João Schapke
Measuring Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning Benchmarks: NeurIPS 2020 Procgen Benchmark
Mar 29, 2021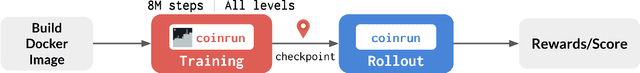
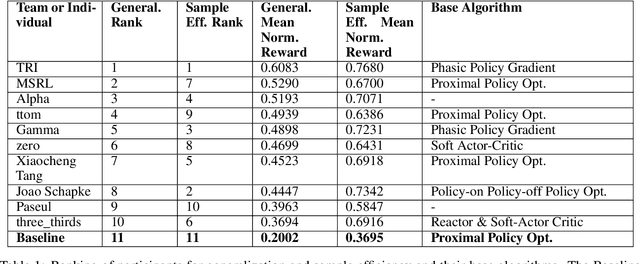
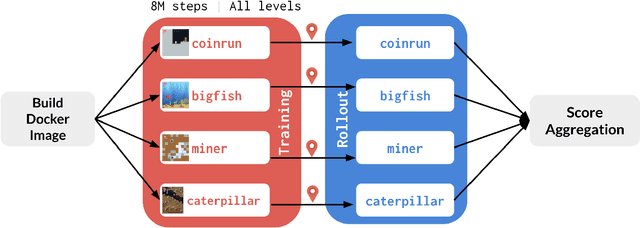
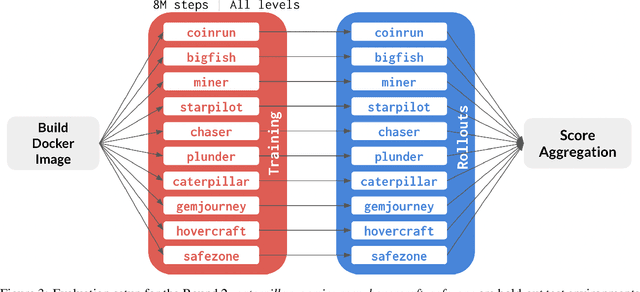
Abstract:The NeurIPS 2020 Procgen Competition was designed as a centralized benchmark with clearly defined tasks for measuring Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning. Generalization remains one of the most fundamental challenges in deep reinforcement learning, and yet we do not have enough benchmarks to measure the progress of the community on Generalization in Reinforcement Learning. We present the design of a centralized benchmark for Reinforcement Learning which can help measure Sample Efficiency and Generalization in Reinforcement Learning by doing end to end evaluation of the training and rollout phases of thousands of user submitted code bases in a scalable way. We designed the benchmark on top of the already existing Procgen Benchmark by defining clear tasks and standardizing the end to end evaluation setups. The design aims to maximize the flexibility available for researchers who wish to design future iterations of such benchmarks, and yet imposes necessary practical constraints to allow for a system like this to scale. This paper presents the competition setup and the details and analysis of the top solutions identified through this setup in context of 2020 iteration of the competition at NeurIPS.
EPGAT: Gene Essentiality Prediction With Graph Attention Networks
Jul 19, 2020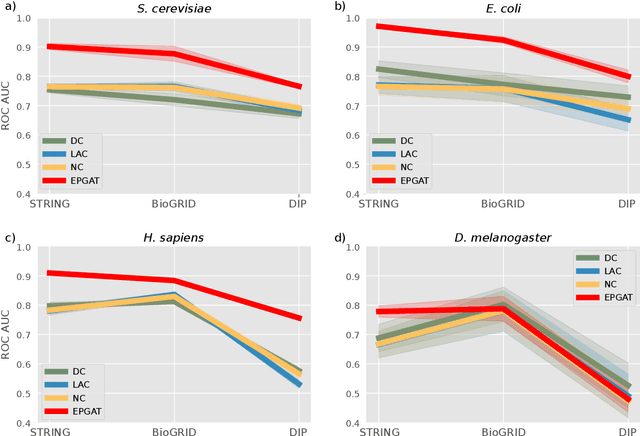
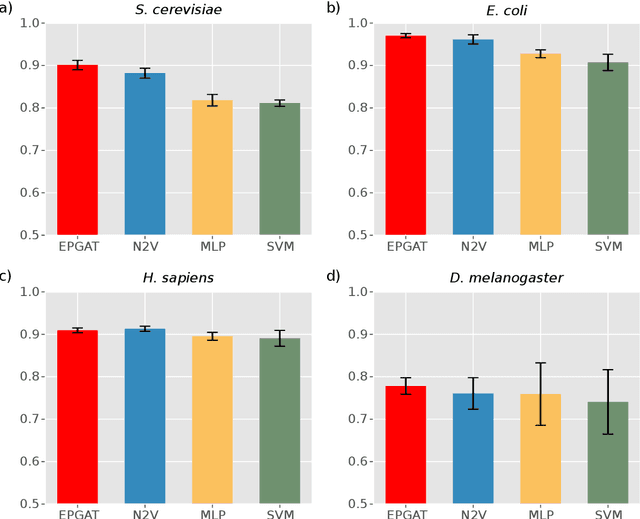
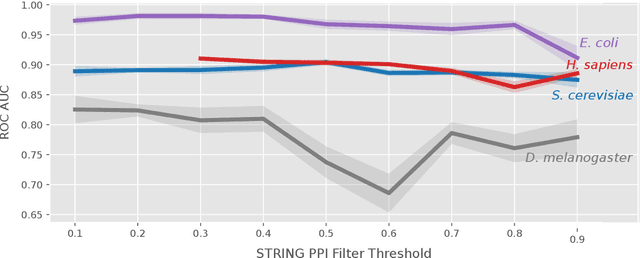
Abstract:The identification of essential genes/proteins is a critical step towards a better understanding of human biology and pathology. Computational approaches helped to mitigate experimental constraints by exploring machine learning (ML) methods and the correlation of essentiality with biological information, especially protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, to predict essential genes. Nonetheless, their performance is still limited, as network-based centralities are not exclusive proxies of essentiality, and traditional ML methods are unable to learn from non-Euclidean domains such as graphs. Given these limitations, we proposed EPGAT, an approach for essentiality prediction based on Graph Attention Networks (GATs), which are attention-based Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) that operate on graph-structured data. Our model directly learns patterns of gene essentiality from PPI networks, integrating additional evidence from multiomics data encoded as node attributes. We benchmarked EPGAT for four organisms, including humans, accurately predicting gene essentiality with AUC score ranging from 0.78 to 0.97. Our model significantly outperformed network-based and shallow ML-based methods and achieved a very competitive performance against the state-of-the-art node2vec embedding method. Notably, EPGAT was the most robust approach in scenarios with limited and imbalanced training data. Thus, the proposed approach offers a powerful and effective way to identify essential genes and proteins.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge