Jose Sotelo
MelGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Conditional Waveform Synthesis
Oct 28, 2019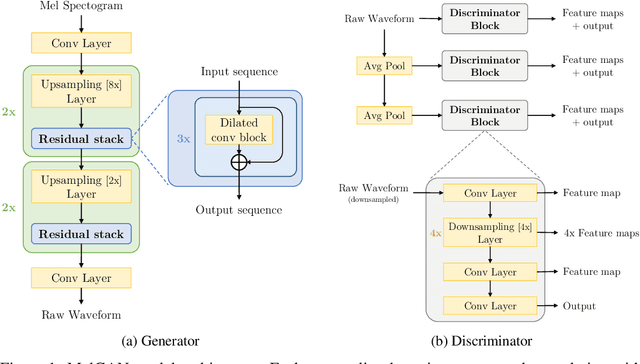
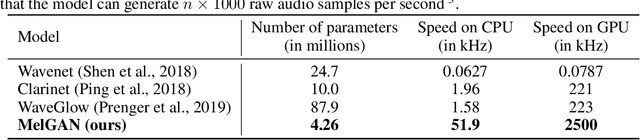
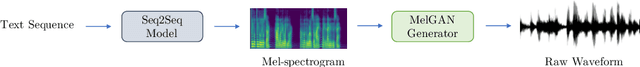
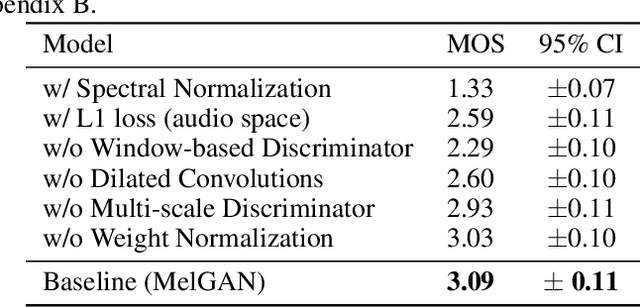
Abstract:Previous works (Donahue et al., 2018a; Engel et al., 2019a) have found that generating coherent raw audio waveforms with GANs is challenging. In this paper, we show that it is possible to train GANs reliably to generate high quality coherent waveforms by introducing a set of architectural changes and simple training techniques. Subjective evaluation metric (Mean Opinion Score, or MOS) shows the effectiveness of the proposed approach for high quality mel-spectrogram inversion. To establish the generality of the proposed techniques, we show qualitative results of our model in speech synthesis, music domain translation and unconditional music synthesis. We evaluate the various components of the model through ablation studies and suggest a set of guidelines to design general purpose discriminators and generators for conditional sequence synthesis tasks. Our model is non-autoregressive, fully convolutional, with significantly fewer parameters than competing models and generalizes to unseen speakers for mel-spectrogram inversion. Our pytorch implementation runs at more than 100x faster than realtime on GTX 1080Ti GPU and more than 2x faster than real-time on CPU, without any hardware specific optimization tricks.
ObamaNet: Photo-realistic lip-sync from text
Dec 06, 2017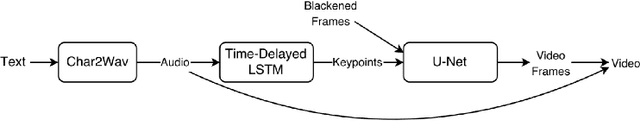
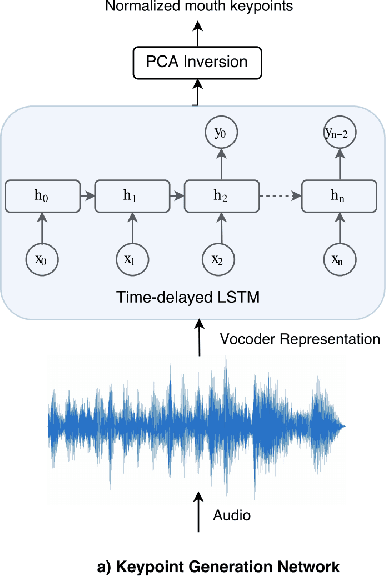
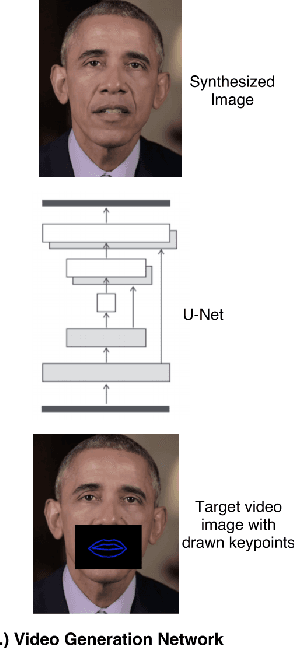

Abstract:We present ObamaNet, the first architecture that generates both audio and synchronized photo-realistic lip-sync videos from any new text. Contrary to other published lip-sync approaches, ours is only composed of fully trainable neural modules and does not rely on any traditional computer graphics methods. More precisely, we use three main modules: a text-to-speech network based on Char2Wav, a time-delayed LSTM to generate mouth-keypoints synced to the audio, and a network based on Pix2Pix to generate the video frames conditioned on the keypoints.
A Robust Adaptive Stochastic Gradient Method for Deep Learning
Mar 02, 2017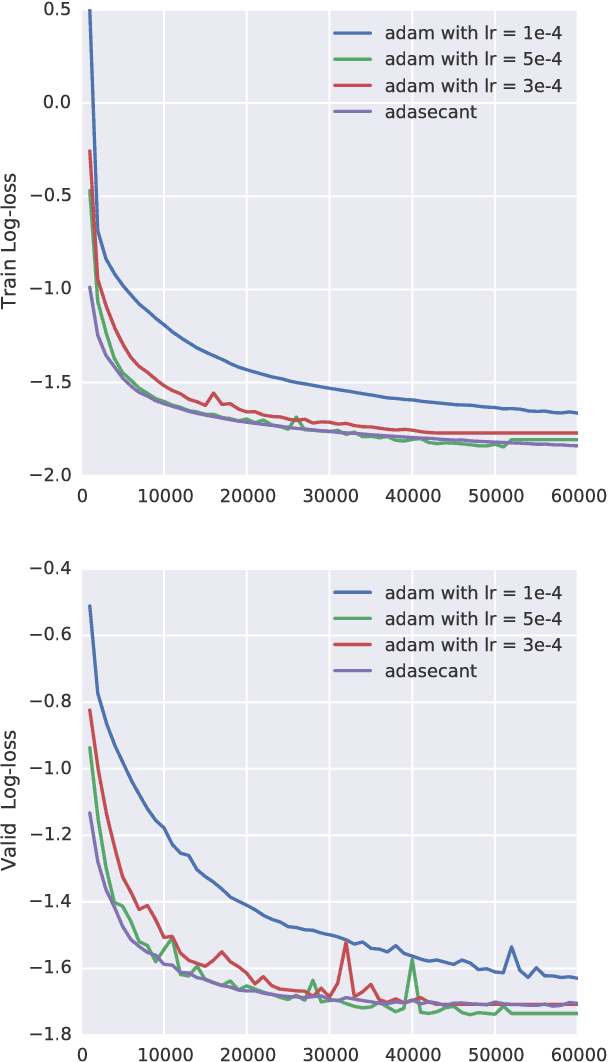

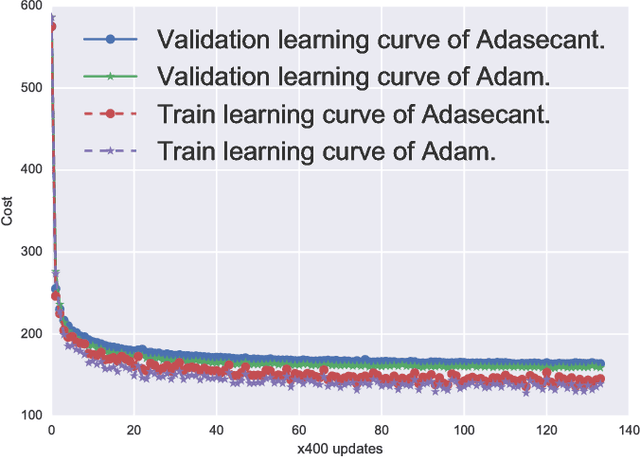
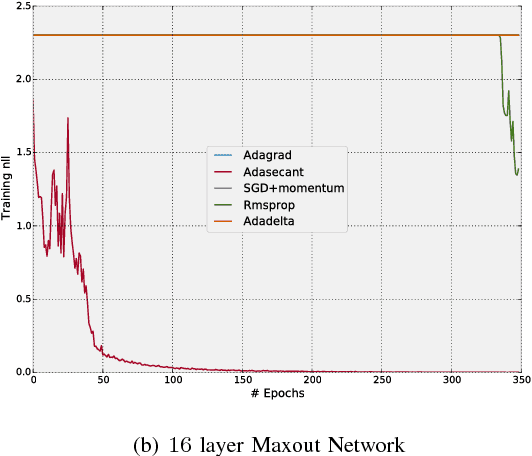
Abstract:Stochastic gradient algorithms are the main focus of large-scale optimization problems and led to important successes in the recent advancement of the deep learning algorithms. The convergence of SGD depends on the careful choice of learning rate and the amount of the noise in stochastic estimates of the gradients. In this paper, we propose an adaptive learning rate algorithm, which utilizes stochastic curvature information of the loss function for automatically tuning the learning rates. The information about the element-wise curvature of the loss function is estimated from the local statistics of the stochastic first order gradients. We further propose a new variance reduction technique to speed up the convergence. In our experiments with deep neural networks, we obtained better performance compared to the popular stochastic gradient algorithms.
SampleRNN: An Unconditional End-to-End Neural Audio Generation Model
Feb 11, 2017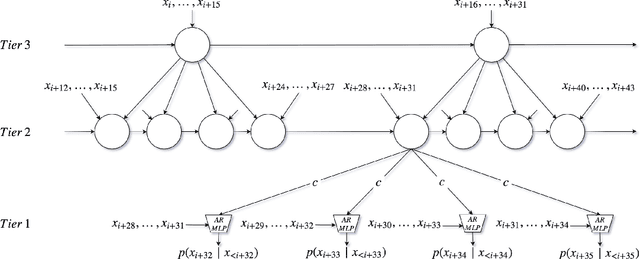

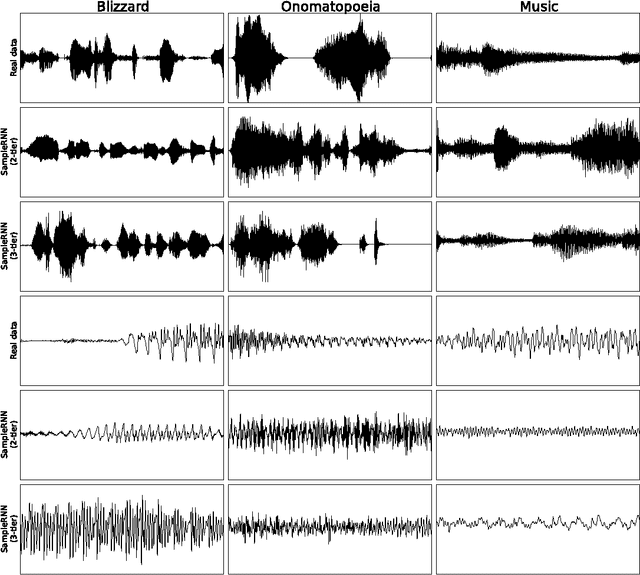
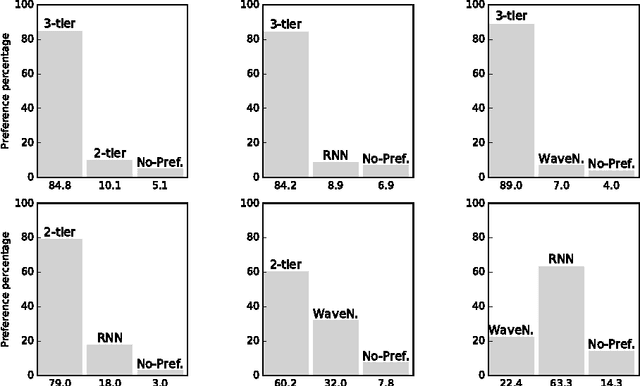
Abstract:In this paper we propose a novel model for unconditional audio generation based on generating one audio sample at a time. We show that our model, which profits from combining memory-less modules, namely autoregressive multilayer perceptrons, and stateful recurrent neural networks in a hierarchical structure is able to capture underlying sources of variations in the temporal sequences over very long time spans, on three datasets of different nature. Human evaluation on the generated samples indicate that our model is preferred over competing models. We also show how each component of the model contributes to the exhibited performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge