Jonathan Garibaldi
SoftED: Metrics for Soft Evaluation of Time Series Event Detection
Apr 02, 2023



Abstract:Time series event detection methods are evaluated mainly by standard classification metrics that focus solely on detection accuracy. However, inaccuracy in detecting an event can often result from its preceding or delayed effects reflected in neighboring detections. These detections are valuable to trigger necessary actions or help mitigate unwelcome consequences. In this context, current metrics are insufficient and inadequate for the context of event detection. There is a demand for metrics that incorporate both the concept of time and temporal tolerance for neighboring detections. This paper introduces SoftED metrics, a new set of metrics designed for soft evaluating event detection methods. They enable the evaluation of both detection accuracy and the degree to which their detections represent events. They improved event detection evaluation by associating events and their representative detections, incorporating temporal tolerance in over 36\% of experiments compared to the usual classification metrics. SoftED metrics were validated by domain specialists that indicated their contribution to detection evaluation and method selection.
FU-net: Multi-class Image Segmentation Using Feedback Weighted U-net
Apr 28, 2020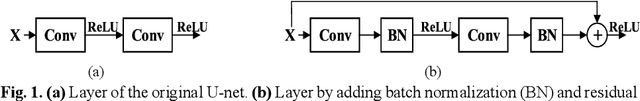
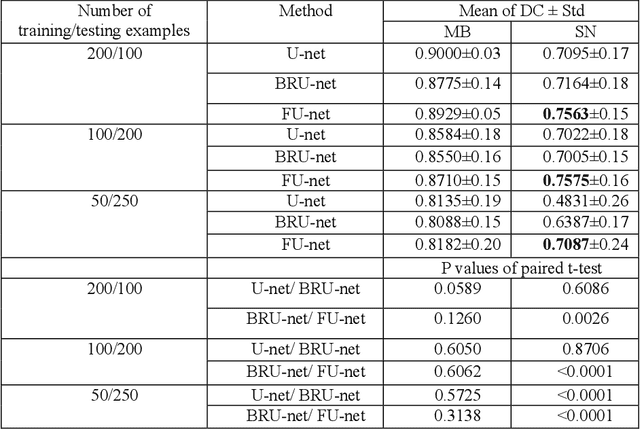

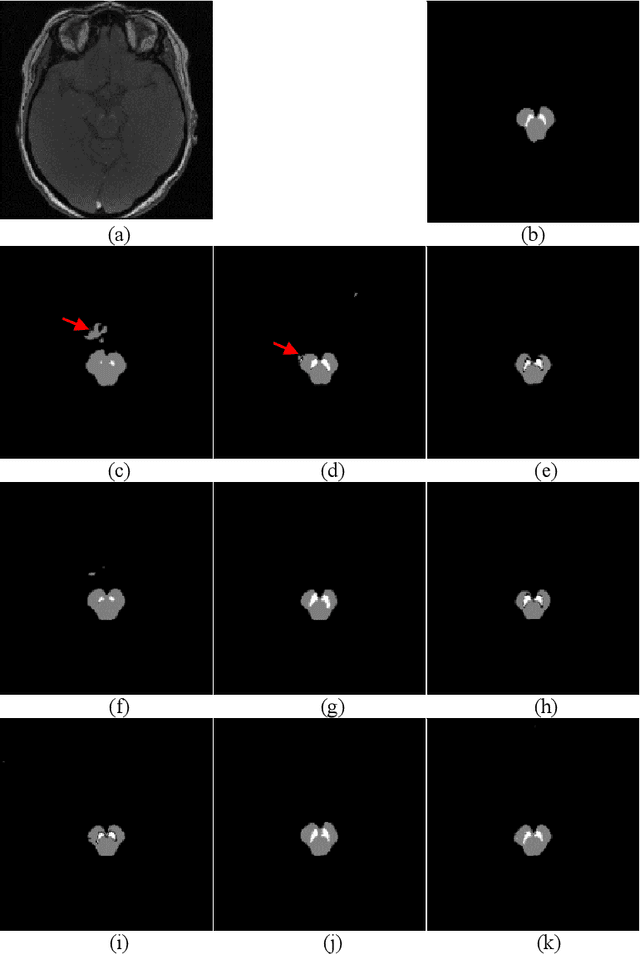
Abstract:In this paper, we present a generic deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for multi-class image segmentation. It is based on a well-established supervised end-to-end DCNN model, known as U-net. U-net is firstly modified by adding widely used batch normalization and residual block (named as BRU-net) to improve the efficiency of model training. Based on BRU-net, we further introduce a dynamically weighted cross-entropy loss function. The weighting scheme is calculated based on the pixel-wise prediction accuracy during the training process. Assigning higher weights to pixels with lower segmentation accuracies enables the network to learn more from poorly predicted image regions. Our method is named as feedback weighted U-net (FU-net). We have evaluated our method based on T1- weighted brain MRI for the segmentation of midbrain and substantia nigra, where the number of pixels in each class is extremely unbalanced to each other. Based on the dice coefficient measurement, our proposed FU-net has outperformed BRU-net and U-net with statistical significance, especially when only a small number of training examples are available. The code is publicly available in GitHub (GitHub link: https://github.com/MinaJf/FU-net).
* Accepted for publication at International Conference on Image and Graphics (ICIG 2019)
DRU-net: An Efficient Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 28, 2020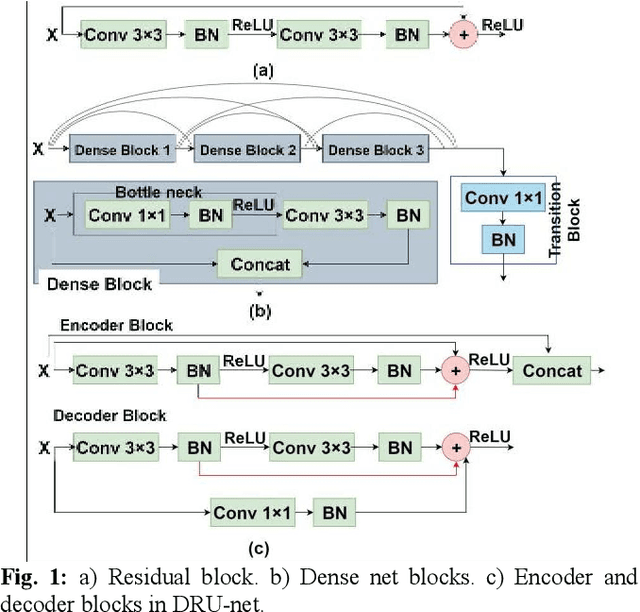
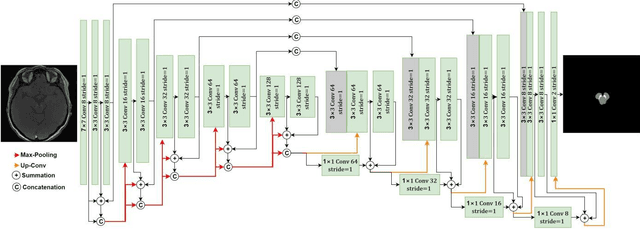
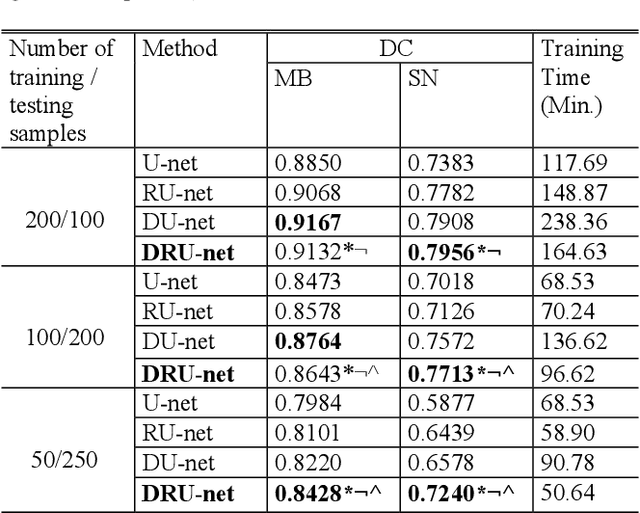
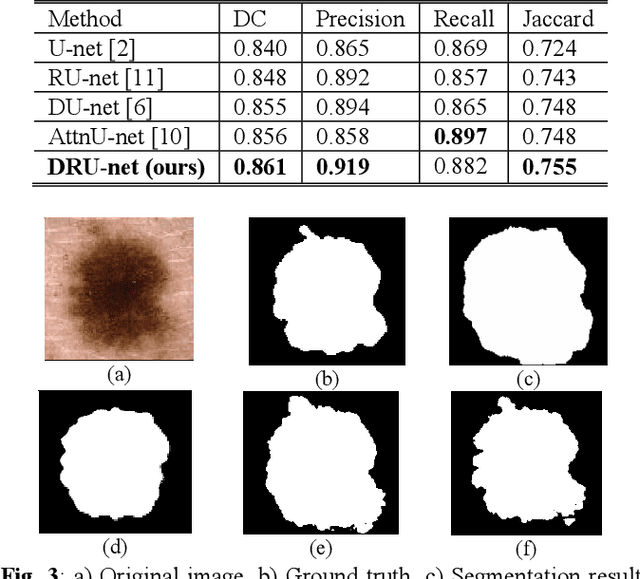
Abstract:Residual network (ResNet) and densely connected network (DenseNet) have significantly improved the training efficiency and performance of deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) mainly for object classification tasks. In this paper, we propose an efficient network architecture by considering advantages of both networks. The proposed method is integrated into an encoder-decoder DCNN model for medical image segmentation. Our method adds additional skip connections compared to ResNet but uses significantly fewer model parameters than DenseNet. We evaluate the proposed method on a public dataset (ISIC 2018 grand-challenge) for skin lesion segmentation and a local brain MRI dataset. In comparison with ResNet-based, DenseNet-based and attention network (AttnNet) based methods within the same encoder-decoder network structure, our method achieves significantly higher segmentation accuracy with fewer number of model parameters than DenseNet and AttnNet. The code is available on GitHub (GitHub link: https://github.com/MinaJf/DRU-net).
* Accepted for publication at IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020, 5 pages, 3 figures
Personalising Mobile Advertising Based on Users Installed Apps
Feb 24, 2015



Abstract:Mobile advertising is a billion pound industry that is rapidly expanding. The success of an advert is measured based on how users interact with it. In this paper we investigate whether the application of unsupervised learning and association rule mining could be used to enable personalised targeting of mobile adverts with the aim of increasing the interaction rate. Over May and June 2014 we recorded advert interactions such as tapping the advert or watching the whole advert video along with the set of apps a user has installed at the time of the interaction. Based on the apps that the users have installed we applied k-means clustering to profile the users into one of ten classes. Due to the large number of apps considered we implemented dimension reduction to reduced the app feature space by mapping the apps to their iTunes category and clustered users based on the percentage of their apps that correspond to each iTunes app category. The clustering was externally validated by investigating differences between the way the ten profiles interact with the various adverts genres (lifestyle, finance and entertainment adverts). In addition association rule mining was performed to find whether the time of the day that the advert is served and the number of apps a user has installed makes certain profiles more likely to interact with the advert genres. The results showed there were clear differences in the way the profiles interact with the different advert genres and the results of this paper suggest that mobile advert targeting would improve the frequency that users interact with an advert.
Mimicking the Behaviour of Idiotypic AIS Robot Controllers Using Probabilistic Systems
Mar 22, 2010



Abstract:Previous work has shown that robot navigation systems that employ an architecture based upon the idiotypic network theory of the immune system have an advantage over control techniques that rely on reinforcement learning only. This is thought to be a result of intelligent behaviour selection on the part of the idiotypic robot. In this paper an attempt is made to imitate idiotypic dynamics by creating controllers that use reinforcement with a number of different probabilistic schemes to select robot behaviour. The aims are to show that the idiotypic system is not merely performing some kind of periodic random behaviour selection, and to try to gain further insight into the processes that govern the idiotypic mechanism. Trials are carried out using simulated Pioneer robots that undertake navigation exercises. Results show that a scheme that boosts the probability of selecting highly-ranked alternative behaviours to 50% during stall conditions comes closest to achieving the properties of the idiotypic system, but remains unable to match it in terms of all round performance.
* 7 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables, 13th World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics: WMSCI 2009, Orlando, Florida, USA
Idiotypic Immune Networks in Mobile Robot Control
Mar 20, 2008Abstract:Jerne's idiotypic network theory postulates that the immune response involves inter-antibody stimulation and suppression as well as matching to antigens. The theory has proved the most popular Artificial Immune System (ais) model for incorporation into behavior-based robotics but guidelines for implementing idiotypic selection are scarce. Furthermore, the direct effects of employing the technique have not been demonstrated in the form of a comparison with non-idiotypic systems. This paper aims to address these issues. A method for integrating an idiotypic ais network with a Reinforcement Learning based control system (rl) is described and the mechanisms underlying antibody stimulation and suppression are explained in detail. Some hypotheses that account for the network advantage are put forward and tested using three systems with increasing idiotypic complexity. The basic rl, a simplified hybrid ais-rl that implements idiotypic selection independently of derived concentration levels and a full hybrid ais-rl scheme are examined. The test bed takes the form of a simulated Pioneer robot that is required to navigate through maze worlds detecting and tracking door markers.
Genetic-Algorithm Seeding Of Idiotypic Networks For Mobile-Robot Navigation
Mar 11, 2008



Abstract:Robot-control designers have begun to exploit the properties of the human immune system in order to produce dynamic systems that can adapt to complex, varying, real-world tasks. Jernes idiotypic-network theory has proved the most popular artificial-immune-system (AIS) method for incorporation into behaviour-based robotics, since idiotypic selection produces highly adaptive responses. However, previous efforts have mostly focused on evolving the network connections and have often worked with a single, pre-engineered set of behaviours, limiting variability. This paper describes a method for encoding behaviours as a variable set of attributes, and shows that when the encoding is used with a genetic algorithm (GA), multiple sets of diverse behaviours can develop naturally and rapidly, providing much greater scope for flexible behaviour-selection. The algorithm is tested extensively with a simulated e-puck robot that navigates around a maze by tracking colour. Results show that highly successful behaviour sets can be generated within about 25 minutes, and that much greater diversity can be obtained when multiple autonomous populations are used, rather than a single one.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge