Elias Villalvazo-Avila
A metric learning approach for endoscopic kidney stone identification
Jul 13, 2023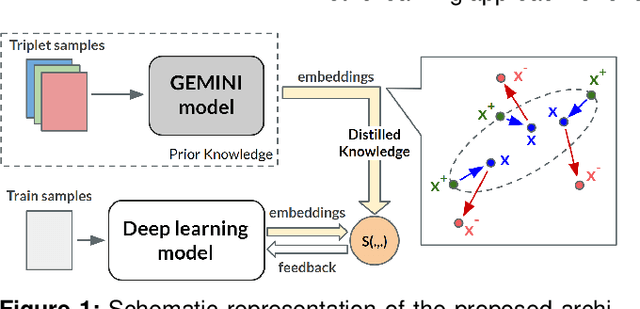
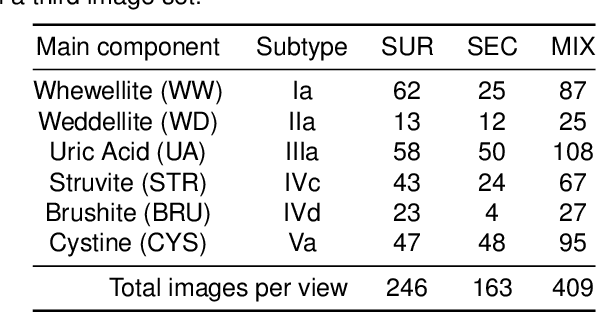
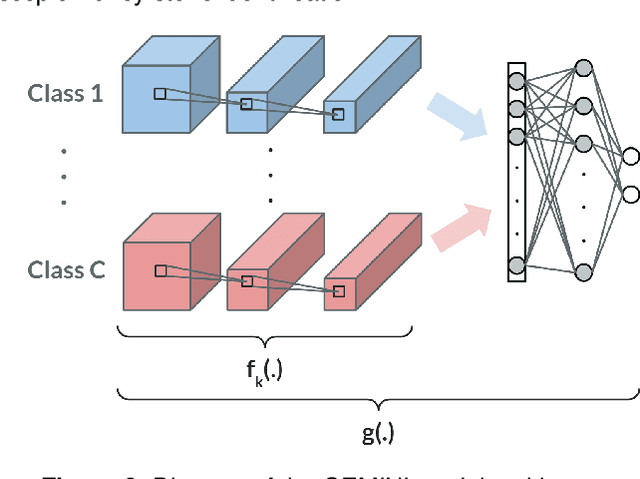
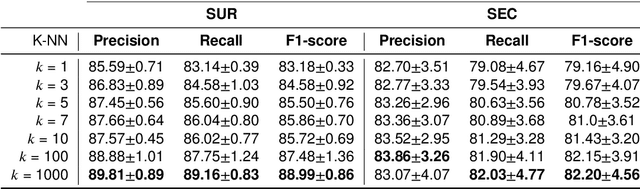
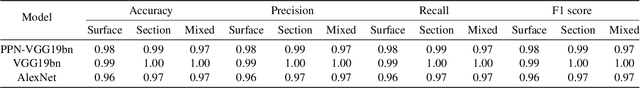
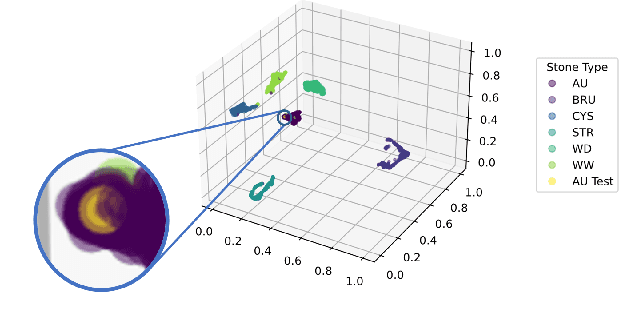
Abstract:Several Deep Learning (DL) methods have recently been proposed for an automated identification of kidney stones during an ureteroscopy to enable rapid therapeutic decisions. Even if these DL approaches led to promising results, they are mainly appropriate for kidney stone types for which numerous labelled data are available. However, only few labelled images are available for some rare kidney stone types. This contribution exploits Deep Metric Learning (DML) methods i) to handle such classes with few samples, ii) to generalize well to out of distribution samples, and iii) to cope better with new classes which are added to the database. The proposed Guided Deep Metric Learning approach is based on a novel architecture which was designed to learn data representations in an improved way. The solution was inspired by Few-Shot Learning (FSL) and makes use of a teacher-student approach. The teacher model (GEMINI) generates a reduced hypothesis space based on prior knowledge from the labeled data, and is used it as a guide to a student model (i.e., ResNet50) through a Knowledge Distillation scheme. Extensive tests were first performed on two datasets separately used for the recognition, namely a set of images acquired for the surfaces of the kidney stone fragments, and a set of images of the fragment sections. The proposed DML-approach improved the identification accuracy by 10% and 12% in comparison to DL-methods and other DML-approaches, respectively. Moreover, model embeddings from the two dataset types were merged in an organized way through a multi-view scheme to simultaneously exploit the information of surface and section fragments. Test with the resulting mixed model improves the identification accuracy by at least 3% and up to 30% with respect to DL-models and shallow machine learning methods, respectively.
Improving automatic endoscopic stone recognition using a multi-view fusion approach enhanced with two-step transfer learning
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:This contribution presents a deep-learning method for extracting and fusing image information acquired from different viewpoints, with the aim to produce more discriminant object features for the identification of the type of kidney stones seen in endoscopic images. The model was further improved with a two-step transfer learning approach and by attention blocks to refine the learned feature maps. Deep feature fusion strategies improved the results of single view extraction backbone models by more than 6% in terms of accuracy of the kidney stones classification.
Improved Kidney Stone Recognition Through Attention and Multi-View Feature Fusion Strategies
Nov 05, 2022Abstract:This contribution presents a deep learning method for the extraction and fusion of information relating to kidney stone fragments acquired from different viewpoints of the endoscope. Surface and section fragment images are jointly used during the training of the classifier to improve the discrimination power of the features by adding attention layers at the end of each convolutional block. This approach is specifically designed to mimic the morpho-constitutional analysis performed in ex-vivo by biologists to visually identify kidney stones by inspecting both views. The addition of attention mechanisms to the backbone improved the results of single view extraction backbones by 4% on average. Moreover, in comparison to the state-of-the-art, the fusion of the deep features improved the overall results up to 11% in terms of kidney stone classification accuracy.
Interpretable Deep Learning Classifier by Detection of Prototypical Parts on Kidney Stones Images
Jun 02, 2022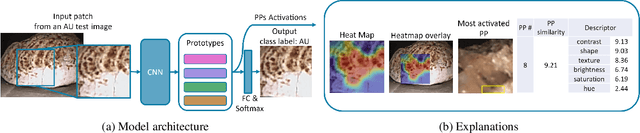

Abstract:Identifying the type of kidney stones can allow urologists to determine their formation cause, improving the early prescription of appropriate treatments to diminish future relapses. However, currently, the associated ex-vivo diagnosis (known as morpho-constitutional analysis, MCA) is time-consuming, expensive, and requires a great deal of experience, as it requires a visual analysis component that is highly operator dependant. Recently, machine learning methods have been developed for in-vivo endoscopic stone recognition. Shallow methods have been demonstrated to be reliable and interpretable but exhibit low accuracy, while deep learning-based methods yield high accuracy but are not explainable. However, high stake decisions require understandable computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) to suggest a course of action based on reasonable evidence, rather than merely prescribe one. Herein, we investigate means for learning part-prototypes (PPs) that enable interpretable models. Our proposal suggests a classification for a kidney stone patch image and provides explanations in a similar way as those used on the MCA method.
Comparing feature fusion strategies for Deep Learning-based kidney stone identification
May 31, 2022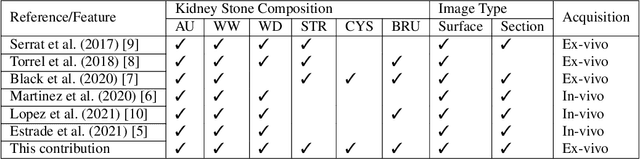
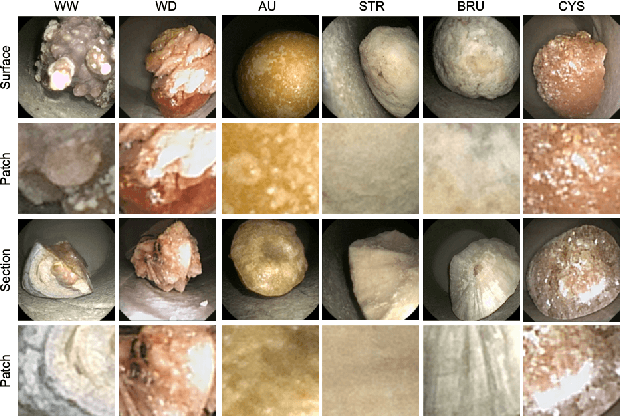
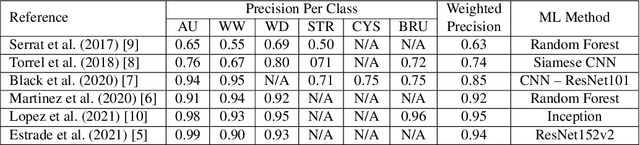
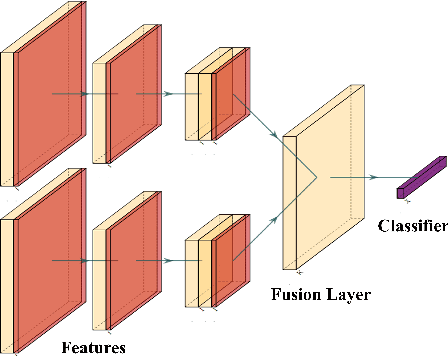
Abstract:This contribution presents a deep-learning method for extracting and fusing image information acquired from different viewpoints with the aim to produce more discriminant object features. Our approach was specifically designed to mimic the morpho-constitutional analysis used by urologists to visually classify kidney stones by inspecting the sections and surfaces of their fragments. Deep feature fusion strategies improved the results of single view extraction backbone models by more than 10\% in terms of precision of the kidney stones classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge