Kerry Taylor
How Does A Text Preprocessing Pipeline Affect Ontology Syntactic Matching?
Nov 06, 2024Abstract:The generic text preprocessing pipeline, comprising Tokenisation, Normalisation, Stop Words Removal, and Stemming/Lemmatisation, has been implemented in many ontology matching (OM) systems. However, the lack of standardisation in text preprocessing creates diversity in mapping results. In this paper, we investigate the effect of the text preprocessing pipeline on OM tasks at syntactic levels. Our experiments on 8 Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) track repositories with 49 distinct alignments indicate: (1) Tokenisation and Normalisation are currently more effective than Stop Words Removal and Stemming/Lemmatisation; and (2) The selection of Lemmatisation and Stemming is task-specific. We recommend standalone Lemmatisation or Stemming with post-hoc corrections. We find that (3) Porter Stemmer and Snowball Stemmer perform better than Lancaster Stemmer; and that (4) Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging does not help Lemmatisation. To repair less effective Stop Words Removal and Stemming/Lemmatisation used in OM tasks, we propose a novel context-based pipeline repair approach that significantly improves matching correctness and overall matching performance. We also discuss the use of text preprocessing pipeline in the new era of large language models (LLMs).
OM4OV: Leveraging Ontology Matching for Ontology Versioning
Sep 30, 2024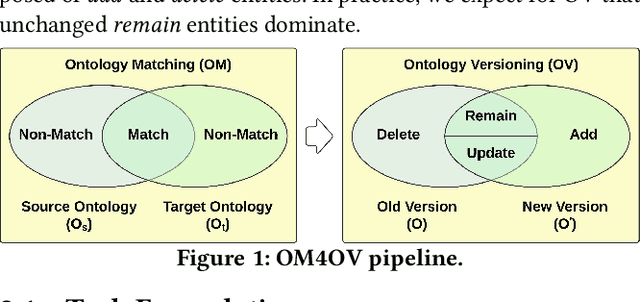
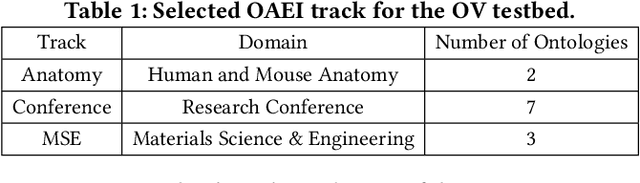
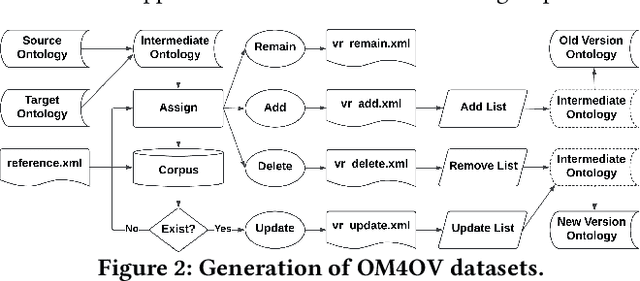
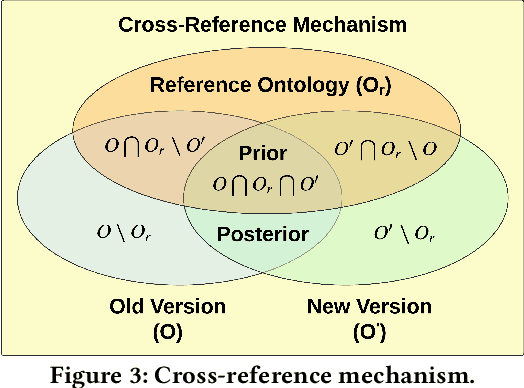
Abstract:Due to the dynamic nature of the semantic web, ontology version control is required to capture time-varying information, most importantly for widely-used ontologies. Despite the long-standing recognition of ontology versioning (OV) as a crucial component for efficient ontology management, the growing size of ontologies and accumulating errors caused by manual labour overwhelm current OV approaches. In this paper, we propose yet another approach to performing OV using existing ontology matching (OM) techniques and systems. We introduce a unified OM4OV pipeline. From an OM perspective, we reconstruct a new task formulation, performance measurement, and dataset construction for OV tasks. Reusing the prior alignment(s) from OM, we also propose a cross-reference mechanism to effectively reduce the matching candidature and improve overall OV performance. We experimentally validate the OM4OV pipeline and its cross-reference mechanism using three datasets from the Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) and exploit insights on OM used for OV tasks.
OAEI-LLM: A Benchmark Dataset for Understanding Large Language Model Hallucinations in Ontology Matching
Sep 21, 2024Abstract:Hallucinations of large language models (LLMs) commonly occur in domain-specific downstream tasks, with no exception in ontology matching (OM). The prevalence of using LLMs for OM raises the need for benchmarks to better understand LLM hallucinations. The OAEI-LLM dataset is an extended version of the Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) datasets that evaluate LLM-specific hallucinations in OM tasks. We outline the methodology used in dataset construction and schema extension, and provide examples of potential use cases.
Agent-OM: Leveraging Large Language Models for Ontology Matching
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM-based agents have become revolutionary in data engineering and have been applied creatively in various domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With thoughtful consideration of several specific challenges to leverage LLMs for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM, consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of simple prompt-based OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve very close results to the best long-standing performance on simple OM tasks and significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
Implicit Mixture of Interpretable Experts for Global and Local Interpretability
Dec 01, 2022



Abstract:We investigate the feasibility of using mixtures of interpretable experts (MoIE) to build interpretable image classifiers on MNIST10. MoIE uses a black-box router to assign each input to one of many inherently interpretable experts, thereby providing insight into why a particular classification decision was made. We find that a naively trained MoIE will learn to 'cheat', whereby the black-box router will solve the classification problem by itself, with each expert simply learning a constant function for one particular class. We propose to solve this problem by introducing interpretable routers and training the black-box router's decisions to match the interpretable router. In addition, we propose a novel implicit parameterization scheme that allows us to build mixtures of arbitrary numbers of experts, allowing us to study how classification performance, local and global interpretability vary as the number of experts is increased. Our new model, dubbed Implicit Mixture of Interpretable Experts (IMoIE) can match state-of-the-art classification accuracy on MNIST10 while providing local interpretability, and can provide global interpretability albeit at the cost of reduced classification accuracy.
A Pipeline for Analysing Grant Applications
Oct 30, 2022



Abstract:Data mining techniques can transform massive amounts of unstructured data into quantitative data that quickly reveal insights, trends, and patterns behind the original data. In this paper, a data mining model is applied to analyse the 2019 grant applications submitted to an Australian Government research funding agency to investigate whether grant schemes successfully identifies innovative project proposals, as intended. The grant applications are peer-reviewed research proposals that include specific ``innovation and creativity'' (IC) scores assigned by reviewers. In addition to predicting the IC score for each research proposal, we are particularly interested in understanding the vocabulary of innovative proposals. In order to solve this problem, various data mining models and feature encoding algorithms are studied and explored. As a result, we propose a model with the best performance, a Random Forest (RF) classifier over documents encoded with features denoting the presence or absence of unigrams. In specific, the unigram terms are encoded by a modified Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) algorithm, which only implements the IDF part of TF-IDF. Besides the proposed model, this paper also presents a rigorous experimental pipeline for analysing grant applications, and the experimental results prove its feasibility.
TNNT: The Named Entity Recognition Toolkit
Aug 31, 2021
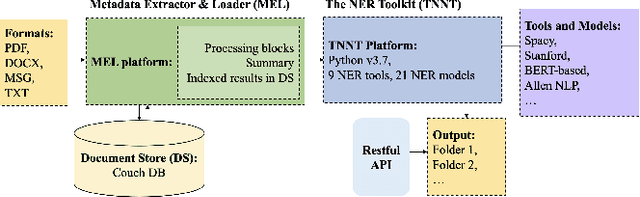
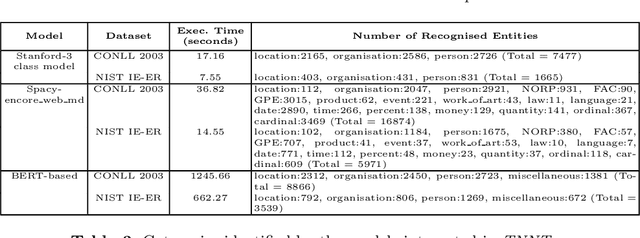
Abstract:Extraction of categorised named entities from text is a complex task given the availability of a variety of Named Entity Recognition (NER) models and the unstructured information encoded in different source document formats. Processing the documents to extract text, identifying suitable NER models for a task, and obtaining statistical information is important in data analysis to make informed decisions. This paper presents TNNT, a toolkit that automates the extraction of categorised named entities from unstructured information encoded in source documents, using diverse state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools and NER models. TNNT integrates 21 different NER models as part of a Knowledge Graph Construction Pipeline (KGCP) that takes a document set as input and processes it based on the defined settings, applying the selected blocks of NER models to output the results. The toolkit generates all results with an integrated summary of the extracted entities, enabling enhanced data analysis to support the KGCP, and also, to aid further NLP tasks.
Enhancing Automated Decision Support across Medical and Oral Health Domains with Semantic Web Technologies
Mar 30, 2014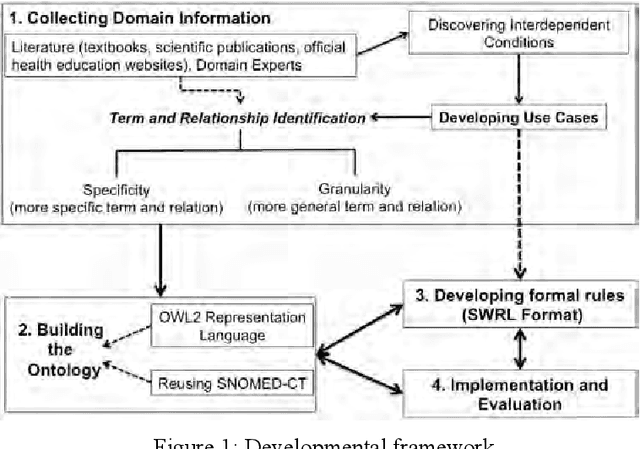



Abstract:Research has shown that the general health and oral health of an individual are closely related. Accordingly, current practice of isolating the information base of medical and oral health domains can be dangerous and detrimental to the health of the individual. However, technical issues such as heterogeneous data collection and storage formats, limited sharing of patient information and lack of decision support over the shared information are the principal reasons for the current state of affairs. To address these issues, the following research investigates the development and application of a cross-domain ontology and rules to build an evidence-based and reusable knowledge base consisting of the inter-dependent conditions from the two domains. Through example implementation of the knowledge base in Protege, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in reasoning over and providing decision support for cross-domain patient information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge