Sandaru Seneviratne
TNNT: The Named Entity Recognition Toolkit
Aug 31, 2021
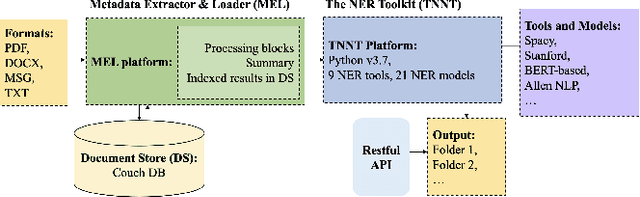
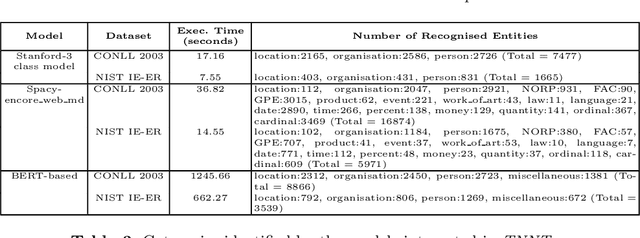
Abstract:Extraction of categorised named entities from text is a complex task given the availability of a variety of Named Entity Recognition (NER) models and the unstructured information encoded in different source document formats. Processing the documents to extract text, identifying suitable NER models for a task, and obtaining statistical information is important in data analysis to make informed decisions. This paper presents TNNT, a toolkit that automates the extraction of categorised named entities from unstructured information encoded in source documents, using diverse state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools and NER models. TNNT integrates 21 different NER models as part of a Knowledge Graph Construction Pipeline (KGCP) that takes a document set as input and processes it based on the defined settings, applying the selected blocks of NER models to output the results. The toolkit generates all results with an integrated summary of the extracted entities, enabling enhanced data analysis to support the KGCP, and also, to aid further NLP tasks.
Concept Discovery through Information Extraction in Restaurant Domain
Jun 12, 2019



Abstract:Concept identification is a crucial step in understanding and building a knowledge base for any particular domain. However, it is not a simple task in very large domains such as restaurants and hotel. In this paper, a novel approach of identifying a concept hierarchy and classifying unseen words into identified concepts related to restaurant domain is presented. Sorting, identifying, classifying of domain-related words manually is tedious and therefore, the proposed process is automated to a great extent. Word embedding, hierarchical clustering, classification algorithms are effectively used to obtain concepts related to the restaurant domain. Further, this approach can also be extended to create a semi-automatic ontology on restaurant domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge