Peter Zeng
LVLMs and Humans Ground Differently in Referential Communication
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:For generative AI agents to partner effectively with human users, the ability to accurately predict human intent is critical. But this ability to collaborate remains limited by a critical deficit: an inability to model common ground. Here, we present a referential communication experiment with a factorial design involving director-matcher pairs (human-human, human-AI, AI-human, and AI-AI) that interact with multiple turns in repeated rounds to match pictures of objects not associated with any obvious lexicalized labels. We release the online pipeline for data collection, the tools and analyses for accuracy, efficiency, and lexical overlap, and a corpus of 356 dialogues (89 pairs over 4 rounds each) that unmasks LVLMs' limitations in interactively resolving referring expressions, a crucial skill that underlies human language use.
Synthetic Audio Helps for Cognitive State Tasks
Feb 10, 2025

Abstract:The NLP community has broadly focused on text-only approaches of cognitive state tasks, but audio can provide vital missing cues through prosody. We posit that text-to-speech models learn to track aspects of cognitive state in order to produce naturalistic audio, and that the signal audio models implicitly identify is orthogonal to the information that language models exploit. We present Synthetic Audio Data fine-tuning (SAD), a framework where we show that 7 tasks related to cognitive state modeling benefit from multimodal training on both text and zero-shot synthetic audio data from an off-the-shelf TTS system. We show an improvement over the text-only modality when adding synthetic audio data to text-only corpora. Furthermore, on tasks and corpora that do contain gold audio, we show our SAD framework achieves competitive performance with text and synthetic audio compared to text and gold audio.
* John Murzaku and Adil Soubki contributed equally to this work
Gram2Vec: An Interpretable Document Vectorizer
Jun 17, 2024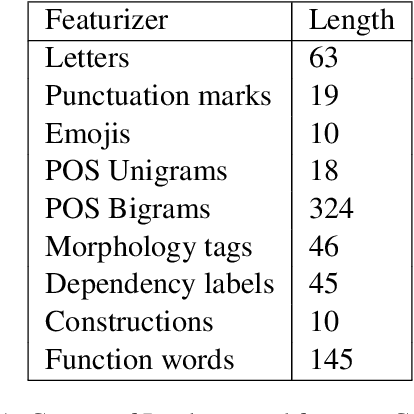



Abstract:We present Gram2Vec, a grammatical style embedding algorithm that embeds documents into a higher dimensional space by extracting the normalized relative frequencies of grammatical features present in the text. Compared to neural approaches, Gram2Vec offers inherent interpretability based on how the feature vectors are generated. In our demo, we present a way to visualize a mapping of authors to documents based on their Gram2Vec vectors and highlight the ability to drop or add features to view which authors make certain linguistic choices. Next, we use authorship attribution as an application to show how Gram2Vec can explain why a document is attributed to a certain author, using cosine similarities between the Gram2Vec feature vectors to calculate the distances between candidate documents and a query document.
Views Are My Own, But Also Yours: Benchmarking Theory of Mind using Common Ground
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating the theory of mind (ToM) capabilities of language models (LMs) has recently received much attention. However, many existing benchmarks rely on synthetic data which risks misaligning the resulting experiments with human behavior. We introduce the first ToM dataset based on naturally occurring spoken dialogs, Common-ToM, and show that LMs struggle to demonstrate ToM. We then show that integrating a simple, explicit representation of beliefs improves LM performance on Common-ToM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge