John Murzaku
OmniVox: Zero-Shot Emotion Recognition with Omni-LLMs
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:The use of omni-LLMs (large language models that accept any modality as input), particularly for multimodal cognitive state tasks involving speech, is understudied. We present OmniVox, the first systematic evaluation of four omni-LLMs on the zero-shot emotion recognition task. We evaluate on two widely used multimodal emotion benchmarks: IEMOCAP and MELD, and find zero-shot omni-LLMs outperform or are competitive with fine-tuned audio models. Alongside our audio-only evaluation, we also evaluate omni-LLMs on text only and text and audio. We present acoustic prompting, an audio-specific prompting strategy for omni-LLMs which focuses on acoustic feature analysis, conversation context analysis, and step-by-step reasoning. We compare our acoustic prompting to minimal prompting and full chain-of-thought prompting techniques. We perform a context window analysis on IEMOCAP and MELD, and find that using context helps, especially on IEMOCAP. We conclude with an error analysis on the generated acoustic reasoning outputs from the omni-LLMs.
ECLAIR: Enhanced Clarification for Interactive Responses
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:We present ECLAIR (Enhanced CLArification for Interactive Responses), a novel unified and end-to-end framework for interactive disambiguation in enterprise AI assistants. ECLAIR generates clarification questions for ambiguous user queries and resolves ambiguity based on the user's response.We introduce a generalized architecture capable of integrating ambiguity information from multiple downstream agents, enhancing context-awareness in resolving ambiguities and allowing enterprise specific definition of agents. We further define agents within our system that provide domain-specific grounding information. We conduct experiments comparing ECLAIR to few-shot prompting techniques and demonstrate ECLAIR's superior performance in clarification question generation and ambiguity resolution.
Zero-Shot Belief: A Hard Problem for LLMs
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:We present two LLM-based approaches to zero-shot source-and-target belief prediction on FactBank: a unified system that identifies events, sources, and belief labels in a single pass, and a hybrid approach that uses a fine-tuned DeBERTa tagger for event detection. We show that multiple open-sourced, closed-source, and reasoning-based LLMs struggle with the task. Using the hybrid approach, we achieve new state-of-the-art results on FactBank and offer a detailed error analysis. Our approach is then tested on the Italian belief corpus ModaFact.
Synthetic Audio Helps for Cognitive State Tasks
Feb 10, 2025

Abstract:The NLP community has broadly focused on text-only approaches of cognitive state tasks, but audio can provide vital missing cues through prosody. We posit that text-to-speech models learn to track aspects of cognitive state in order to produce naturalistic audio, and that the signal audio models implicitly identify is orthogonal to the information that language models exploit. We present Synthetic Audio Data fine-tuning (SAD), a framework where we show that 7 tasks related to cognitive state modeling benefit from multimodal training on both text and zero-shot synthetic audio data from an off-the-shelf TTS system. We show an improvement over the text-only modality when adding synthetic audio data to text-only corpora. Furthermore, on tasks and corpora that do contain gold audio, we show our SAD framework achieves competitive performance with text and synthetic audio compared to text and gold audio.
* John Murzaku and Adil Soubki contributed equally to this work
Training LLMs to Recognize Hedges in Spontaneous Narratives
Aug 06, 2024
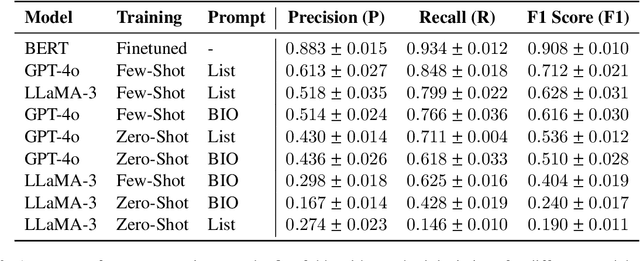

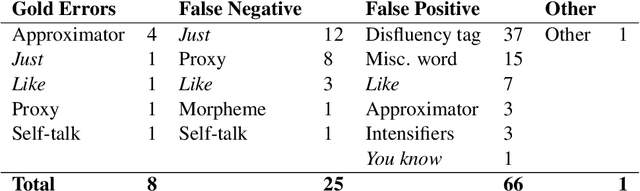
Abstract:Hedges allow speakers to mark utterances as provisional, whether to signal non-prototypicality or "fuzziness", to indicate a lack of commitment to an utterance, to attribute responsibility for a statement to someone else, to invite input from a partner, or to soften critical feedback in the service of face-management needs. Here we focus on hedges in an experimentally parameterized corpus of 63 Roadrunner cartoon narratives spontaneously produced from memory by 21 speakers for co-present addressees, transcribed to text (Galati and Brennan, 2010). We created a gold standard of hedges annotated by human coders (the Roadrunner-Hedge corpus) and compared three LLM-based approaches for hedge detection: fine-tuning BERT, and zero and few-shot prompting with GPT-4o and LLaMA-3. The best-performing approach was a fine-tuned BERT model, followed by few-shot GPT-4o. After an error analysis on the top performing approaches, we used an LLM-in-the-Loop approach to improve the gold standard coding, as well as to highlight cases in which hedges are ambiguous in linguistically interesting ways that will guide future research. This is the first step in our research program to train LLMs to interpret and generate collateral signals appropriately and meaningfully in conversation.
* Amie Paige, Adil Soubki, and John Murzaku contributed equally to this study
Multimodal Belief Prediction
Jun 11, 2024
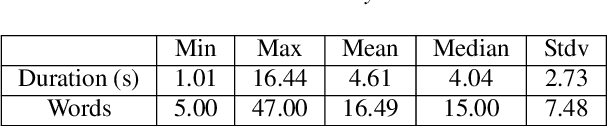


Abstract:Recognizing a speaker's level of commitment to a belief is a difficult task; humans do not only interpret the meaning of the words in context, but also understand cues from intonation and other aspects of the audio signal. Many papers and corpora in the NLP community have approached the belief prediction task using text-only approaches. We are the first to frame and present results on the multimodal belief prediction task. We use the CB-Prosody corpus (CBP), containing aligned text and audio with speaker belief annotations. We first report baselines and significant features using acoustic-prosodic features and traditional machine learning methods. We then present text and audio baselines for the CBP corpus fine-tuning on BERT and Whisper respectively. Finally, we present our multimodal architecture which fine-tunes on BERT and Whisper and uses multiple fusion methods, improving on both modalities alone.
* John Murzaku and Adil Soubki contributed equally to this work
Views Are My Own, But Also Yours: Benchmarking Theory of Mind using Common Ground
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating the theory of mind (ToM) capabilities of language models (LMs) has recently received much attention. However, many existing benchmarks rely on synthetic data which risks misaligning the resulting experiments with human behavior. We introduce the first ToM dataset based on naturally occurring spoken dialogs, Common-ToM, and show that LMs struggle to demonstrate ToM. We then show that integrating a simple, explicit representation of beliefs improves LM performance on Common-ToM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge