized the stability and found that PieAPP is the most stable among the four deep IQAs.
NTIRE 2021 Challenge on Perceptual Image Quality Assessment
May 11, 2021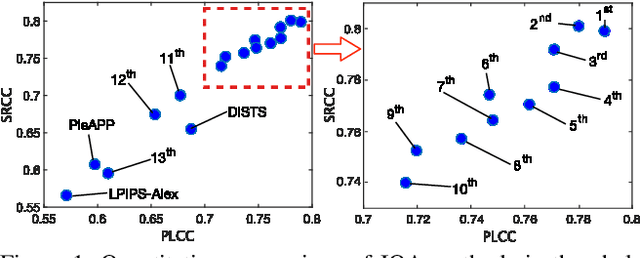
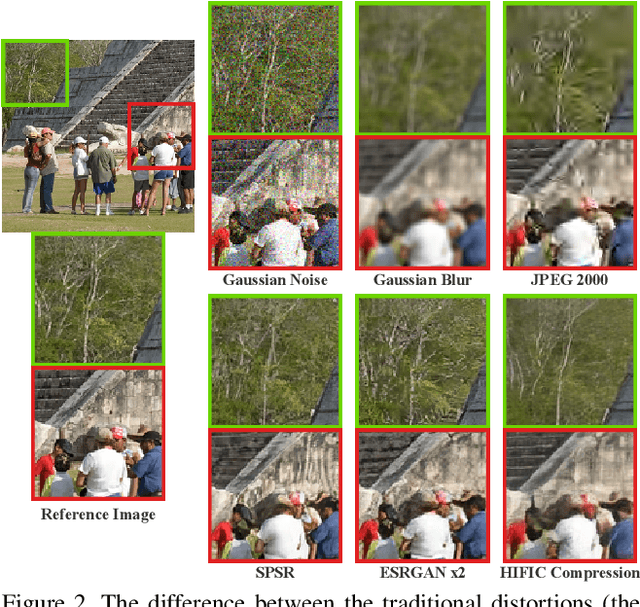
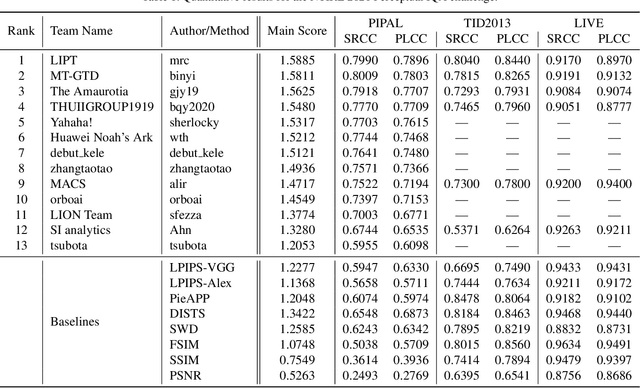

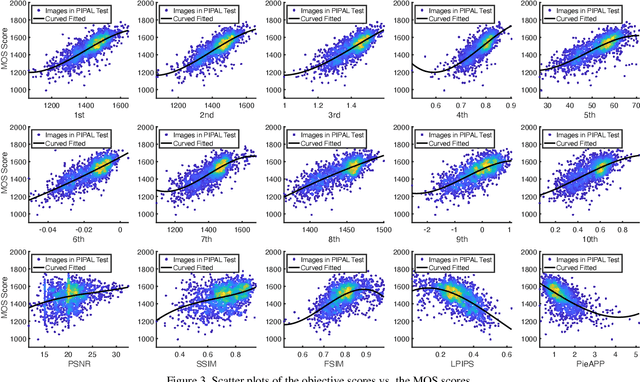
Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2021 challenge on perceptual image quality assessment (IQA), held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement workshop (NTIRE) workshop at CVPR 2021. As a new type of image processing technology, perceptual image processing algorithms based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have produced images with more realistic textures. These output images have completely different characteristics from traditional distortions, thus pose a new challenge for IQA methods to evaluate their visual quality. In comparison with previous IQA challenges, the training and testing datasets in this challenge include the outputs of perceptual image processing algorithms and the corresponding subjective scores. Thus they can be used to develop and evaluate IQA methods on GAN-based distortions. The challenge has 270 registered participants in total. In the final testing stage, 13 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all of them have achieved much better results than existing IQA methods, while the winning method can demonstrate state-of-the-art performance.
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Nov 04, 2020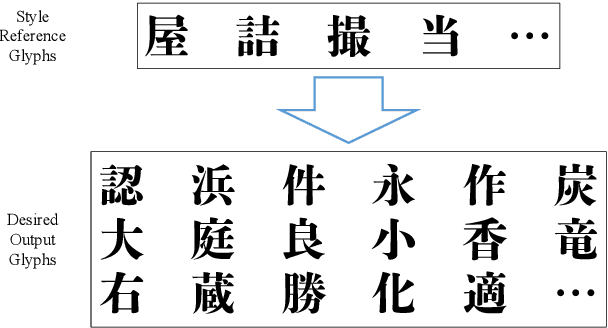
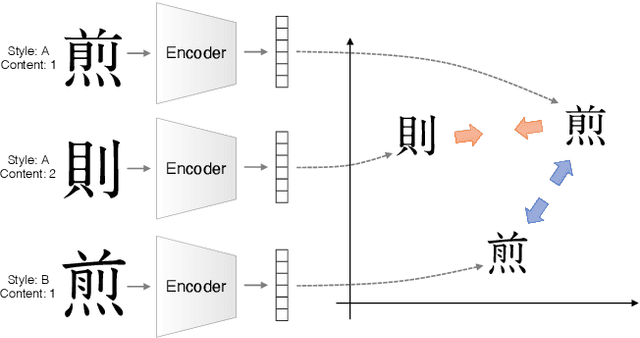
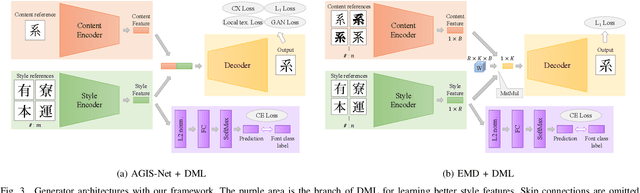

Abstract:Designing fonts for languages with a large number of characters, such as Japanese and Chinese, is an extremely labor-intensive and time-consuming task. In this study, we addressed the problem of automatically generating Japanese typographic fonts from only a few font samples, where the synthesized glyphs are expected to have coherent characteristics, such as skeletons, contours, and serifs. Existing methods often fail to generate fine glyph images when the number of style reference glyphs is extremely limited. Herein, we proposed a simple but powerful framework for extracting better style features. This framework introduces deep metric learning to style encoders. We performed experiments using black-and-white and shape-distinctive font datasets and demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Building a Manga Dataset "Manga109" with Annotations for Multimedia Applications
May 12, 2020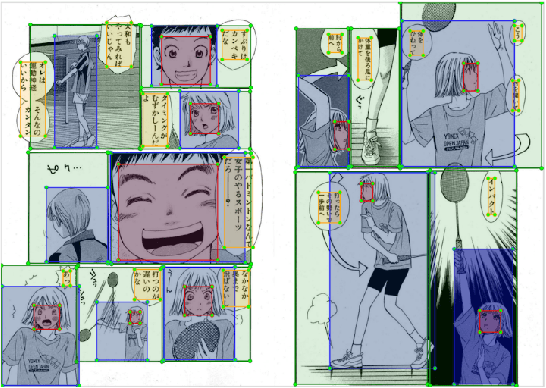
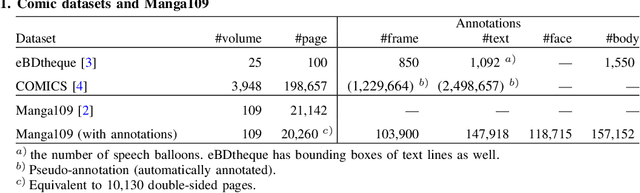
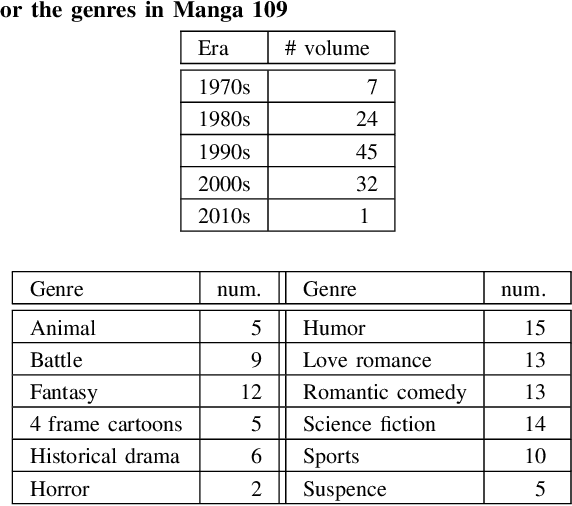
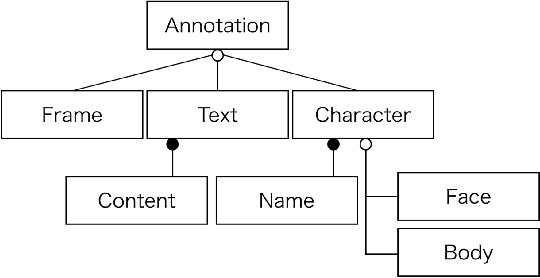
Abstract:Manga, or comics, which are a type of multimodal artwork, have been left behind in the recent trend of deep learning applications because of the lack of a proper dataset. Hence, we built Manga109, a dataset consisting of a variety of 109 Japanese comic books (94 authors and 21,142 pages) and made it publicly available by obtaining author permissions for academic use. We carefully annotated the frames, speech texts, character faces, and character bodies; the total number of annotations exceeds 500k. This dataset provides numerous manga images and annotations, which will be beneficial for use in machine learning algorithms and their evaluation. In addition to academic use, we obtained further permission for a subset of the dataset for industrial use. In this article, we describe the details of the dataset and present a few examples of multimedia processing applications (detection, retrieval, and generation) that apply existing deep learning methods and are made possible by the dataset.
* 10 pages, 8 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge