Jonathan El-Beze
Deep Prototypical-Parts Ease Morphological Kidney Stone Identification and are Competitively Robust to Photometric Perturbations
Apr 08, 2023Abstract:Identifying the type of kidney stones can allow urologists to determine their cause of formation, improving the prescription of appropriate treatments to diminish future relapses. Currently, the associated ex-vivo diagnosis (known as Morpho-constitutional Analysis, MCA) is time-consuming, expensive and requires a great deal of experience, as it requires a visual analysis component that is highly operator dependant. Recently, machine learning methods have been developed for in-vivo endoscopic stone recognition. Deep Learning (DL) based methods outperform non-DL methods in terms of accuracy but lack explainability. Despite this trade-off, when it comes to making high-stakes decisions, it's important to prioritize understandable Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CADx) that suggests a course of action based on reasonable evidence, rather than a model prescribing a course of action. In this proposal, we learn Prototypical Parts (PPs) per kidney stone subtype, which are used by the DL model to generate an output classification. Using PPs in the classification task enables case-based reasoning explanations for such output, thus making the model interpretable. In addition, we modify global visual characteristics to describe their relevance to the PPs and the sensitivity of our model's performance. With this, we provide explanations with additional information at the sample, class and model levels in contrast to previous works. Although our implementation's average accuracy is lower than state-of-the-art (SOTA) non-interpretable DL models by 1.5 %, our models perform 2.8% better on perturbed images with a lower standard deviation, without adversarial training. Thus, Learning PPs has the potential to create more robust DL models.
Improving automatic endoscopic stone recognition using a multi-view fusion approach enhanced with two-step transfer learning
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:This contribution presents a deep-learning method for extracting and fusing image information acquired from different viewpoints, with the aim to produce more discriminant object features for the identification of the type of kidney stones seen in endoscopic images. The model was further improved with a two-step transfer learning approach and by attention blocks to refine the learned feature maps. Deep feature fusion strategies improved the results of single view extraction backbone models by more than 6% in terms of accuracy of the kidney stones classification.
Improved Kidney Stone Recognition Through Attention and Multi-View Feature Fusion Strategies
Nov 05, 2022Abstract:This contribution presents a deep learning method for the extraction and fusion of information relating to kidney stone fragments acquired from different viewpoints of the endoscope. Surface and section fragment images are jointly used during the training of the classifier to improve the discrimination power of the features by adding attention layers at the end of each convolutional block. This approach is specifically designed to mimic the morpho-constitutional analysis performed in ex-vivo by biologists to visually identify kidney stones by inspecting both views. The addition of attention mechanisms to the backbone improved the results of single view extraction backbones by 4% on average. Moreover, in comparison to the state-of-the-art, the fusion of the deep features improved the overall results up to 11% in terms of kidney stone classification accuracy.
Boosting Kidney Stone Identification in Endoscopic Images Using Two-Step Transfer Learning
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Knowing the cause of kidney stone formation is crucial to establish treatments that prevent recurrence. There are currently different approaches for determining the kidney stone type. However, the reference ex-vivo identification procedure can take up to several weeks, while an in-vivo visual recognition requires highly trained specialists. Machine learning models have been developed to provide urologists with an automated classification of kidney stones during an ureteroscopy; however, there is a general lack in terms of quality of the training data and methods. In this work, a two-step transfer learning approach is used to train the kidney stone classifier. The proposed approach transfers knowledge learned on a set of images of kidney stones acquired with a CCD camera (ex-vivo dataset) to a final model that classifies images from endoscopic images (ex-vivo dataset). The results show that learning features from different domains with similar information helps to improve the performance of a model that performs classification in real conditions (for instance, uncontrolled lighting conditions and blur). Finally, in comparison to models that are trained from scratch or by initializing ImageNet weights, the obtained results suggest that the two-step approach extracts features improving the identification of kidney stones in endoscopic images.
Interpretable Deep Learning Classifier by Detection of Prototypical Parts on Kidney Stones Images
Jun 02, 2022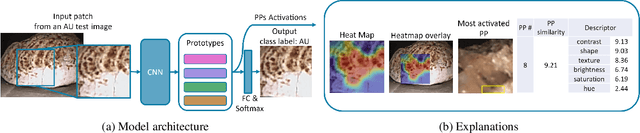
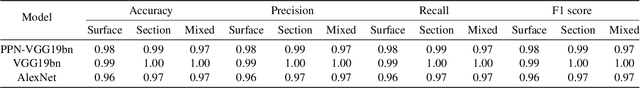

Abstract:Identifying the type of kidney stones can allow urologists to determine their formation cause, improving the early prescription of appropriate treatments to diminish future relapses. However, currently, the associated ex-vivo diagnosis (known as morpho-constitutional analysis, MCA) is time-consuming, expensive, and requires a great deal of experience, as it requires a visual analysis component that is highly operator dependant. Recently, machine learning methods have been developed for in-vivo endoscopic stone recognition. Shallow methods have been demonstrated to be reliable and interpretable but exhibit low accuracy, while deep learning-based methods yield high accuracy but are not explainable. However, high stake decisions require understandable computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) to suggest a course of action based on reasonable evidence, rather than merely prescribe one. Herein, we investigate means for learning part-prototypes (PPs) that enable interpretable models. Our proposal suggests a classification for a kidney stone patch image and provides explanations in a similar way as those used on the MCA method.
Comparing feature fusion strategies for Deep Learning-based kidney stone identification
May 31, 2022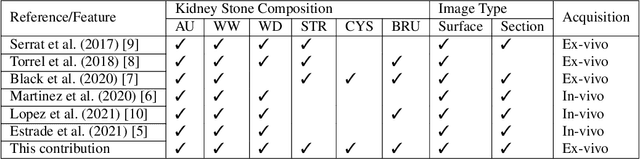
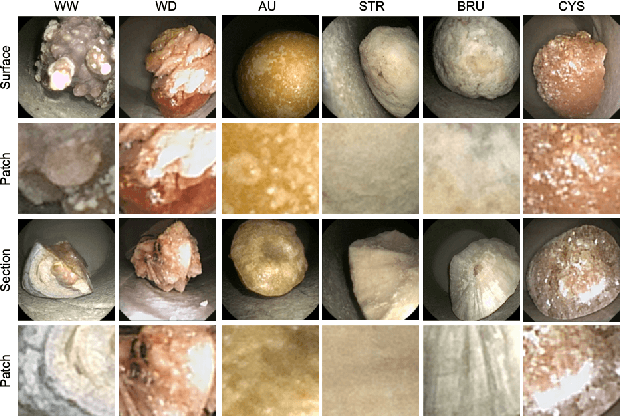
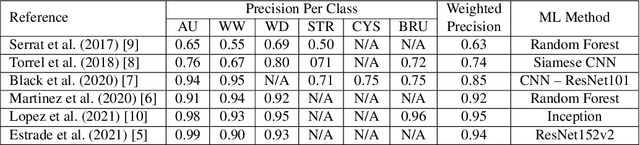
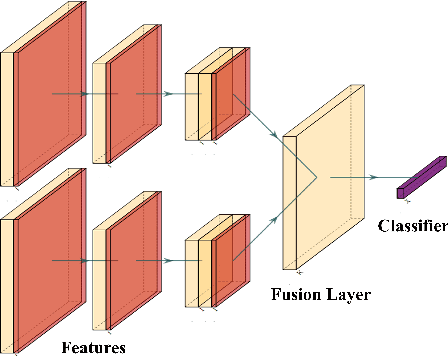
Abstract:This contribution presents a deep-learning method for extracting and fusing image information acquired from different viewpoints with the aim to produce more discriminant object features. Our approach was specifically designed to mimic the morpho-constitutional analysis used by urologists to visually classify kidney stones by inspecting the sections and surfaces of their fragments. Deep feature fusion strategies improved the results of single view extraction backbone models by more than 10\% in terms of precision of the kidney stones classification.
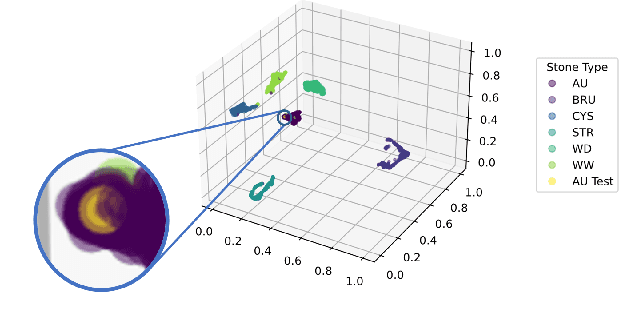
On the generalization capabilities of FSL methods through domain adaptation: a case study in endoscopic kidney stone image classification
May 02, 2022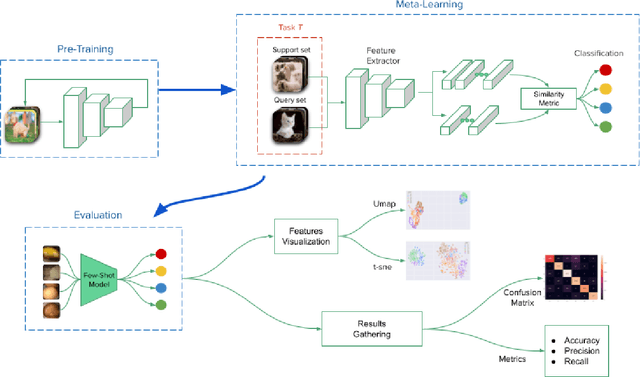
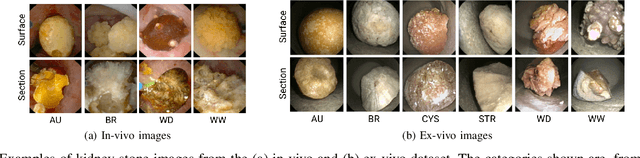
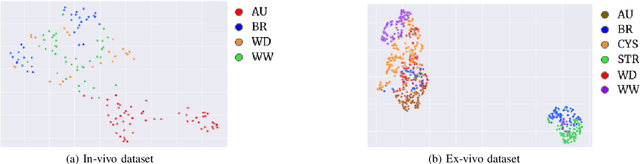
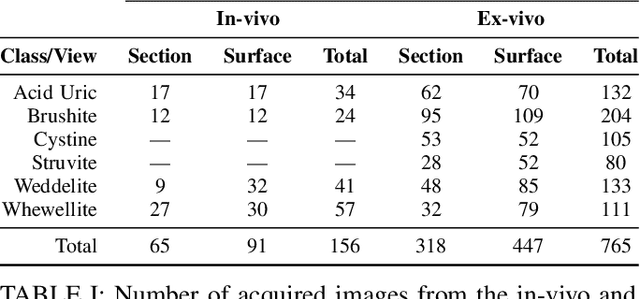
Abstract:Deep learning has shown great promise in diverse areas of computer vision, such as image classification, object detection and semantic segmentation, among many others. However, as it has been repeatedly demonstrated, deep learning methods trained on a dataset do not generalize well to datasets from other domains or even to similar datasets, due to data distribution shifts. In this work, we propose the use of a meta-learning based few-shot learning approach to alleviate these problems. In order to demonstrate its efficacy, we use two datasets of kidney stones samples acquired with different endoscopes and different acquisition conditions. The results show how such methods are indeed capable of handling domain-shifts by attaining an accuracy of 74.38% and 88.52% in the 5-way 5-shot and 5-way 20-shot settings respectively. Instead, in the same dataset, traditional Deep Learning (DL) methods attain only an accuracy of 45%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge