John M. Cioffi
Continuous-Utility Direct Preference Optimization
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large language model reasoning is often treated as a monolithic capability, relying on binary preference supervision that fails to capture partial progress or fine-grained reasoning quality. We introduce Continuous Utility Direct Preference Optimization (CU-DPO), a framework that aligns models to a portfolio of prompt-based cognitive strategies by replacing binary labels with continuous scores that capture fine-grained reasoning quality. We prove that learning with K strategies yields a Theta(K log K) improvement in sample complexity over binary preferences, and that DPO converges to the entropy-regularized utility-maximizing policy. To exploit this signal, we propose a two-stage training pipeline: (i) strategy selection, which optimizes the model to choose the best strategy for a given problem via best-vs-all comparisons, and (ii) execution refinement, which trains the model to correctly execute the selected strategy using margin-stratified pairs. On mathematical reasoning benchmarks, CU-DPO improves strategy selection accuracy from 35-46 percent to 68-78 percent across seven base models, yielding consistent downstream reasoning gains of up to 6.6 points on in-distribution datasets with effective transfer to out-of-distribution tasks.
On the Fundamental Limits of LLMs at Scale
Nov 17, 2025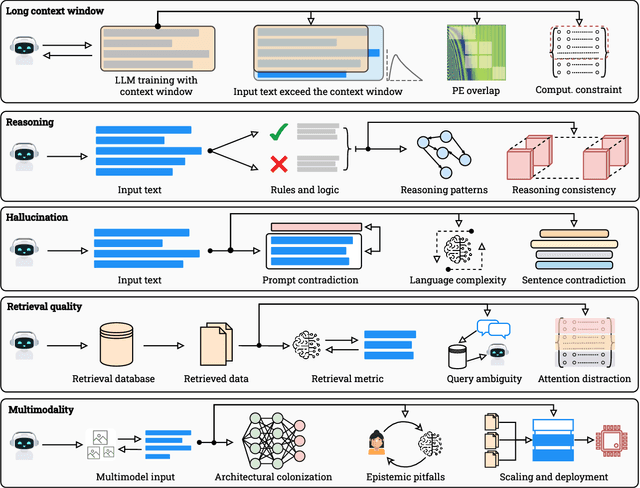
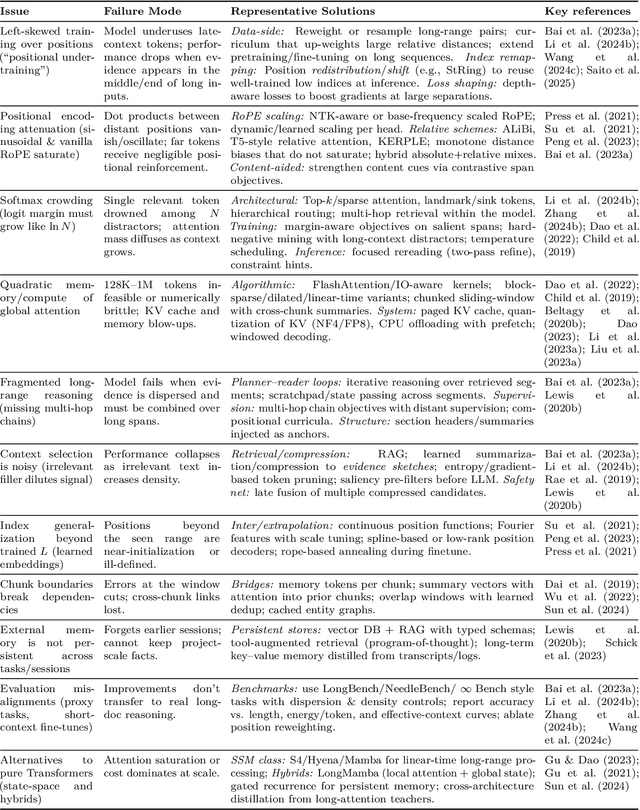
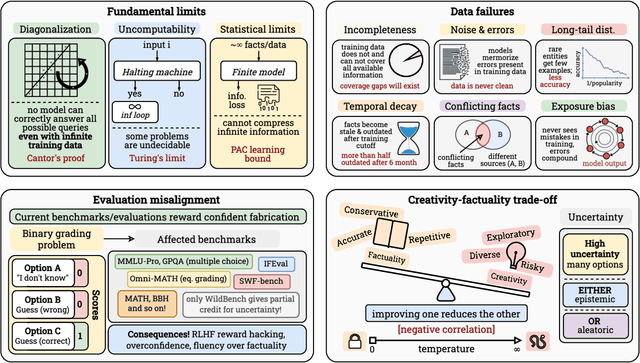
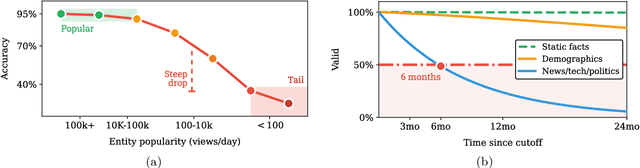
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have benefited enormously from scaling, yet these gains are bounded by five fundamental limitations: (1) hallucination, (2) context compression, (3) reasoning degradation, (4) retrieval fragility, and (5) multimodal misalignment. While existing surveys describe these phenomena empirically, they lack a rigorous theoretical synthesis connecting them to the foundational limits of computation, information, and learning. This work closes that gap by presenting a unified, proof-informed framework that formalizes the innate theoretical ceilings of LLM scaling. First, computability and uncomputability imply an irreducible residue of error: for any computably enumerable model family, diagonalization guarantees inputs on which some model must fail, and undecidable queries (e.g., halting-style tasks) induce infinite failure sets for all computable predictors. Second, information-theoretic and statistical constraints bound attainable accuracy even on decidable tasks, finite description length enforces compression error, and long-tail factual knowledge requires prohibitive sample complexity. Third, geometric and computational effects compress long contexts far below their nominal size due to positional under-training, encoding attenuation, and softmax crowding. We further show how likelihood-based training favors pattern completion over inference, how retrieval under token limits suffers from semantic drift and coupling noise, and how multimodal scaling inherits shallow cross-modal alignment. Across sections, we pair theorems and empirical evidence to outline where scaling helps, where it saturates, and where it cannot progress, providing both theoretical foundations and practical mitigation paths like bounded-oracle retrieval, positional curricula, and sparse or hierarchical attention.
Retrieval Augmented Generation with Multi-Modal LLM Framework for Wireless Environments
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Future wireless networks aim to deliver high data rates and lower power consumption while ensuring seamless connectivity, necessitating robust optimization. Large language models (LLMs) have been deployed for generalized optimization scenarios. To take advantage of generative AI (GAI) models, we propose retrieval augmented generation (RAG) for multi-sensor wireless environment perception. Utilizing domain-specific prompt engineering, we apply RAG to efficiently harness multimodal data inputs from sensors in a wireless environment. Key pre-processing pipelines including image-to-text conversion, object detection, and distance calculations for multimodal RAG input from multi-sensor data are proposed to obtain a unified vector database crucial for optimizing LLMs in global wireless tasks. Our evaluation, conducted with OpenAI's GPT and Google's Gemini models, demonstrates an 8%, 8%, 10%, 7%, and 12% improvement in relevancy, faithfulness, completeness, similarity, and accuracy, respectively, compared to conventional LLM-based designs. Furthermore, our RAG-based LLM framework with vectorized databases is computationally efficient, providing real-time convergence under latency constraints.
Optimum Power Allocation for Low Rank Wi-Fi Channels: A Comparison with Deep RL Framework
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Upcoming Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) systems require high data rates ($\geq$ 500 Mbps) and low power consumption for seamless experience. With an increasing number of subscribing users, the total number of antennas across all transmitting users far exceeds the number of antennas at the access point (AP). This results in a low rank wireless channel, presenting a bottleneck for uplink communication systems. The current uplink systems that use orthogonal multiple access (OMA) and the proposed non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA), fail to achieve the required data rates / power consumption under predominantly low rank channel scenarios. This paper introduces an optimal power sub carrier allocation algorithm for multi-carrier NOMA, named minPMAC, and an associated time-sharing algorithm that adaptively changes successive interference cancellation decoding orders to maximize sum data rates in these low rank channels. This Lagrangian based optimization technique, although globally optimum, is prohibitive in terms of runtime, proving inefficient for real-time scenarios. Hence, we propose a novel near-optimal deep reinforcement learning-based energy sum optimization (DRL-minPMAC) which achieves real-time efficiency. Extensive experimental evaluations show that minPMAC achieves 28\% and 39\% higher data rates than NOMA and OMA baselines. Furthermore, the proposed DRL-minPMAC runs ~5 times faster than minPMAC and achieves 83\% of the global optimum data rates in real time
Optimum Power-Subcarrier Allocation and Time-Sharing in Multicarrier NOMA Uplink
Jan 20, 2025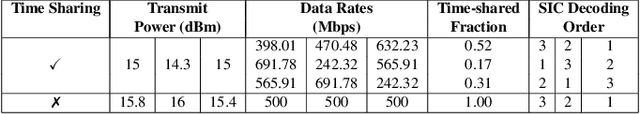
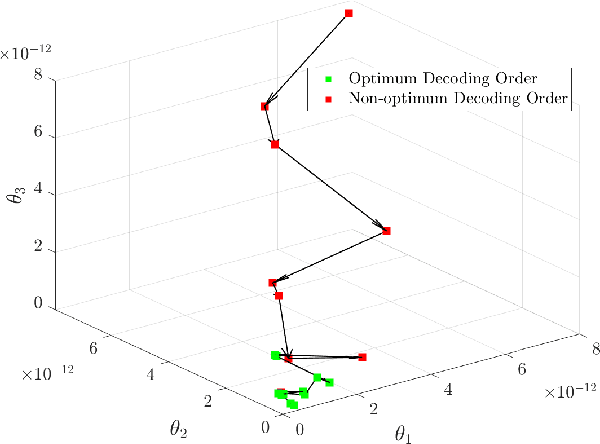
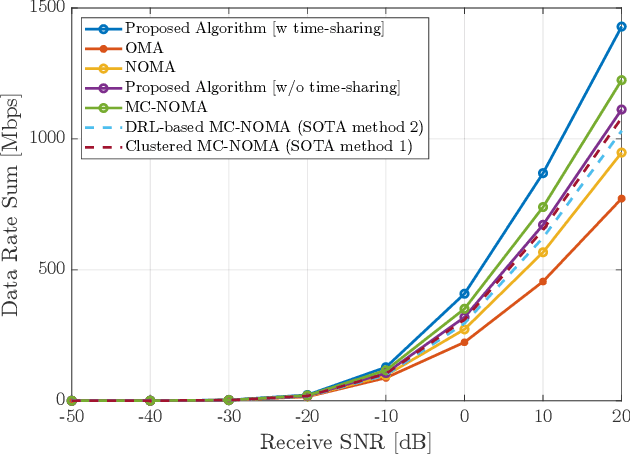
Abstract:Currently used resource allocation methods for uplink multicarrier non-orthogonal multiple access (MC-NOMA) systems have multiple shortcomings. Current approaches either allocate the same power across all subcarriers to a user, or use heuristic-based near-far, strong channel-weak channel user grouping to assign the decoding order for successive interference cancellation (SIC). This paper proposes a novel optimal power-subcarrier allocation for uplink MC-NOMA. This new allocation achieves the optimal power-subcarrier allocation as well as the optimal SIC decoding order. Furthermore, the proposed method includes a time-sharing algorithm that dynamically alters the decoding orders of the participating users to achieve the required data rates, even in cases where any single decoding order fails to do so. Extensive experimental evaluations show that the new method achieves higher sum data rates and lower power consumption compared to current NOMA methods.
Successive Interference Cancellation-aided Diffusion Models for Joint Channel Estimation and Data Detection in Low Rank Channel Scenarios
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a novel joint channel-estimation and source-detection algorithm using successive interference cancellation (SIC)-aided generative score-based diffusion models. Prior work in this area focuses on massive MIMO scenarios, which are typically characterized by full-rank channels, and fail in low-rank channel scenarios. The proposed algorithm outperforms existing methods in joint source-channel estimation, especially in low-rank scenarios where the number of users exceeds the number of antennas at the access point (AP). The proposed score-based iterative diffusion process estimates the gradient of the prior distribution on partial channels, and recursively updates the estimated channel parts as well as the source. Extensive simulation results show that the proposed method outperforms the baseline methods in terms of normalized mean squared error (NMSE) and symbol error rate (SER) in both full-rank and low-rank channel scenarios, while having a more dominant effect in the latter, at various signal-to-noise ratios (SNR).
Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Resource Management in Integrated Terrestrial and Non-Terrestrial Networks
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Efficient spectrum allocation has become crucial as the surge in wireless-connected devices demands seamless support for more users and applications, a trend expected to grow with 6G. Innovations in satellite technologies such as SpaceX's Starlink have enabled non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) to work alongside terrestrial networks (TNs) and allocate spectrum based on regional demands. Existing spectrum sharing approaches in TNs use machine learning for interference minimization through power allocation and spectrum sensing, but the unique characteristics of NTNs like varying orbital dynamics and coverage patterns require more sophisticated coordination mechanisms. The proposed work uses a hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (HDRL) approach for efficient spectrum allocation across TN-NTN networks. DRL agents are present at each TN-NTN hierarchy that dynamically learn and allocate spectrum based on regional trends. This framework is 50x faster than the exhaustive search algorithm while achieving 95\% of optimum spectral efficiency. Moreover, it is 3.75x faster than multi-agent DRL, which is commonly used for spectrum sharing, and has a 12\% higher overall average throughput.
Scaling 6G Subscribers with Fewer BS Antennas using Multi-carrier NOMA in Fixed Wireless Access
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel power allocation and subcarrier optimization algorithm tailored for fixed wireless access (FWA) networks operating under low-rank channel conditions, where the number of subscriber antennas far exceeds those at the base station (BS). As FWA networks grow to support more users, traditional approaches like orthogonal multiple access (OMA) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) struggle to maintain high data rates and energy efficiency due to the limited degrees of freedom in low-rank scenarios. Our proposed solution addresses this by combining optimal power-subcarrier allocation with an adaptive time-sharing algorithm that dynamically adjusts decoding orders to optimize performance across multiple users. The algorithm leverages a generalized decision feedback equalizer (GDFE) approach to effectively manage inter-symbol interference and crosstalk, leading to superior data rates and energy savings. Simulation results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing OMA and NOMA baselines, particularly in low-rank conditions, with substantial gains in both data rate and energy efficiency. The findings highlight the potential of this method to meet the growing demand for scalable, high-performance FWA networks.
Optimal Power Allocation and Time Sharing in Low Rank Multi-carrier Wi-Fi Channels
Oct 29, 2024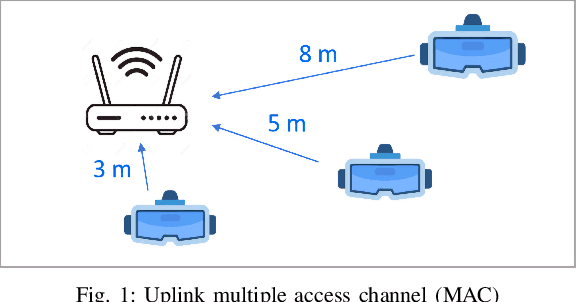
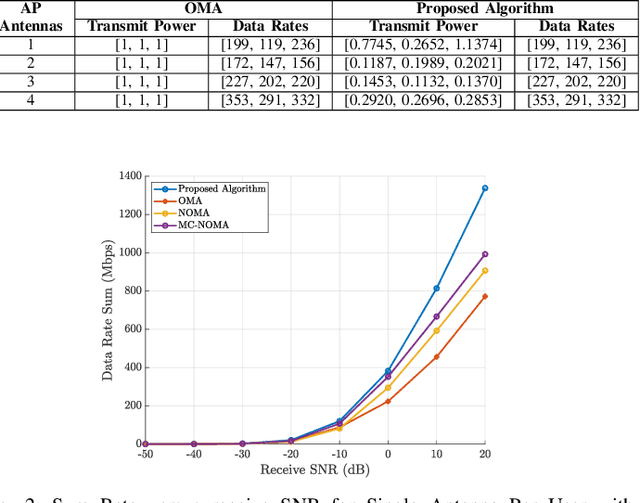
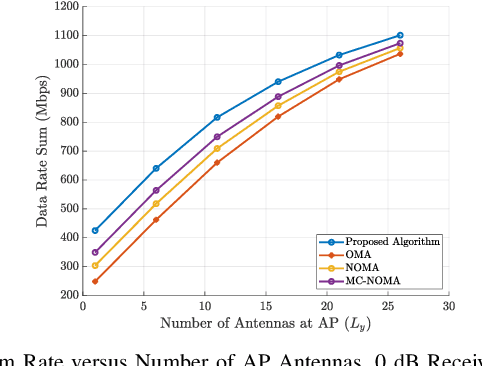
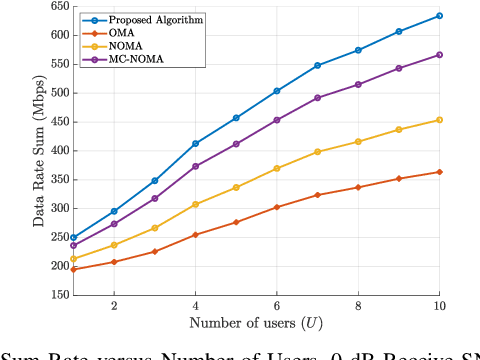
Abstract:The ever-evolving landscape of distributed wireless systems, e.g. multi-user AR/VR systems, demands high data rates (up to 500 Mbps per user) and low power consumption. With increasing number of participating users, uplink data transmission in the situation where the number of transmitter user antennas exceeds the number of access point (AP) antennas presents a low-rank channel problem. Current Wi-Fi standards using orthogonal multiple access (OMA) fail to address these requirements. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA)-based systems, while outperforming the OMA methods, still fall short of the requirement in low-rank channel uplink transmission, because they adhere to a single decoding order for successive interference cancelation (SIC). This paper proposes and develops a novel optimal power-subcarrier allocation algorithm to maximize the achieved data rates for this low rank channel scenario. Additionally, the proposed algorithm implements a novel time-sharing algorithm for simultaneously participating users, which adaptively varies the decoding orders to achieve higher data rates than any single decoding order. Extensive experimental validations demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves 39%, 28%, and 16% higher sum data rates than OMA, NOMA, and multi-carrier NOMA baselines respectively, under low-rank channel conditions, under varying SNR values. We further show that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the baselines with varying numbers of users or AP antennas, showing the effectiveness of the optimal power allocation and time-sharing.
Learned Trimmed-Ridge Regression for Channel Estimation in Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO
Aug 06, 2024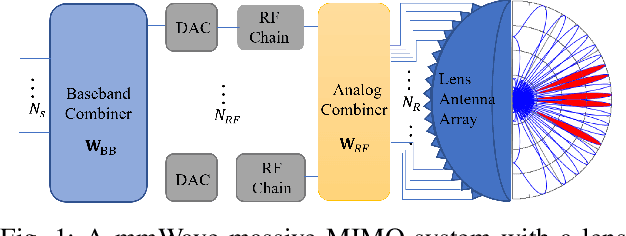
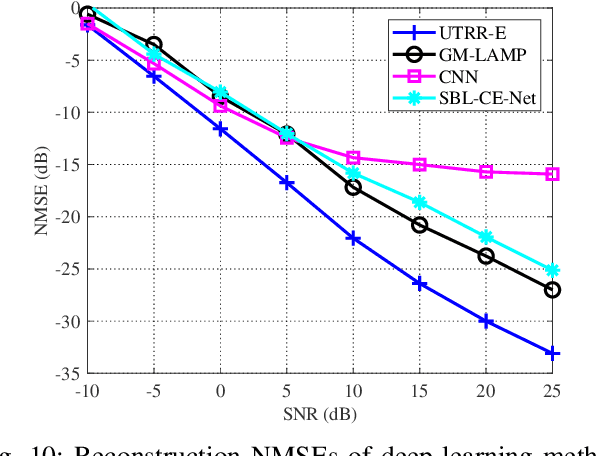
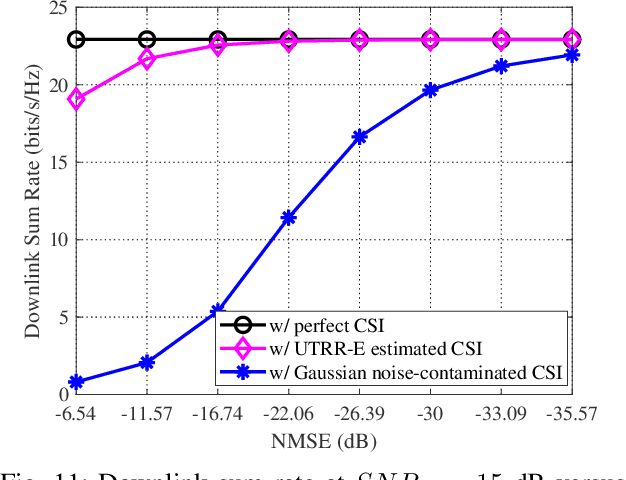
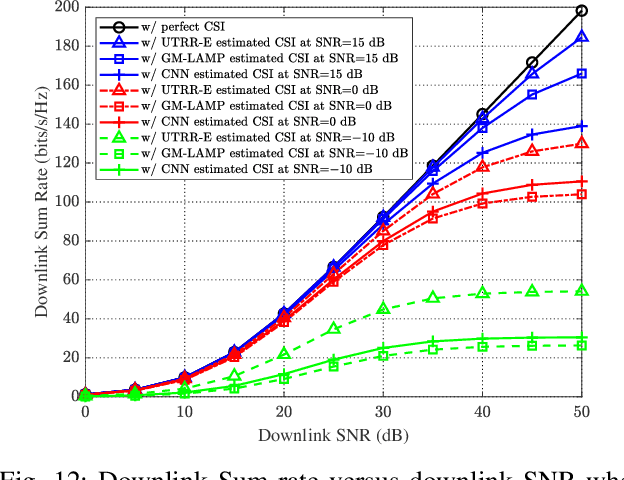
Abstract:Channel estimation poses significant challenges in millimeter-wave massive multiple-input multiple-output systems, especially when the base station has fewer radio-frequency chains than antennas. To address this challenge, one promising solution exploits the beamspace channel sparsity to reconstruct full-dimensional channels from incomplete measurements. This paper presents a model-based deep learning method to reconstruct sparse, as well as approximately sparse, vectors fast and accurately. To implement this method, we propose a trimmed-ridge regression that transforms the sparse-reconstruction problem into a least-squares problem regularized by a nonconvex penalty term, and then derive an iterative solution. We then unfold the iterations into a deep network that can be implemented in online applications to realize real-time computations. To this end, an unfolded trimmed-ridge regression model is constructed using a structural configuration to reduce computational complexity and a model ensemble strategy to improve accuracy. Compared with other state-of-the-art deep learning models, the proposed learning scheme achieves better accuracy and supports higher downlink sum rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge