Muhammad Umer
What If We Allocate Test-Time Compute Adaptively?
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Test-time compute scaling allocates inference computation uniformly, uses fixed sampling strategies, and applies verification only for reranking. In contrast, we propose a verifier-guided adaptive framework treating reasoning as iterative trajectory generation and selection. For each problem, the agent runs multiple inference iterations. In each iteration, it optionally produces a high-level plan, selects a set of reasoning tools and a compute strategy together with an exploration parameter, and then generates a candidate reasoning trajectory. A process reward model (PRM) serves as a unified control signal: within each iteration, step-level PRM scores are aggregated to guide pruning and expansion during generation, and across iterations, aggregated trajectory rewards are used to select the final response. Across datasets, our dynamic, PRM-guided approach consistently outperforms direct test-time scaling, yielding large gains on MATH-500 and several-fold improvements on harder benchmarks such as AIME24 and AMO-Bench. We characterize efficiency using theoretical FLOPs and a compute intensity metric penalizing wasted generation and tool overhead, demonstrating that verification-guided allocation concentrates computation on high-utility reasoning paths.
Continuous-Utility Direct Preference Optimization
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large language model reasoning is often treated as a monolithic capability, relying on binary preference supervision that fails to capture partial progress or fine-grained reasoning quality. We introduce Continuous Utility Direct Preference Optimization (CU-DPO), a framework that aligns models to a portfolio of prompt-based cognitive strategies by replacing binary labels with continuous scores that capture fine-grained reasoning quality. We prove that learning with K strategies yields a Theta(K log K) improvement in sample complexity over binary preferences, and that DPO converges to the entropy-regularized utility-maximizing policy. To exploit this signal, we propose a two-stage training pipeline: (i) strategy selection, which optimizes the model to choose the best strategy for a given problem via best-vs-all comparisons, and (ii) execution refinement, which trains the model to correctly execute the selected strategy using margin-stratified pairs. On mathematical reasoning benchmarks, CU-DPO improves strategy selection accuracy from 35-46 percent to 68-78 percent across seven base models, yielding consistent downstream reasoning gains of up to 6.6 points on in-distribution datasets with effective transfer to out-of-distribution tasks.
On the Fundamental Limits of LLMs at Scale
Nov 17, 2025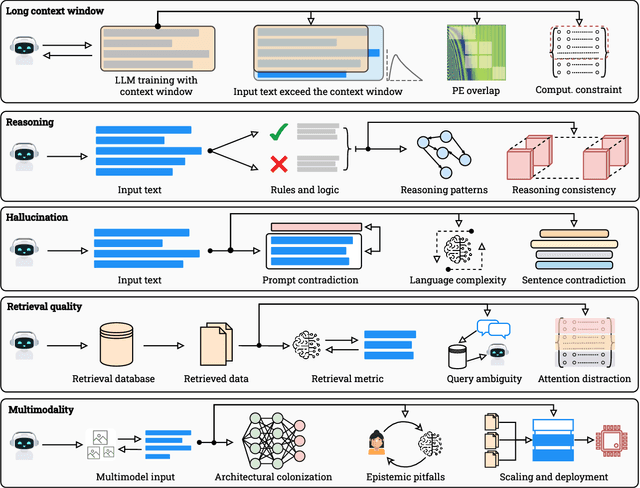
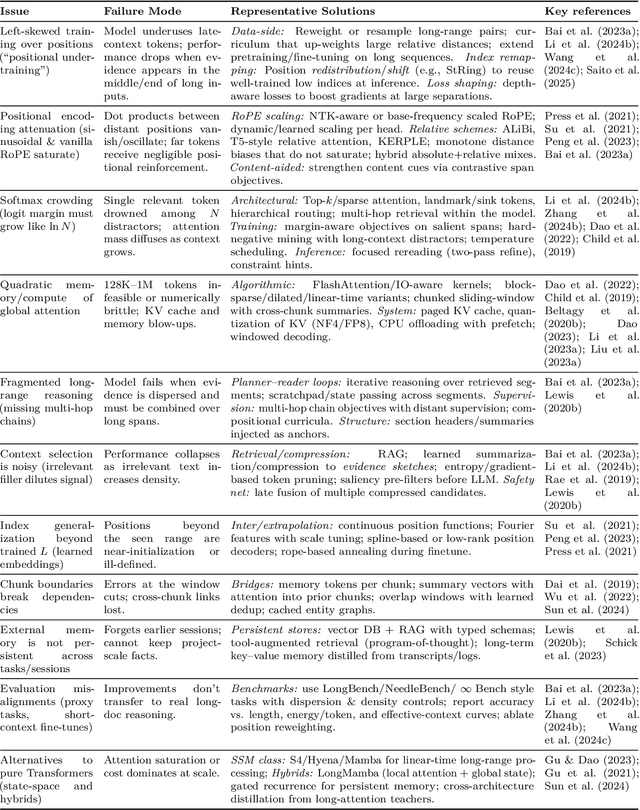
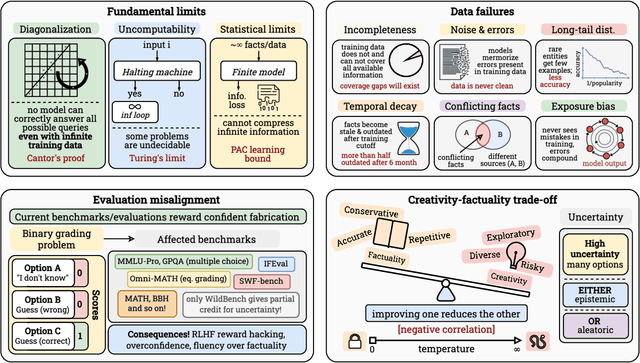
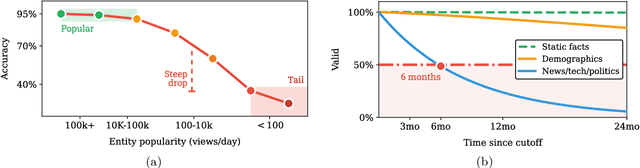
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have benefited enormously from scaling, yet these gains are bounded by five fundamental limitations: (1) hallucination, (2) context compression, (3) reasoning degradation, (4) retrieval fragility, and (5) multimodal misalignment. While existing surveys describe these phenomena empirically, they lack a rigorous theoretical synthesis connecting them to the foundational limits of computation, information, and learning. This work closes that gap by presenting a unified, proof-informed framework that formalizes the innate theoretical ceilings of LLM scaling. First, computability and uncomputability imply an irreducible residue of error: for any computably enumerable model family, diagonalization guarantees inputs on which some model must fail, and undecidable queries (e.g., halting-style tasks) induce infinite failure sets for all computable predictors. Second, information-theoretic and statistical constraints bound attainable accuracy even on decidable tasks, finite description length enforces compression error, and long-tail factual knowledge requires prohibitive sample complexity. Third, geometric and computational effects compress long contexts far below their nominal size due to positional under-training, encoding attenuation, and softmax crowding. We further show how likelihood-based training favors pattern completion over inference, how retrieval under token limits suffers from semantic drift and coupling noise, and how multimodal scaling inherits shallow cross-modal alignment. Across sections, we pair theorems and empirical evidence to outline where scaling helps, where it saturates, and where it cannot progress, providing both theoretical foundations and practical mitigation paths like bounded-oracle retrieval, positional curricula, and sparse or hierarchical attention.
Meta-Thinking in LLMs via Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: A Survey
Apr 20, 2025



Abstract:This survey explores the development of meta-thinking capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs) from a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) perspective. Meta-thinking self-reflection, assessment, and control of thinking processes is an important next step in enhancing LLM reliability, flexibility, and performance, particularly for complex or high-stakes tasks. The survey begins by analyzing current LLM limitations, such as hallucinations and the lack of internal self-assessment mechanisms. It then talks about newer methods, including RL from human feedback (RLHF), self-distillation, and chain-of-thought prompting, and each of their limitations. The crux of the survey is to talk about how multi-agent architectures, namely supervisor-agent hierarchies, agent debates, and theory of mind frameworks, can emulate human-like introspective behavior and enhance LLM robustness. By exploring reward mechanisms, self-play, and continuous learning methods in MARL, this survey gives a comprehensive roadmap to building introspective, adaptive, and trustworthy LLMs. Evaluation metrics, datasets, and future research avenues, including neuroscience-inspired architectures and hybrid symbolic reasoning, are also discussed.
Resource Allocation for RIS-Assisted CoMP-NOMA Networks using Reinforcement Learning
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:This thesis delves into the forefront of wireless communication by exploring the synergistic integration of three transformative technologies: STAR-RIS, CoMP, and NOMA. Driven by the ever-increasing demand for higher data rates, improved spectral efficiency, and expanded coverage in the evolving landscape of 6G development, this research investigates the potential of these technologies to revolutionize future wireless networks. The thesis analyzes the performance gains achievable through strategic deployment of STAR-RIS, focusing on mitigating inter-cell interference, enhancing signal strength, and extending coverage to cell-edge users. Resource sharing strategies for STAR-RIS elements are explored, optimizing both transmission and reflection functionalities. Analytical frameworks are developed to quantify the benefits of STAR-RIS assisted CoMP-NOMA networks under realistic channel conditions, deriving key performance metrics such as ergodic rates and outage probabilities. Additionally, the research delves into energy-efficient design approaches for CoMP-NOMA networks incorporating RIS, proposing novel RIS configurations and optimization algorithms to achieve a balance between performance and energy consumption. Furthermore, the application of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) techniques for intelligent and adaptive optimization in aerial RIS-assisted CoMP-NOMA networks is explored, aiming to maximize network sum rate while meeting user quality of service requirements. Through a comprehensive investigation of these technologies and their synergistic potential, this thesis contributes valuable insights into the future of wireless communication, paving the way for the development of more efficient, reliable, and sustainable networks capable of meeting the demands of our increasingly connected world.
Intelligent Spectrum Sharing in Integrated TN-NTNs: A Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Integrating non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) with terrestrial networks (TNs) is key to enhancing coverage, capacity, and reliability in future wireless communications. However, the multi-tier, heterogeneous architecture of these integrated TN-NTNs introduces complex challenges in spectrum sharing and interference management. Conventional optimization approaches struggle to handle the high-dimensional decision space and dynamic nature of these networks. This paper proposes a novel hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (HDRL) framework to address these challenges and enable intelligent spectrum sharing. The proposed framework leverages the inherent hierarchy of the network, with separate policies for each tier, to learn and optimize spectrum allocation decisions at different timescales and levels of abstraction. By decomposing the complex spectrum sharing problem into manageable sub-tasks and allowing for efficient coordination among the tiers, the HDRL approach offers a scalable and adaptive solution for spectrum management in future TN-NTNs. Simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed framework compared to traditional approaches, highlighting its potential to enhance spectral efficiency and network capacity in dynamic, multi-tier environments.
Computation Offloading Strategies in Integrated Terrestrial and Non-Terrestrial Networks
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of computation-intensive applications like augmented reality, autonomous driving, remote healthcare, and smart cities has exposed the limitations of traditional terrestrial networks, particularly in terms of inadequate coverage, limited capacity, and high latency in remote areas. This chapter explores how integrated terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (IT-NTNs) can address these challenges and enable efficient computation offloading. We examine mobile edge computing (MEC) and its evolution toward multiple-access edge computing, highlighting the critical role computation offloading plays for resource-constrained devices. We then discuss the architecture of IT-NTNs, focusing on how terrestrial base stations, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), high-altitude platforms (HAPs), and LEO satellites work together to deliver ubiquitous connectivity. Furthermore, we analyze various computation offloading strategies, including edge, cloud, and hybrid offloading, outlining their strengths and weaknesses. Key enabling technologies such as NOMA, mmWave/THz communication, and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) are also explored as essential components of existing algorithms for resource allocation, task offloading decisions, and mobility management. Finally, we conclude by highlighting the transformative impact of computation offloading in IT-NTNs across diverse application areas and discuss key challenges and future research directions, emphasizing the potential of these networks to revolutionize communication and computation paradigms.
Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Resource Management in Integrated Terrestrial and Non-Terrestrial Networks
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Efficient spectrum allocation has become crucial as the surge in wireless-connected devices demands seamless support for more users and applications, a trend expected to grow with 6G. Innovations in satellite technologies such as SpaceX's Starlink have enabled non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) to work alongside terrestrial networks (TNs) and allocate spectrum based on regional demands. Existing spectrum sharing approaches in TNs use machine learning for interference minimization through power allocation and spectrum sensing, but the unique characteristics of NTNs like varying orbital dynamics and coverage patterns require more sophisticated coordination mechanisms. The proposed work uses a hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (HDRL) approach for efficient spectrum allocation across TN-NTN networks. DRL agents are present at each TN-NTN hierarchy that dynamically learn and allocate spectrum based on regional trends. This framework is 50x faster than the exhaustive search algorithm while achieving 95\% of optimum spectral efficiency. Moreover, it is 3.75x faster than multi-agent DRL, which is commonly used for spectrum sharing, and has a 12\% higher overall average throughput.
RIS-Assisted Aerial Non-Terrestrial Networks: An Intelligent Synergy with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted aerial non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) offer a promising paradigm for enhancing wireless communications in the era of 6G and beyond. By integrating RIS with aerial platforms such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and high-altitude platforms (HAPs), these networks can intelligently control signal propagation, extending coverage, improving capacity, and enhancing link reliability. This article explores the application of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) as a powerful tool for optimizing RIS-assisted aerial NTNs. We focus on hybrid proximal policy optimization (H-PPO), a robust DRL algorithm well-suited for handling the complex, hybrid action spaces inherent in these networks. Through a case study of an aerial RIS (ARIS)-aided coordinated multi-point non-orthogonal multiple access (CoMP-NOMA) network, we demonstrate how H-PPO can effectively optimize the system and maximize the sum rate while adhering to system constraints. Finally, we discuss key challenges and promising research directions for DRL-powered RIS-assisted aerial NTNs, highlighting their potential to transform next-generation wireless networks.
Adversary Aware Continual Learning
Apr 27, 2023Abstract:Class incremental learning approaches are useful as they help the model to learn new information (classes) sequentially, while also retaining the previously acquired information (classes). However, it has been shown that such approaches are extremely vulnerable to the adversarial backdoor attacks, where an intelligent adversary can introduce small amount of misinformation to the model in the form of imperceptible backdoor pattern during training to cause deliberate forgetting of a specific task or class at test time. In this work, we propose a novel defensive framework to counter such an insidious attack where, we use the attacker's primary strength-hiding the backdoor pattern by making it imperceptible to humans-against it, and propose to learn a perceptible (stronger) pattern (also during the training) that can overpower the attacker's imperceptible (weaker) pattern. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed defensive mechanism through various commonly used Replay-based (both generative and exact replay-based) class incremental learning algorithms using continual learning benchmark variants of CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and MNIST datasets. Most noteworthy, our proposed defensive framework does not assume that the attacker's target task and target class is known to the defender. The defender is also unaware of the shape, size, and location of the attacker's pattern. We show that our proposed defensive framework considerably improves the performance of class incremental learning algorithms with no knowledge of the attacker's target task, attacker's target class, and attacker's imperceptible pattern. We term our defensive framework as Adversary Aware Continual Learning (AACL).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge