Kanzhi Wu
KernelGPA: A Globally Optimal Solution to Deformable SLAM in Closed-form
Oct 28, 2023Abstract:We study the generalized Procrustes analysis (GPA), as a minimal formulation to the simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) problem. We propose KernelGPA, a novel global registration technique to solve SLAM in the deformable environment. We propose the concept of deformable transformation which encodes the entangled pose and deformation. We define deformable transformations using a kernel method, and show that both the deformable transformations and the environment map can be solved globally in closed-form, up to global scale ambiguities. We solve the scale ambiguities by an optimization formulation that maximizes rigidity. We demonstrate KernelGPA using the Gaussian kernel, and validate the superiority of KernelGPA with various datasets. Code and data are available at \url{https://bitbucket.org/FangBai/deformableprocrustes}.
* This paper has been accepted for publication in the International Journal of Robotics Research, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/02783649231195380
An Invariant-EKF VINS Algorithm for Improving Consistency
Mar 01, 2017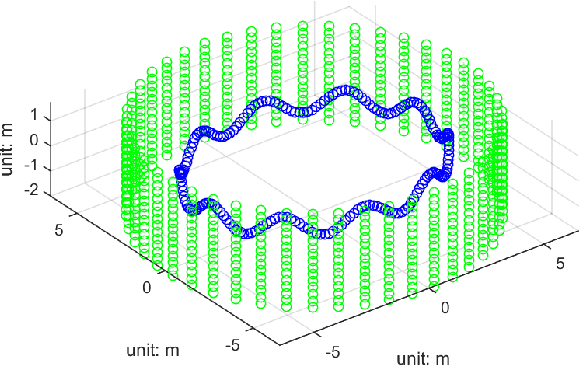
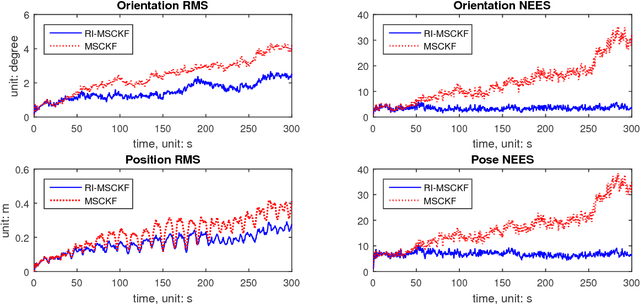


Abstract:The main contribution of this paper is an invariant extended Kalman filter (EKF) for visual inertial navigation systems (VINS). It is demonstrated that the conventional EKF based VINS is not invariant under the stochastic unobservable transformation, associated with translations and a rotation about the gravitational direction. This can lead to inconsistent state estimates as the estimator does not obey a fundamental property of the physical system. To address this issue, we use a novel uncertainty representation to derive a Right Invariant error extended Kalman filter (RIEKF-VINS) that preserves this invariance property. RIEKF-VINS is then adapted to the multistate constraint Kalman filter framework to obtain a consistent state estimator. Both Monte Carlo simulations and real-world experiments are used to validate the proposed method.
Convergence and Consistency Analysis for A 3D Invariant-EKF SLAM
Feb 22, 2017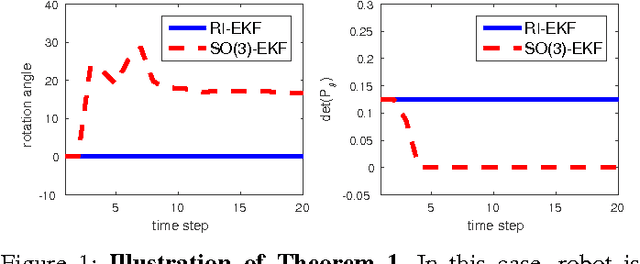
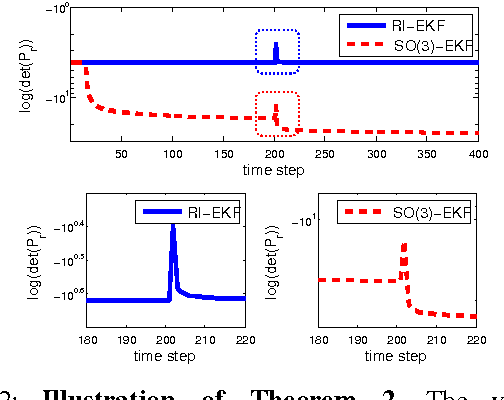
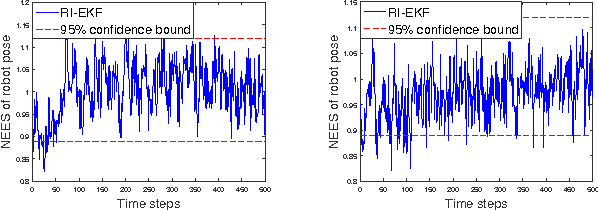
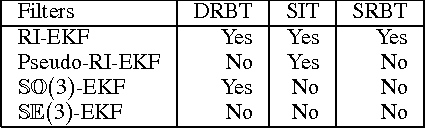
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the convergence and consistency properties of an Invariant-Extended Kalman Filter (RI-EKF) based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithm. Basic convergence properties of this algorithm are proven. These proofs do not require the restrictive assumption that the Jacobians of the motion and observation models need to be evaluated at the ground truth. It is also shown that the output of RI-EKF is invariant under any stochastic rigid body transformation in contrast to $\mathbb{SO}(3)$ based EKF SLAM algorithm ($\mathbb{SO}(3)$-EKF) that is only invariant under deterministic rigid body transformation. Implications of these invariance properties on the consistency of the estimator are also discussed. Monte Carlo simulation results demonstrate that RI-EKF outperforms $\mathbb{SO}(3)$-EKF, Robocentric-EKF and the "First Estimates Jacobian" EKF, for 3D point feature based SLAM.
RISAS: A Novel Rotation, Illumination, Scale Invariant Appearance and Shape Feature
Sep 19, 2016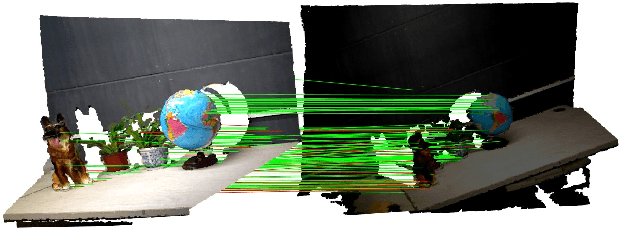
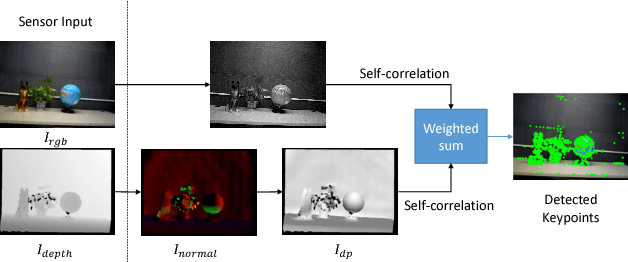
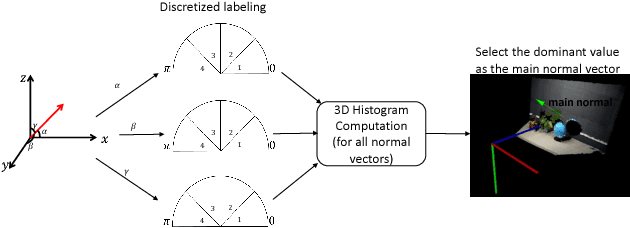

Abstract:This paper presents a novel appearance and shape feature, RISAS, which is robust to viewpoint, illumination, scale and rotation variations. RISAS consists of a keypoint detector and a feature descriptor both of which utilise texture and geometric information present in the appearance and shape channels. A novel response function based on the surface normals is used in combination with the Harris corner detector for selecting keypoints in the scene. A strategy that uses the depth information for scale estimation and background elimination is proposed to select the neighbourhood around the keypoints in order to build precise invariant descriptors. Proposed descriptor relies on the ordering of both grayscale intensity and shape information in the neighbourhood. Comprehensive experiments which confirm the effectiveness of the proposed RGB-D feature when compared with CSHOT and LOIND are presented. Furthermore, we highlight the utility of incorporating texture and shape information in the design of both the detector and the descriptor by demonstrating the enhanced performance of CSHOT and LOIND when combined with RISAS detector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge