Joseph Eichinger
Distributed Resource Allocation for URLLC in IIoT Scenarios: A Multi-Armed Bandit Approach
Nov 22, 2022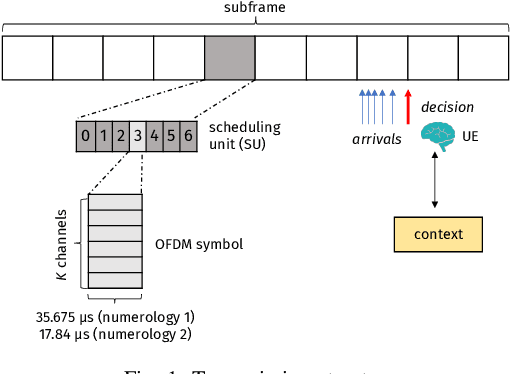
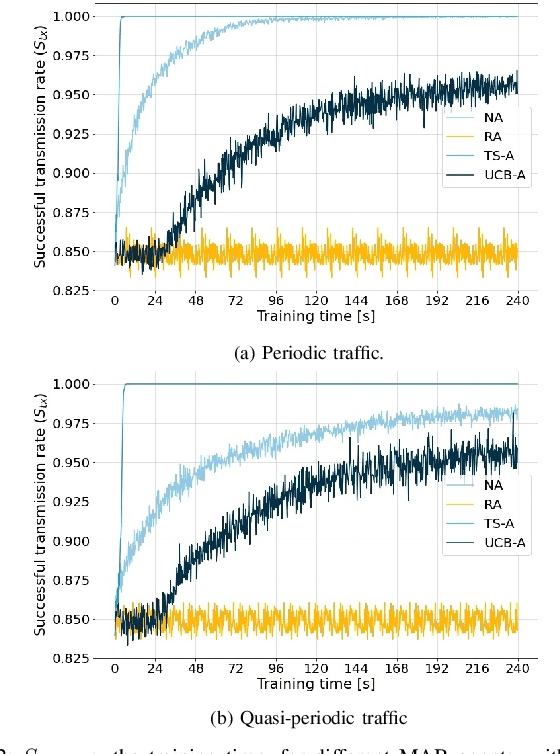
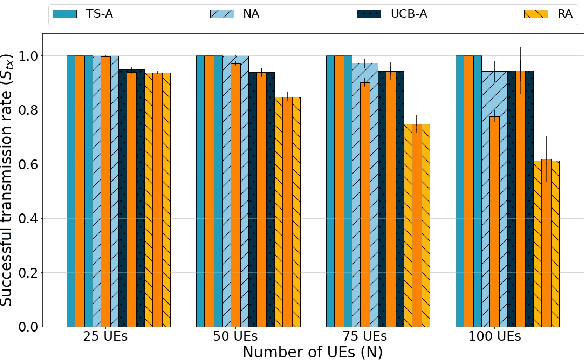
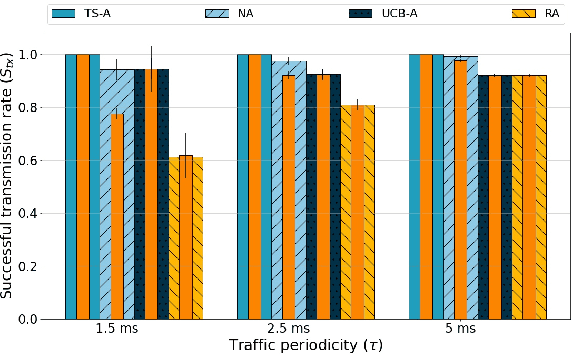
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of enabling inter-machine Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) in future 6G Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) networks. As far as the Radio Access Network (RAN) is concerned, centralized pre-configured resource allocation requires scheduling grants to be disseminated to the User Equipments (UEs) before uplink transmissions, which is not efficient for URLLC, especially in case of flexible/unpredictable traffic. To alleviate this burden, we study a distributed, user-centric scheme based on machine learning in which UEs autonomously select their uplink radio resources without the need to wait for scheduling grants or preconfiguration of connections. Using simulation, we demonstrate that a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) approach represents a desirable solution to allocate resources with URLLC in mind in an IIoT environment, in case of both periodic and aperiodic traffic, even considering highly populated networks and aggressive traffic.
Codebook Based Two-Time Scale Resource Allocation Design for IRS-Assisted eMBB-URLLC Systems
Aug 07, 2022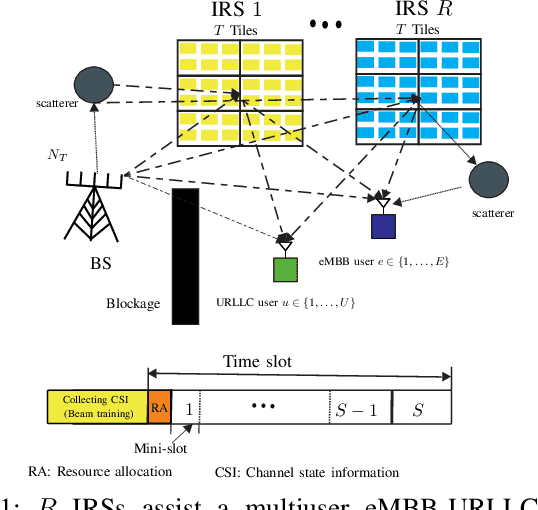
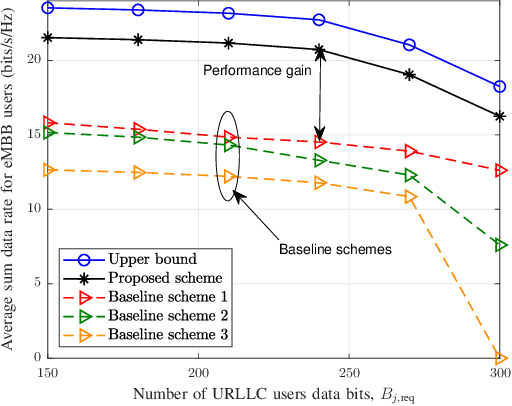
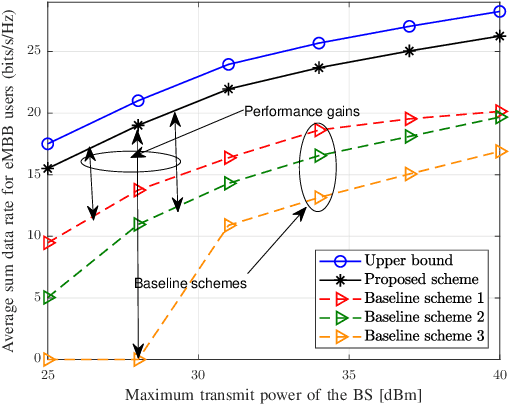
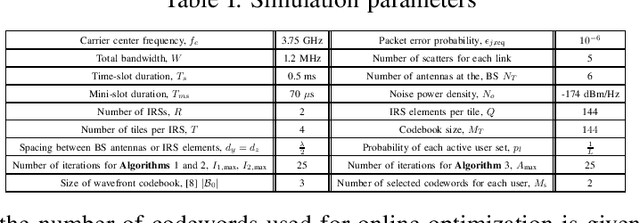
Abstract:This paper investigates the resource allocation algorithm design for wireless systems assisted by large intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) with coexisting enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and ultra reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) users. We consider a two-time scale resource allocation scheme, whereby the base station's precoders are optimized in each mini-slot to adapt to newly arriving URLLC traffic, whereas the IRS phase shifts are reconfigured only in each time slot to avoid excessive base station-IRS signaling. To facilitate efficient resource allocation design for large IRSs, we employ a codebook-based optimization framework, where the IRS is divided into several tiles and the phase-shift elements of each tile are selected from a pre-defined codebook. The resource allocation algorithm design is formulated as an optimization problem for the maximization of the average sum data rate of the eMBB users over a time slot while guaranteeing the quality-of-service (QoS) of each URLLC user in each mini-slot. An iterative algorithm based on alternating optimization (AO) is proposed to find a high-quality suboptimal solution. As a case study, the proposed algorithm is applied in an industrial indoor environment modelled via the Quadriga channel simulator. Our simulation results show that the proposed algorithm design enables the coexistence of eMBB and URLLC users and yields large performance gains compared to three baseline schemes. Furthermore, our simulation results reveal that the proposed two-time scale resource allocation design incurs only a small performance loss compared to the case when the IRSs are optimized in each mini-slot.
Optimization-based Phase-shift Codebook Design for Large IRSs
Mar 03, 2022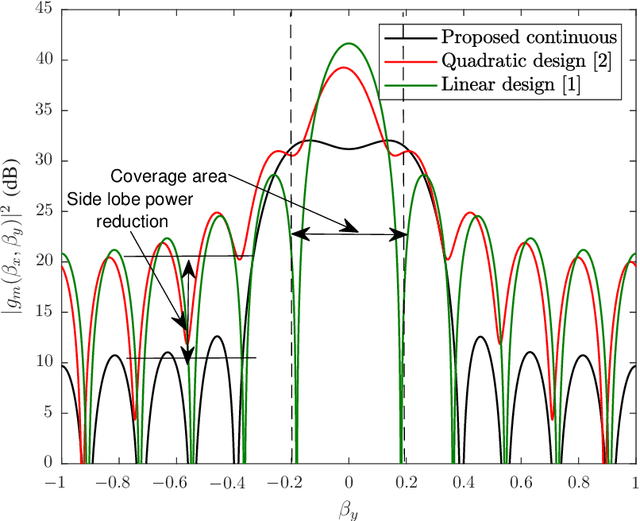
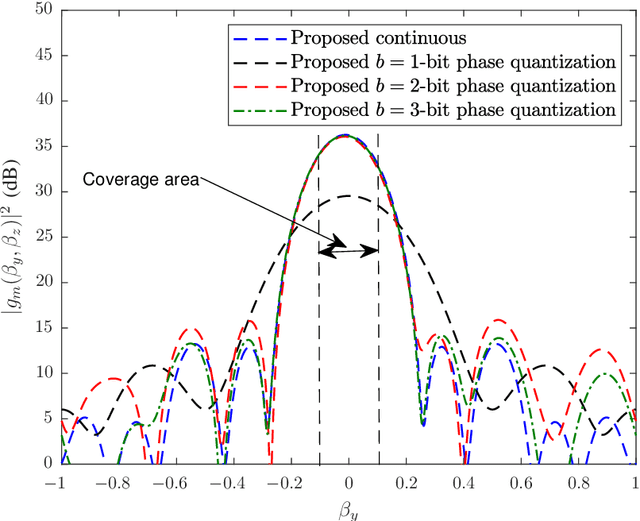
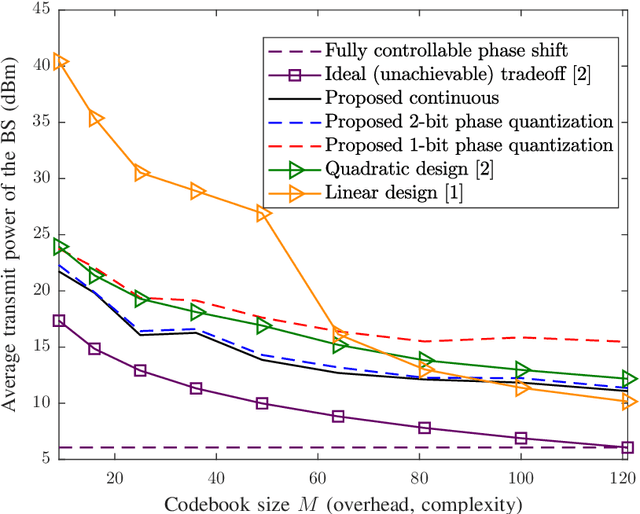
Abstract:In this paper, we focus on large intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) and propose a new codebook construction method to obtain a set of pre-designed phase-shift configurations for the IRS unit cells. Since the complexity of online optimization and the overhead for channel estimation for IRS-assisted communications scale with the size of the phase-shift codebook, the design of small codebooks is of high importance. We consider both continuous and discrete phase shift designs and formulate the codebook construction as optimization problems. To solve the optimization problems, we propose an optimal algorithm for the discrete phaseshift design and a low-complexity sub-optimal solution for the continuous design. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithms facilitate the construction of codebooks of different sizes and with different beamwidths. Moreover, the performance of the discrete phase-shift design with 2-bit quantization is shown to approach that of the continuous phase-shift design. Finally, our simulation results show that the proposed designs enable large transmit power savings compared to the existing linear and quadratic codebook designs.
5G for the Factory of the Future: Wireless Communication in an Industrial Environment
Mar 14, 2019Abstract:In this paper, the application of 5G communication technology in an industrial environment is discussed. It acts as an enabler for the separation of sensors/actors and resources, like memory and computational power. 5G offers characteristics essential for the proposed approach like robustness, ultra-low latency, high data rates and massive number of devices. A demonstrator of a production line was used as an test environment for 5G in a real-world industrial application. A wide variety of heterogeneous sensor systems is used by a mobile robot platform. The collected data is transmitted via a 5G network to various Cloud systems. The product is treated as a cyber-physical system with a RFID tag in conjunction with the product memory system. The dynamic production flow approach is discussed centered around the robot which is used for transportation and inspection of products. This inspection is performed during the transportation and influences the production flow directly. This is desirable in the scope of Industry 4.0 to have an efficient production down to batch size 1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge