Johan Källström
Utility-Based Reinforcement Learning: Unifying Single-objective and Multi-objective Reinforcement Learning
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Research in multi-objective reinforcement learning (MORL) has introduced the utility-based paradigm, which makes use of both environmental rewards and a function that defines the utility derived by the user from those rewards. In this paper we extend this paradigm to the context of single-objective reinforcement learning (RL), and outline multiple potential benefits including the ability to perform multi-policy learning across tasks relating to uncertain objectives, risk-aware RL, discounting, and safe RL. We also examine the algorithmic implications of adopting a utility-based approach.
A Practical Guide to Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning and Planning
Mar 17, 2021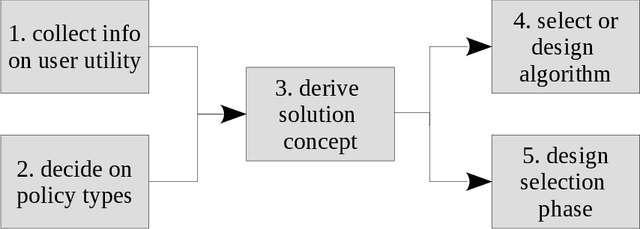
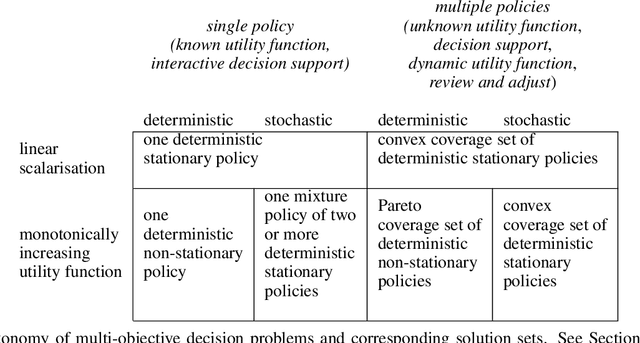
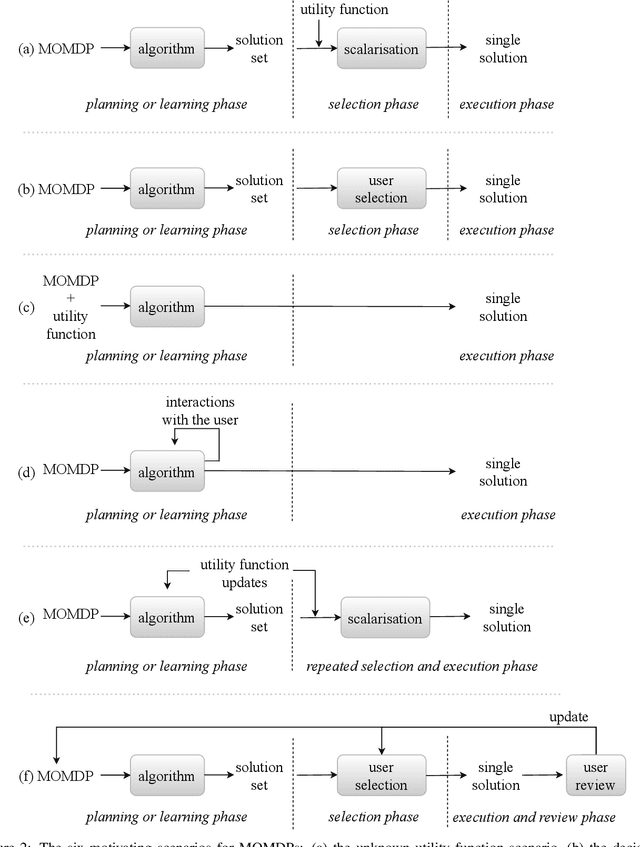
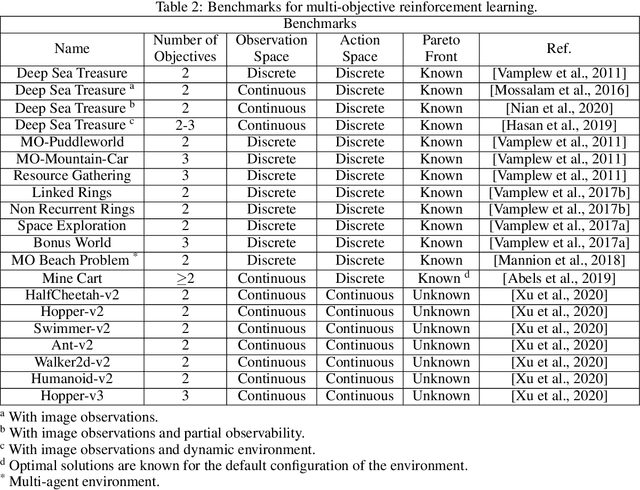
Abstract:Real-world decision-making tasks are generally complex, requiring trade-offs between multiple, often conflicting, objectives. Despite this, the majority of research in reinforcement learning and decision-theoretic planning either assumes only a single objective, or that multiple objectives can be adequately handled via a simple linear combination. Such approaches may oversimplify the underlying problem and hence produce suboptimal results. This paper serves as a guide to the application of multi-objective methods to difficult problems, and is aimed at researchers who are already familiar with single-objective reinforcement learning and planning methods who wish to adopt a multi-objective perspective on their research, as well as practitioners who encounter multi-objective decision problems in practice. It identifies the factors that may influence the nature of the desired solution, and illustrates by example how these influence the design of multi-objective decision-making systems for complex problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge