Kamil Iskra
Benchmarking and In-depth Performance Study of Large Language Models on Habana Gaudi Processors
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:Transformer models have achieved remarkable success in various machine learning tasks but suffer from high computational complexity and resource requirements. The quadratic complexity of the self-attention mechanism further exacerbates these challenges when dealing with long sequences and large datasets. Specialized AI hardware accelerators, such as the Habana GAUDI architecture, offer a promising solution to tackle these issues. GAUDI features a Matrix Multiplication Engine (MME) and a cluster of fully programmable Tensor Processing Cores (TPC). This paper explores the untapped potential of using GAUDI processors to accelerate Transformer-based models, addressing key challenges in the process. Firstly, we provide a comprehensive performance comparison between the MME and TPC components, illuminating their relative strengths and weaknesses. Secondly, we explore strategies to optimize MME and TPC utilization, offering practical insights to enhance computational efficiency. Thirdly, we evaluate the performance of Transformers on GAUDI, particularly in handling long sequences and uncovering performance bottlenecks. Lastly, we evaluate the end-to-end performance of two Transformer-based large language models (LLM) on GAUDI. The contributions of this work encompass practical insights for practitioners and researchers alike. We delve into GAUDI's capabilities for Transformers through systematic profiling, analysis, and optimization exploration. Our study bridges a research gap and offers a roadmap for optimizing Transformer-based model training on the GAUDI architecture.
SOLAR: A Highly Optimized Data Loading Framework for Distributed Training of CNN-based Scientific Surrogates
Nov 04, 2022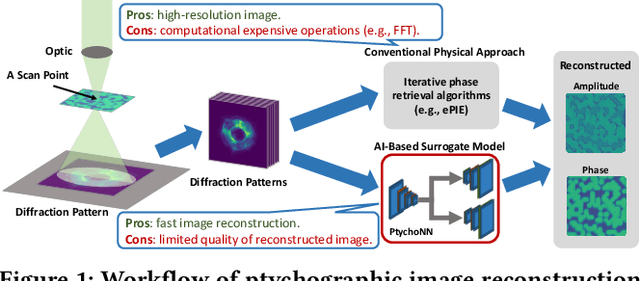
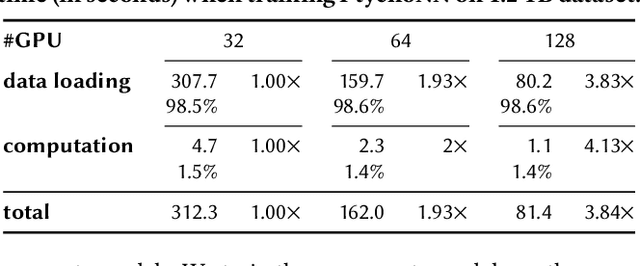
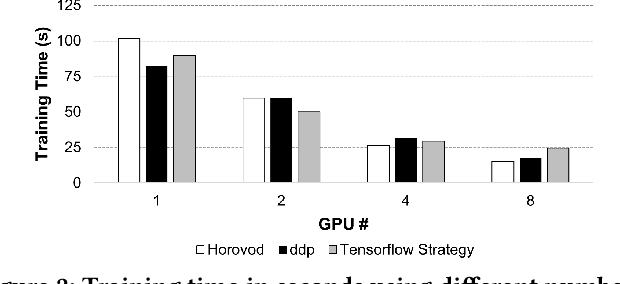
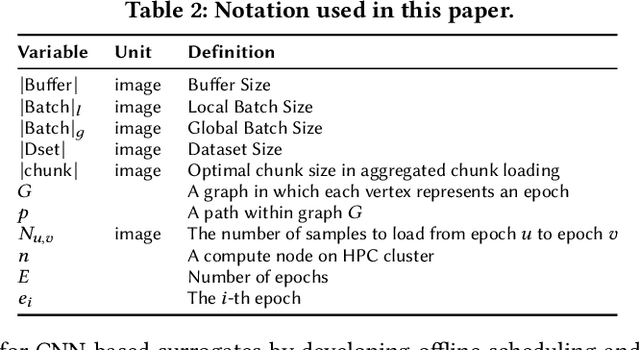
Abstract:CNN-based surrogates have become prevalent in scientific applications to replace conventional time-consuming physical approaches. Although these surrogates can yield satisfactory results with significantly lower computation costs over small training datasets, our benchmarking results show that data-loading overhead becomes the major performance bottleneck when training surrogates with large datasets. In practice, surrogates are usually trained with high-resolution scientific data, which can easily reach the terabyte scale. Several state-of-the-art data loaders are proposed to improve the loading throughput in general CNN training; however, they are sub-optimal when applied to the surrogate training. In this work, we propose SOLAR, a surrogate data loader, that can ultimately increase loading throughput during the training. It leverages our three key observations during the benchmarking and contains three novel designs. Specifically, SOLAR first generates a pre-determined shuffled index list and accordingly optimizes the global access order and the buffer eviction scheme to maximize the data reuse and the buffer hit rate. It then proposes a tradeoff between lightweight computational imbalance and heavyweight loading workload imbalance to speed up the overall training. It finally optimizes its data access pattern with HDF5 to achieve a better parallel I/O throughput. Our evaluation with three scientific surrogates and 32 GPUs illustrates that SOLAR can achieve up to 24.4X speedup over PyTorch Data Loader and 3.52X speedup over state-of-the-art data loaders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge