Kaiyang Wan
AI Security Beyond Core Domains: Resume Screening as a Case Study of Adversarial Vulnerabilities in Specialized LLM Applications
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at text comprehension and generation, making them ideal for automated tasks like code review and content moderation. However, our research identifies a vulnerability: LLMs can be manipulated by "adversarial instructions" hidden in input data, such as resumes or code, causing them to deviate from their intended task. Notably, while defenses may exist for mature domains such as code review, they are often absent in other common applications such as resume screening and peer review. This paper introduces a benchmark to assess this vulnerability in resume screening, revealing attack success rates exceeding 80% for certain attack types. We evaluate two defense mechanisms: prompt-based defenses achieve 10.1% attack reduction with 12.5% false rejection increase, while our proposed FIDS (Foreign Instruction Detection through Separation) using LoRA adaptation achieves 15.4% attack reduction with 10.4% false rejection increase. The combined approach provides 26.3% attack reduction, demonstrating that training-time defenses outperform inference-time mitigations in both security and utility preservation.
Evaluate Bias without Manual Test Sets: A Concept Representation Perspective for LLMs
May 21, 2025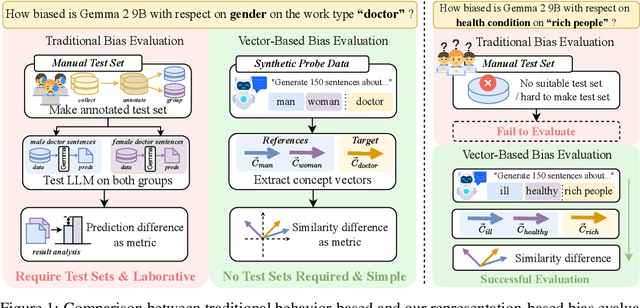
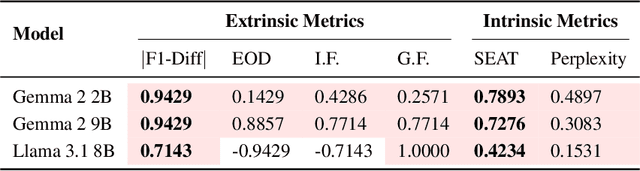
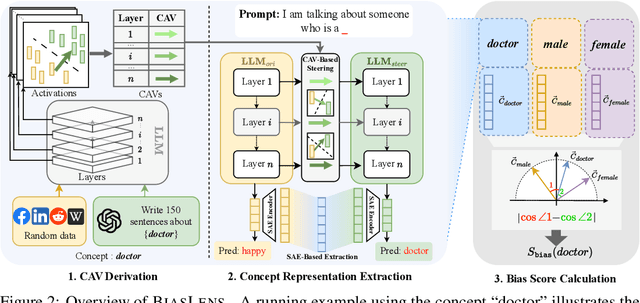
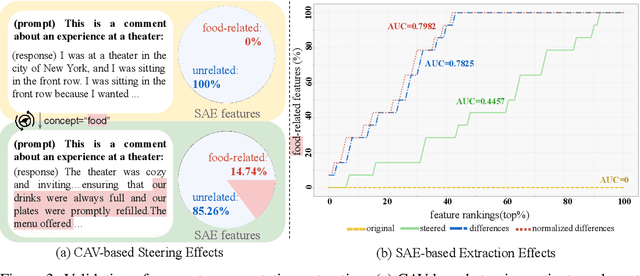
Abstract:Bias in Large Language Models (LLMs) significantly undermines their reliability and fairness. We focus on a common form of bias: when two reference concepts in the model's concept space, such as sentiment polarities (e.g., "positive" and "negative"), are asymmetrically correlated with a third, target concept, such as a reviewing aspect, the model exhibits unintended bias. For instance, the understanding of "food" should not skew toward any particular sentiment. Existing bias evaluation methods assess behavioral differences of LLMs by constructing labeled data for different social groups and measuring model responses across them, a process that requires substantial human effort and captures only a limited set of social concepts. To overcome these limitations, we propose BiasLens, a test-set-free bias analysis framework based on the structure of the model's vector space. BiasLens combines Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) with Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) to extract interpretable concept representations, and quantifies bias by measuring the variation in representational similarity between the target concept and each of the reference concepts. Even without labeled data, BiasLens shows strong agreement with traditional bias evaluation metrics (Spearman correlation r > 0.85). Moreover, BiasLens reveals forms of bias that are difficult to detect using existing methods. For example, in simulated clinical scenarios, a patient's insurance status can cause the LLM to produce biased diagnostic assessments. Overall, BiasLens offers a scalable, interpretable, and efficient paradigm for bias discovery, paving the way for improving fairness and transparency in LLMs.
A Cognitive Writing Perspective for Constrained Long-Form Text Generation
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Like humans, Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to generate high-quality long-form text that adheres to strict requirements in a single pass. This challenge is unsurprising, as successful human writing, according to the Cognitive Writing Theory, is a complex cognitive process involving iterative planning, translating, reviewing, and monitoring. Motivated by these cognitive principles, we aim to equip LLMs with human-like cognitive writing capabilities through CogWriter, a novel training-free framework that transforms LLM constrained long-form text generation into a systematic cognitive writing paradigm. Our framework consists of two key modules: (1) a Planning Agent that performs hierarchical planning to decompose the task, and (2) multiple Generation Agents that execute these plans in parallel. The system maintains quality via continuous monitoring and reviewing mechanisms, which evaluate outputs against specified requirements and trigger necessary revisions. CogWriter demonstrates exceptional performance on LongGenBench, a benchmark for complex constrained long-form text generation. Even when using Qwen-2.5-14B as its backbone, CogWriter surpasses GPT-4o by 22% in complex instruction completion accuracy while reliably generating texts exceeding 10,000 words. We hope this cognitive science-inspired approach provides a paradigm for LLM writing advancements: \href{https://github.com/KaiyangWan/CogWriter}{CogWriter}.
Text2NKG: Fine-Grained N-ary Relation Extraction for N-ary relational Knowledge Graph Construction
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Beyond traditional binary relational facts, n-ary relational knowledge graphs (NKGs) are comprised of n-ary relational facts containing more than two entities, which are closer to real-world facts with broader applications. However, the construction of NKGs still significantly relies on manual labor, and n-ary relation extraction still remains at a course-grained level, which is always in a single schema and fixed arity of entities. To address these restrictions, we propose Text2NKG, a novel fine-grained n-ary relation extraction framework for n-ary relational knowledge graph construction. We introduce a span-tuple classification approach with hetero-ordered merging to accomplish fine-grained n-ary relation extraction in different arity. Furthermore, Text2NKG supports four typical NKG schemas: hyper-relational schema, event-based schema, role-based schema, and hypergraph-based schema, with high flexibility and practicality. Experimental results demonstrate that Text2NKG outperforms the previous state-of-the-art model by nearly 20\% points in the $F_1$ scores on the fine-grained n-ary relation extraction benchmark in the hyper-relational schema. Our code and datasets are publicly available.
HAHE: Hierarchical Attention for Hyper-Relational Knowledge Graphs in Global and Local Level
May 15, 2023Abstract:Link Prediction on Hyper-relational Knowledge Graphs (HKG) is a worthwhile endeavor. HKG consists of hyper-relational facts (H-Facts), composed of a main triple and several auxiliary attribute-value qualifiers, which can effectively represent factually comprehensive information. The internal structure of HKG can be represented as a hypergraph-based representation globally and a semantic sequence-based representation locally. However, existing research seldom simultaneously models the graphical and sequential structure of HKGs, limiting HKGs' representation. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel Hierarchical Attention model for HKG Embedding (HAHE), including global-level and local-level attention. The global-level attention can model the graphical structure of HKG using hypergraph dual-attention layers, while the local-level attention can learn the sequential structure inside H-Facts via heterogeneous self-attention layers. Experiment results indicate that HAHE achieves state-of-the-art performance in link prediction tasks on HKG standard datasets. In addition, HAHE addresses the issue of HKG multi-position prediction for the first time, increasing the applicability of the HKG link prediction task. Our code is publicly available.
NQE: N-ary Query Embedding for Complex Query Answering over Hyper-relational Knowledge Graphs
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Complex query answering (CQA) is an essential task for multi-hop and logical reasoning on knowledge graphs (KGs). Currently, most approaches are limited to queries among binary relational facts and pay less attention to n-ary facts (n>=2) containing more than two entities, which are more prevalent in the real world. Moreover, previous CQA methods can only make predictions for a few given types of queries and cannot be flexibly extended to more complex logical queries, which significantly limits their applications. To overcome these challenges, in this work, we propose a novel N-ary Query Embedding (NQE) model for CQA over hyper-relational knowledge graphs (HKGs), which include massive n-ary facts. The NQE utilizes a dual-heterogeneous Transformer encoder and fuzzy logic theory to satisfy all n-ary FOL queries, including existential quantifiers, conjunction, disjunction, and negation. We also propose a parallel processing algorithm that can train or predict arbitrary n-ary FOL queries in a single batch, regardless of the kind of each query, with good flexibility and extensibility. In addition, we generate a new CQA dataset WD50K-NFOL, including diverse n-ary FOL queries over WD50K. Experimental results on WD50K-NFOL and other standard CQA datasets show that NQE is the state-of-the-art CQA method over HKGs with good generalization capability. Our code and dataset are publicly available.
DHGE: Dual-view Hyper-Relational Knowledge Graph Embedding for Link Prediction and Entity Typing
Jul 18, 2022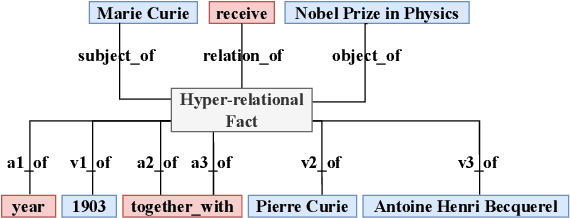
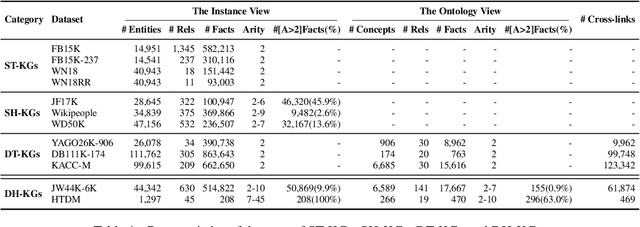
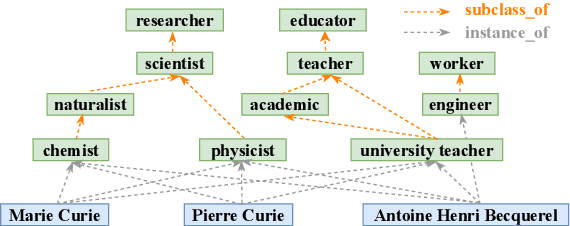
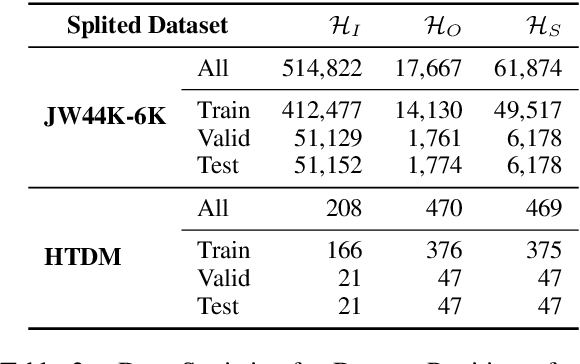
Abstract:In the field of representation learning on knowledge graphs (KGs), a hyper-relational fact consists of a main triple and several auxiliary attribute value descriptions, which is considered to be more comprehensive and specific than a triple-based fact. However, the existing hyper-relational KG embedding methods in a single view are limited in application due to weakening the hierarchical structure representing the affiliation between entities. To break this limitation, we propose a dual-view hyper-relational KG (DH-KG) structure which contains a hyper-relational instance view for entities and a hyper-relational ontology view for concepts abstracted hierarchically from entities to jointly model hyper-relational and hierarchical information. In this paper, we first define link prediction and entity typing tasks on DH-KG and construct two DH-KG datasets, JW44K-6K extracted from Wikidata and HTDM based on medical data. Furthermore, We propose a DH-KG embedding model DHGE, based on GRAN encoder, HGNN, and joint learning. Experimental results show that DHGE outperforms baseline models on DH-KG. We also provide an example of the application of this technology in the field of hypertension medication. Our model and datasets are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge