Jon Barron
EVER: Exact Volumetric Ellipsoid Rendering for Real-time View Synthesis
Oct 02, 2024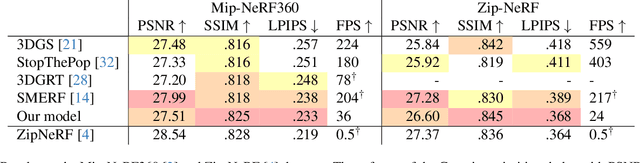
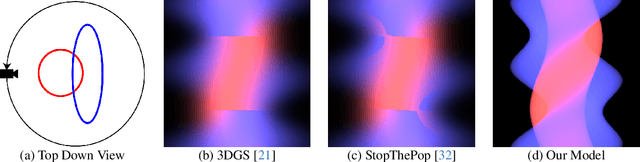
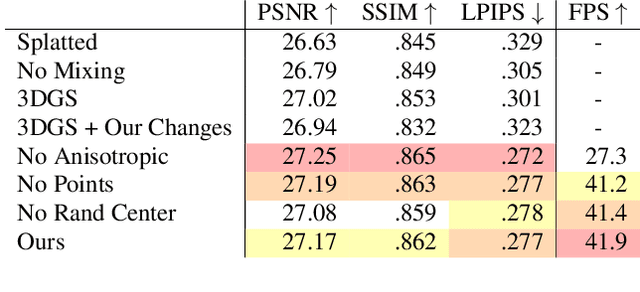
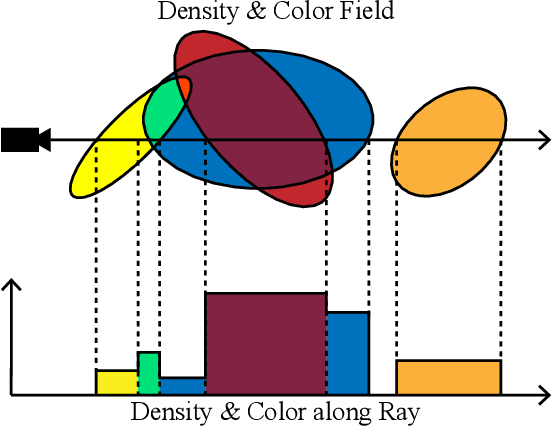
Abstract:We present Exact Volumetric Ellipsoid Rendering (EVER), a method for real-time differentiable emission-only volume rendering. Unlike recent rasterization based approach by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), our primitive based representation allows for exact volume rendering, rather than alpha compositing 3D Gaussian billboards. As such, unlike 3DGS our formulation does not suffer from popping artifacts and view dependent density, but still achieves frame rates of $\sim\!30$ FPS at 720p on an NVIDIA RTX4090. Since our approach is built upon ray tracing it enables effects such as defocus blur and camera distortion (e.g. such as from fisheye cameras), which are difficult to achieve by rasterization. We show that our method is more accurate with fewer blending issues than 3DGS and follow-up work on view-consistent rendering, especially on the challenging large-scale scenes from the Zip-NeRF dataset where it achieves sharpest results among real-time techniques.
Fast and High-Quality Image Denoising via Malleable Convolutions
Jan 04, 2022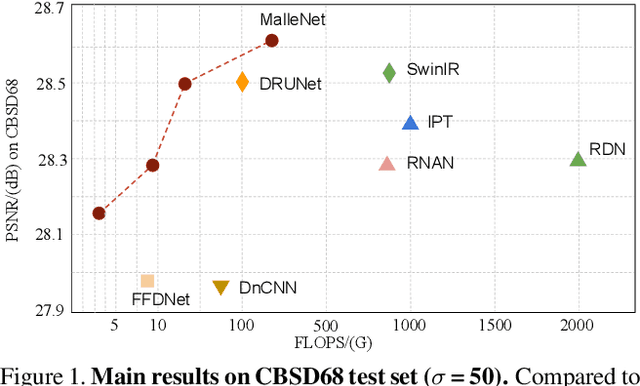
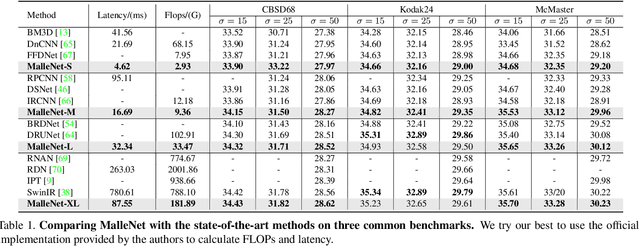
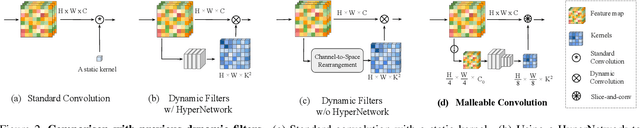
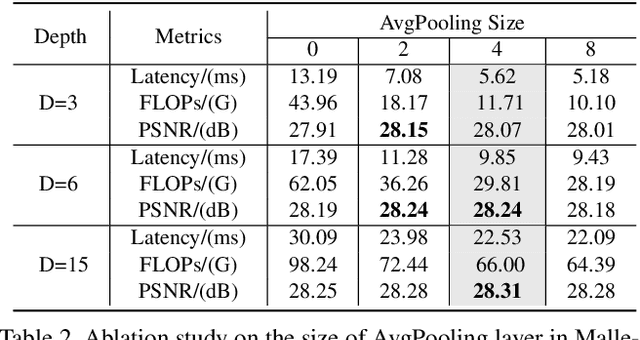
Abstract:Many image processing networks apply a single set of static convolutional kernels across the entire input image, which is sub-optimal for natural images, as they often consist of heterogeneous visual patterns. Recent works in classification, segmentation, and image restoration have demonstrated that dynamic kernels outperform static kernels at modeling local image statistics. However, these works often adopt per-pixel convolution kernels, which introduce high memory and computation costs. To achieve spatial-varying processing without significant overhead, we present Malleable Convolution (MalleConv), as an efficient variant of dynamic convolution. The weights of MalleConv are dynamically produced by an efficient predictor network capable of generating content-dependent outputs at specific spatial locations. Unlike previous works, MalleConv generates a much smaller set of spatially-varying kernels from input, which enlarges the network's receptive field and significantly reduces computational and memory costs. These kernels are then applied to a full-resolution feature map through an efficient slice-and-conv operator with minimum memory overhead. We further build an efficient denoising network using MalleConv, coined as MalleNet. It achieves high quality results without very deep architecture, e.g., reaching 8.91x faster speed compared to the best performed denoising algorithms (SwinIR), while maintaining similar performance. We also show that a single MalleConv added to a standard convolution-based backbone can contribute significantly to reducing the computational cost or boosting image quality at a similar cost. Project page: https://yifanjiang.net/MalleConv.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge