Kazushige Okayasu
Pre-training without Natural Images
Jan 21, 2021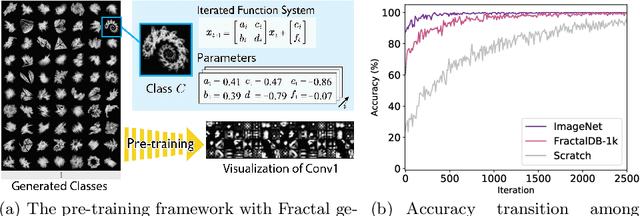
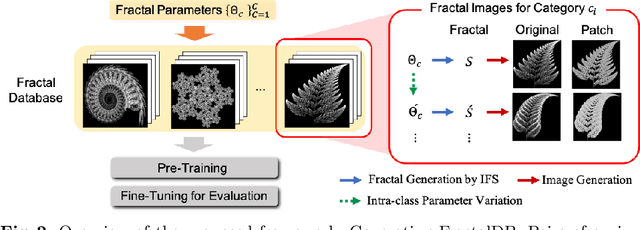

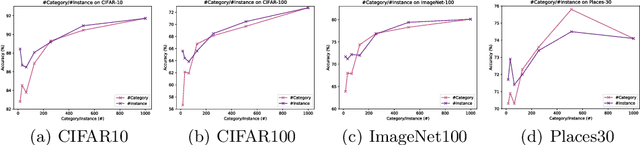
Abstract:Is it possible to use convolutional neural networks pre-trained without any natural images to assist natural image understanding? The paper proposes a novel concept, Formula-driven Supervised Learning. We automatically generate image patterns and their category labels by assigning fractals, which are based on a natural law existing in the background knowledge of the real world. Theoretically, the use of automatically generated images instead of natural images in the pre-training phase allows us to generate an infinite scale dataset of labeled images. Although the models pre-trained with the proposed Fractal DataBase (FractalDB), a database without natural images, does not necessarily outperform models pre-trained with human annotated datasets at all settings, we are able to partially surpass the accuracy of ImageNet/Places pre-trained models. The image representation with the proposed FractalDB captures a unique feature in the visualization of convolutional layers and attentions.
cvpaper.challenge in 2016: Futuristic Computer Vision through 1,600 Papers Survey
Jul 20, 2017

Abstract:The paper gives futuristic challenges disscussed in the cvpaper.challenge. In 2015 and 2016, we thoroughly study 1,600+ papers in several conferences/journals such as CVPR/ICCV/ECCV/NIPS/PAMI/IJCV.
Could you guess an interesting movie from the posters?: An evaluation of vision-based features on movie poster database
Apr 07, 2017
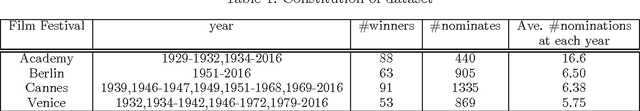
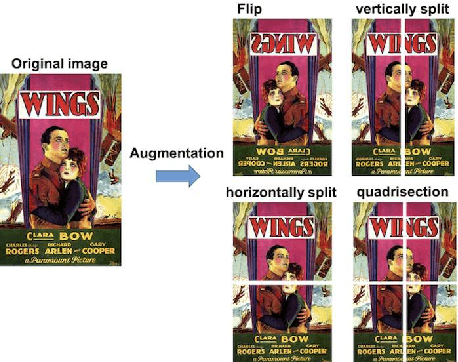
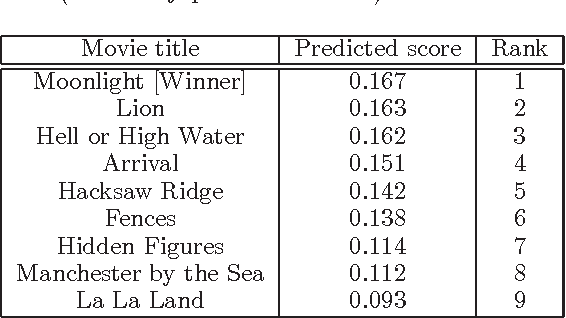
Abstract:In this paper, we aim to estimate the Winner of world-wide film festival from the exhibited movie poster. The task is an extremely challenging because the estimation must be done with only an exhibited movie poster, without any film ratings and box-office takings. In order to tackle this problem, we have created a new database which is consist of all movie posters included in the four biggest film festivals. The movie poster database (MPDB) contains historic movies over 80 years which are nominated a movie award at each year. We apply a couple of feature types, namely hand-craft, mid-level and deep feature to extract various information from a movie poster. Our experiments showed suggestive knowledge, for example, the Academy award estimation can be better rate with a color feature and a facial emotion feature generally performs good rate on the MPDB. The paper may suggest a possibility of modeling human taste for a movie recommendation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge