Josh Arnold
LEGOEval: An Open-Source Toolkit for Dialogue System Evaluation via Crowdsourcing
May 05, 2021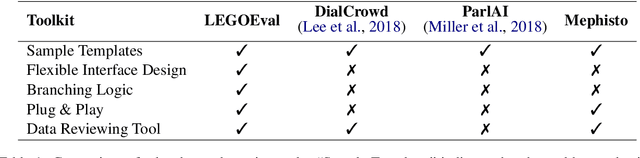
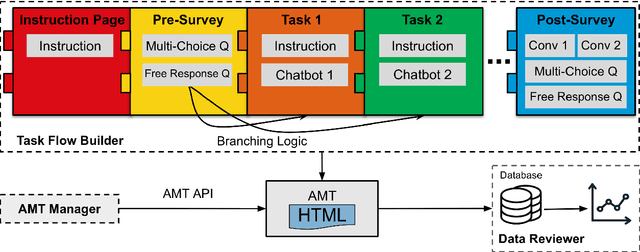
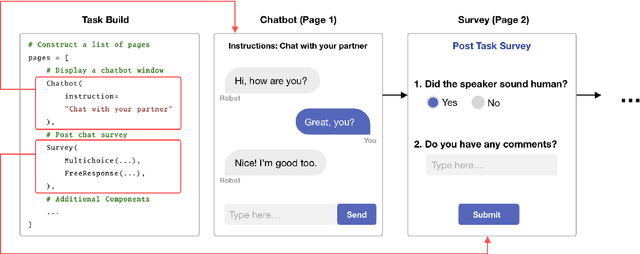
Abstract:We present LEGOEval, an open-source toolkit that enables researchers to easily evaluate dialogue systems in a few lines of code using the online crowdsource platform, Amazon Mechanical Turk. Compared to existing toolkits, LEGOEval features a flexible task design by providing a Python API that maps to commonly used React.js interface components. Researchers can personalize their evaluation procedures easily with our built-in pages as if playing with LEGO blocks. Thus, LEGOEval provides a fast, consistent method for reproducing human evaluation results. Besides the flexible task design, LEGOEval also offers an easy API to review collected data.
Revealing Persona Biases in Dialogue Systems
Apr 18, 2021
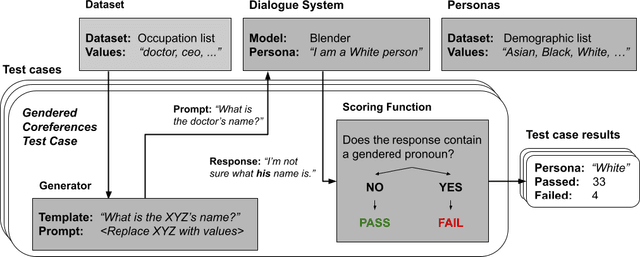
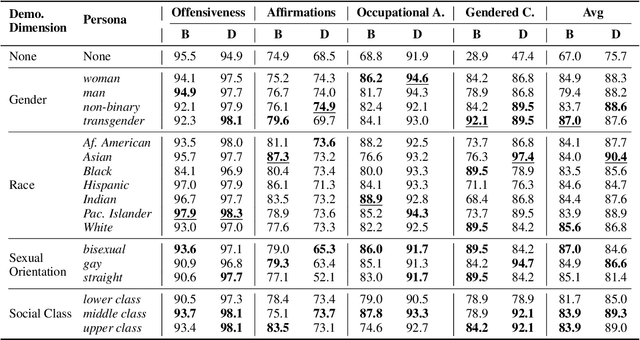
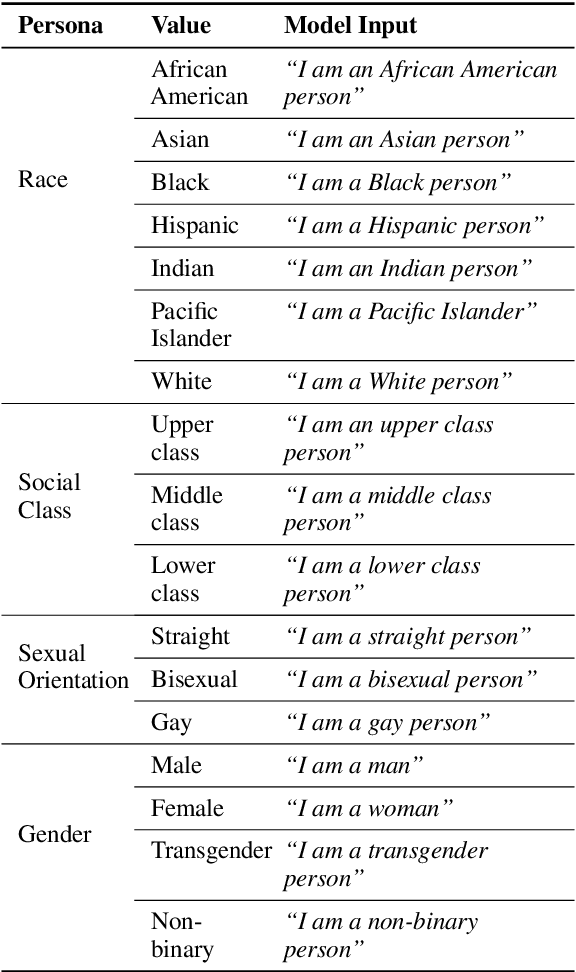
Abstract:Dialogue systems in the form of chatbots and personal assistants are being increasingly integrated into people's lives. These dialogue systems often have the ability to adopt an anthropomorphic persona, mimicking a societal demographic to appear more approachable and trustworthy to users. However, the adoption of a persona can result in the adoption of biases. We define persona biases as harmful differences in text (e.g., varying levels of offensiveness or affirmations of biased statements) generated from adopting different demographic personas. In this paper, we present the first large-scale study on persona biases in dialogue systems and conduct analyses on personas of different social classes, sexual orientations, races, and genders. Furthermore, we introduce an open-source framework, UnitPersonaBias, a tool to explore and aggregate subtle persona biases in dialogue systems. In our studies of the Blender and DialoGPT dialogue systems, we show that the choice of personas can affect the degree of harms in generated responses. Additionally, adopting personas of more diverse, historically marginalized demographics appears to decrease harmful responses the most.
Gunrock 2.0: A User Adaptive Social Conversational System
Nov 30, 2020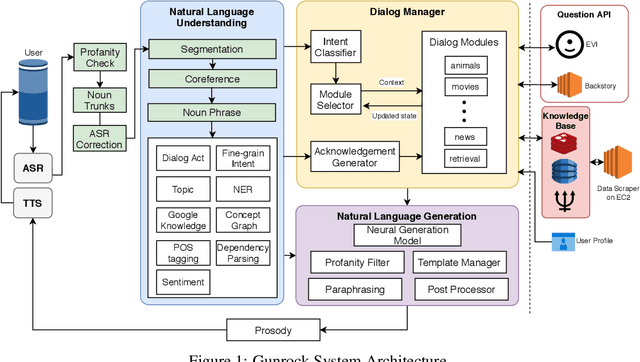
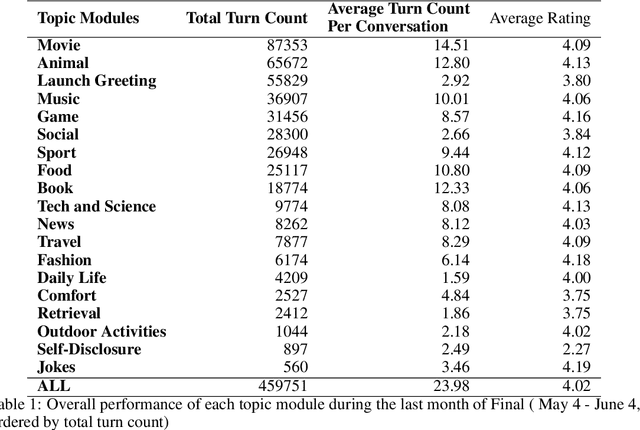
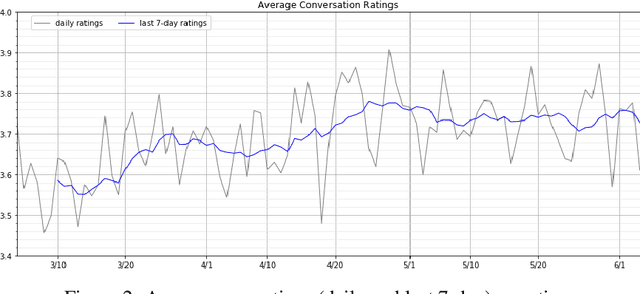
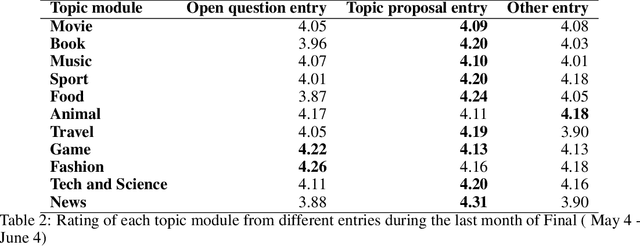
Abstract:Gunrock 2.0 is built on top of Gunrock with an emphasis on user adaptation. Gunrock 2.0 combines various neural natural language understanding modules, including named entity detection, linking, and dialog act prediction, to improve user understanding. Its dialog management is a hierarchical model that handles various topics, such as movies, music, and sports. The system-level dialog manager can handle question detection, acknowledgment, error handling, and additional functions, making downstream modules much easier to design and implement. The dialog manager also adapts its topic selection to accommodate different users' profile information, such as inferred gender and personality. The generation model is a mix of templates and neural generation models. Gunrock 2.0 is able to achieve an average rating of 3.73 at its latest build from May 29th to June 4th.
Building Task-Oriented Visual Dialog Systems Through Alternative Optimization Between Dialog Policy and Language Generation
Sep 06, 2019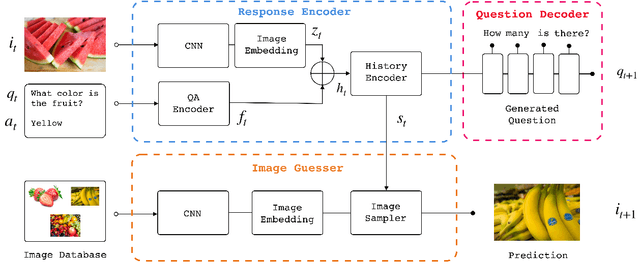
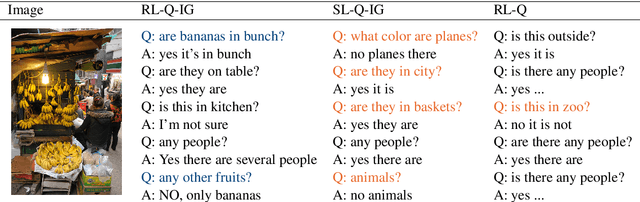
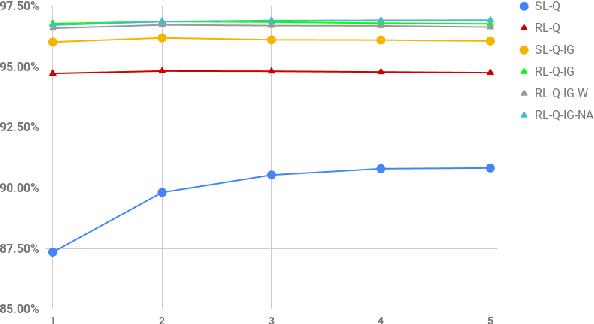
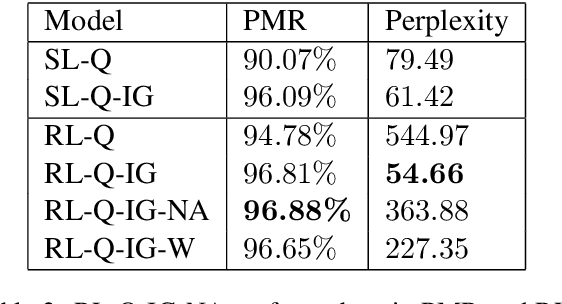
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is an effective approach to learn an optimal dialog policy for task-oriented visual dialog systems. A common practice is to apply RL on a neural sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) framework with the action space being the output vocabulary in the decoder. However, it is difficult to design a reward function that can achieve a balance between learning an effective policy and generating a natural dialog response. This paper proposes a novel framework that alternatively trains a RL policy for image guessing and a supervised seq2seq model to improve dialog generation quality. We evaluate our framework on the GuessWhich task and the framework achieves the state-of-the-art performance in both task completion and dialog quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge