Magdalena Markowska
Views Are My Own, But Also Yours: Benchmarking Theory of Mind using Common Ground
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating the theory of mind (ToM) capabilities of language models (LMs) has recently received much attention. However, many existing benchmarks rely on synthetic data which risks misaligning the resulting experiments with human behavior. We introduce the first ToM dataset based on naturally occurring spoken dialogs, Common-ToM, and show that LMs struggle to demonstrate ToM. We then show that integrating a simple, explicit representation of beliefs improves LM performance on Common-ToM.
Finding Common Ground: Annotating and Predicting Common Ground in Spoken Conversations
Nov 02, 2023

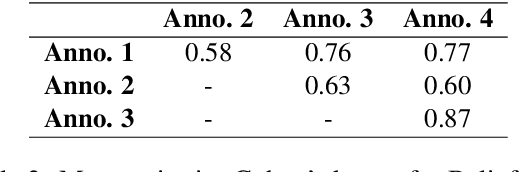

Abstract:When we communicate with other humans, we do not simply generate a sequence of words. Rather, we use our cognitive state (beliefs, desires, intentions) and our model of the audience's cognitive state to create utterances that affect the audience's cognitive state in the intended manner. An important part of cognitive state is the common ground, which is the content the speaker believes, and the speaker believes the audience believes, and so on. While much attention has been paid to common ground in cognitive science, there has not been much work in natural language processing. In this paper, we introduce a new annotation and corpus to capture common ground. We then describe some initial experiments extracting propositions from dialog and tracking their status in the common ground from the perspective of each speaker.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge