Joyce H Keyak
Hip Fracture Prediction using the First Principal Component Derived from FEA-Computed Fracture Loads
Oct 03, 2022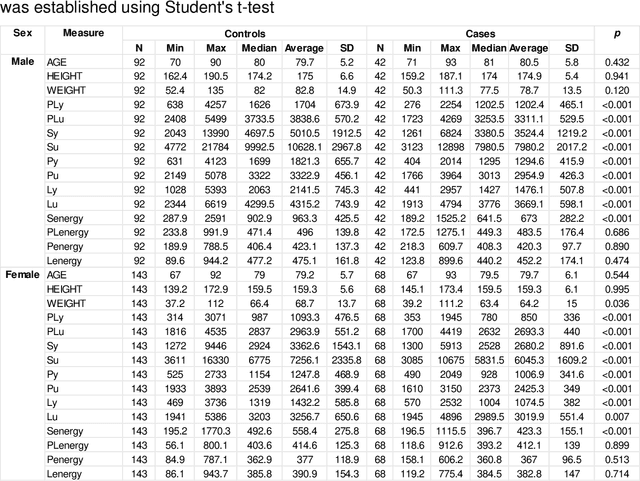
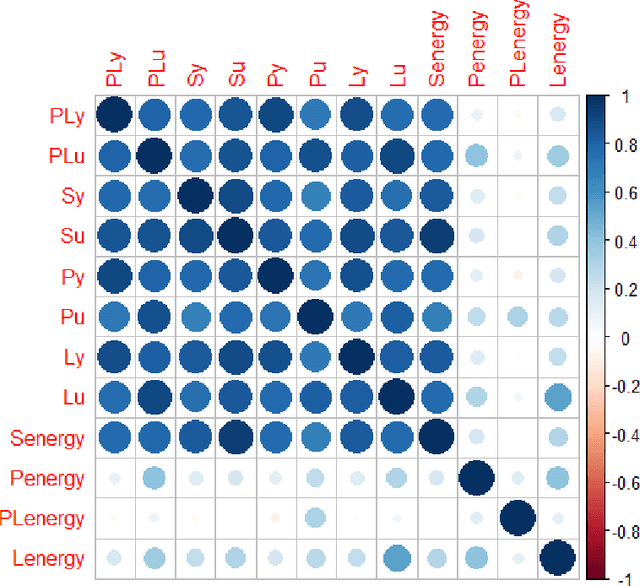
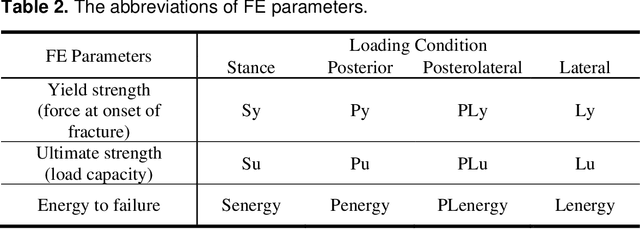
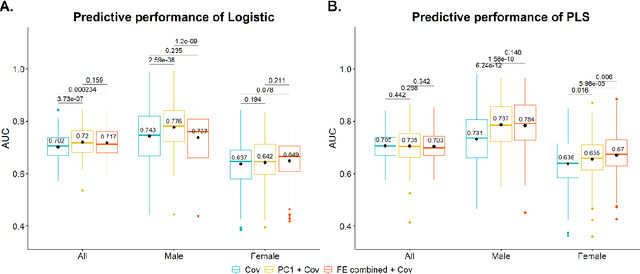
Abstract:Hip fracture risk assessment is an important but challenging task. Quantitative CT-based patient specific finite element analysis (FEA) computes the force (fracture load) to break the proximal femur in a particular loading condition. It provides different structural information about the proximal femur that can influence a subject overall fracture risk. To obtain a more robust measure of fracture risk, we used principal component analysis (PCA) to develop a global FEA computed fracture risk index that incorporates the FEA-computed yield and ultimate failure loads and energies to failure in four loading conditions (single-limb stance and impact from a fall onto the posterior, posterolateral, and lateral aspects of the greater trochanter) of 110 hip fracture subjects and 235 age and sex matched control subjects from the AGES-Reykjavik study. We found that the first PC (PC1) of the FE parameters was the only significant predictor of hip fracture. Using a logistic regression model, we determined if prediction performance for hip fracture using PC1 differed from that using FE parameters combined by stratified random resampling with respect to hip fracture status. The results showed that the average of the area under the receive operating characteristic curve (AUC) using PC1 was always higher than that using all FE parameters combined in the male subjects. The AUC of PC1 and AUC of the FE parameters combined were not significantly different than that in the female subjects or in all subjects
Multi-view information fusion using multi-view variational autoencoders to predict proximal femoral strength
Oct 03, 2022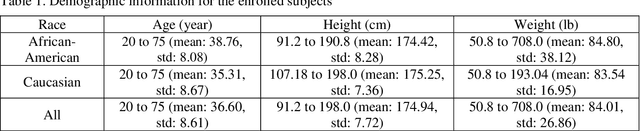
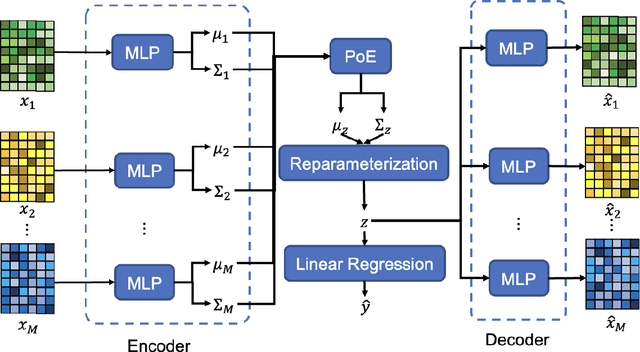
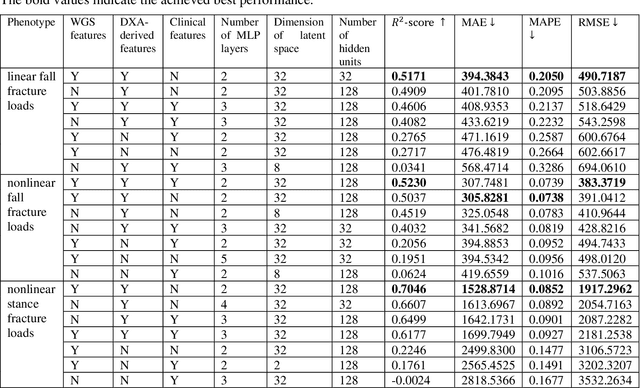
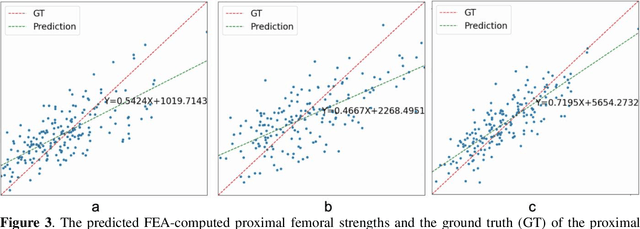
Abstract:Background and aim: Hip fracture can be devastating. The proximal femoral strength can be computed by subject-specific finite element (FE) analysis (FEA) using quantitative CT images. The aim of this paper is to design a deep learning-based model for hip fracture prediction with multi-view information fusion. Method: We developed a multi-view variational autoencoder (MMVAE) for feature representation learning and designed the product of expert model (PoE) for multi-view information fusion.We performed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to select the most relevant genetic features with proximal femoral strengths and integrated genetic features with DXA-derived imaging features and clinical variables for proximal femoral strength prediction. Results: The designed model achieved the mean absolute percentage error of 0.2050,0.0739 and 0.0852 for linear fall, nonlinear fall and nonlinear stance fracture load prediction, respectively. For linear fall and nonlinear stance fracture load prediction, integrating genetic and DXA-derived imaging features were beneficial; while for nonlinear fall fracture load prediction, integrating genetic features, DXA-derived imaging features as well as clinical variables, the model achieved the best performance. Conclusion: The proposed model is capable of predicting proximal femoral strengths using genetic features, DXA-derived imaging features as well as clinical variables. Compared to performing FEA using QCT images to calculate proximal femoral strengths, the presented method is time-efficient and cost effective, and radiation dosage is limited. From the technique perspective, the final models can be applied to other multi-view information integration tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge