Jyotish Poonganam
Learn-to-Race Challenge 2022: Benchmarking Safe Learning and Cross-domain Generalisation in Autonomous Racing
May 10, 2022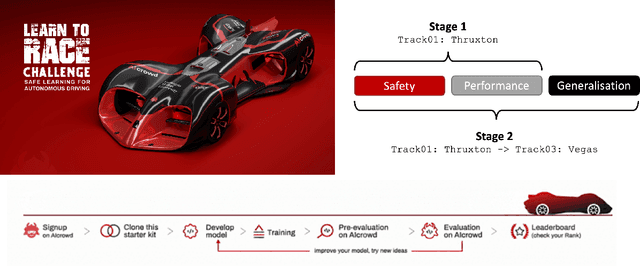
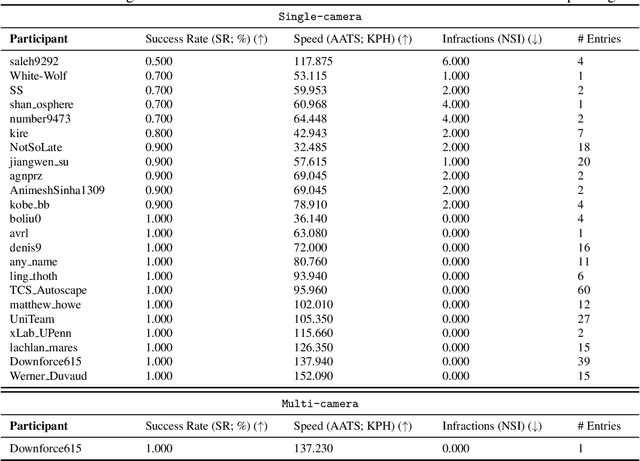

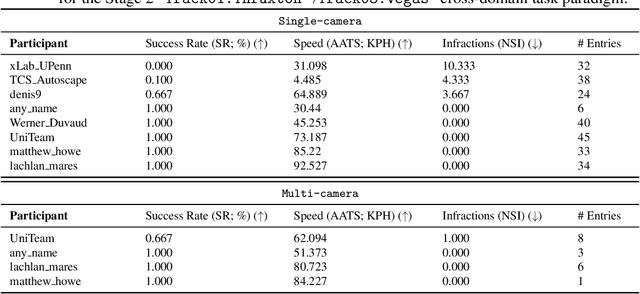
Abstract:We present the results of our autonomous racing virtual challenge, based on the newly-released Learn-to-Race (L2R) simulation framework, which seeks to encourage interdisciplinary research in autonomous driving and to help advance the state of the art on a realistic benchmark. Analogous to racing being used to test cutting-edge vehicles, we envision autonomous racing to serve as a particularly challenging proving ground for autonomous agents as: (i) they need to make sub-second, safety-critical decisions in a complex, fast-changing environment; and (ii) both perception and control must be robust to distribution shifts, novel road features, and unseen obstacles. Thus, the main goal of the challenge is to evaluate the joint safety, performance, and generalisation capabilities of reinforcement learning agents on multi-modal perception, through a two-stage process. In the first stage of the challenge, we evaluate an autonomous agent's ability to drive as fast as possible, while adhering to safety constraints. In the second stage, we additionally require the agent to adapt to an unseen racetrack through safe exploration. In this paper, we describe the new L2R Task 2.0 benchmark, with refined metrics and baseline approaches. We also provide an overview of deployment, evaluation, and rankings for the inaugural instance of the L2R Autonomous Racing Virtual Challenge (supported by Carnegie Mellon University, Arrival Ltd., AICrowd, Amazon Web Services, and Honda Research), which officially used the new L2R Task 2.0 benchmark and received over 20,100 views, 437 active participants, 46 teams, and 733 model submissions -- from 88+ unique institutions, in 58+ different countries. Finally, we release leaderboard results from the challenge and provide description of the two top-ranking approaches in cross-domain model transfer, across multiple sensor configurations and simulated races.
Measuring Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning Benchmarks: NeurIPS 2020 Procgen Benchmark
Mar 29, 2021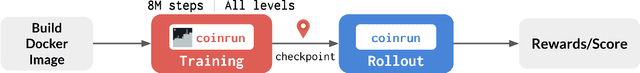
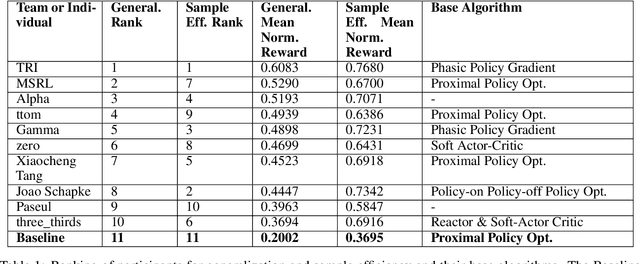
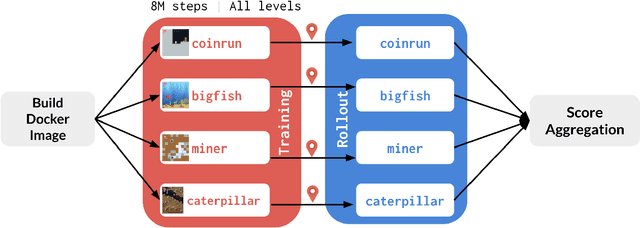
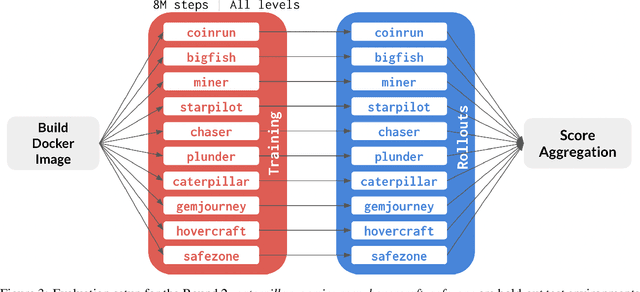
Abstract:The NeurIPS 2020 Procgen Competition was designed as a centralized benchmark with clearly defined tasks for measuring Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning. Generalization remains one of the most fundamental challenges in deep reinforcement learning, and yet we do not have enough benchmarks to measure the progress of the community on Generalization in Reinforcement Learning. We present the design of a centralized benchmark for Reinforcement Learning which can help measure Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning by doing end to end evaluation of the training and rollout phases of thousands of user submitted code bases in a scalable way. We designed the benchmark on top of the already existing Procgen Benchmark by defining clear tasks and standardizing the end to end evaluation setups. The design aims to maximize the flexibility available for researchers who wish to design future iterations of such benchmarks, and yet imposes necessary practical constraints to allow for a system like this to scale. This paper presents the competition setup and the details and analysis of the top solutions identified through this setup in context of 2020 iteration of the competition at NeurIPS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge