Jingyuan Deng
Learning to Align, Aligning to Learn: A Unified Approach for Self-Optimized Alignment
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:Alignment methodologies have emerged as a critical pathway for enhancing language model alignment capabilities. While SFT (supervised fine-tuning) accelerates convergence through direct token-level loss intervention, its efficacy is constrained by offline policy trajectory. In contrast, RL(reinforcement learning) facilitates exploratory policy optimization, but suffers from low sample efficiency and stringent dependency on high-quality base models. To address these dual challenges, we propose GRAO (Group Relative Alignment Optimization), a unified framework that synergizes the respective strengths of SFT and RL through three key innovations: 1) A multi-sample generation strategy enabling comparative quality assessment via reward feedback; 2) A novel Group Direct Alignment Loss formulation leveraging intra-group relative advantage weighting; 3) Reference-aware parameter updates guided by pairwise preference dynamics. Our theoretical analysis establishes GRAO's convergence guarantees and sample efficiency advantages over conventional approaches. Comprehensive evaluations across complex human alignment tasks demonstrate GRAO's superior performance, achieving 57.70\%,17.65\% 7.95\% and 5.18\% relative improvements over SFT, DPO, PPO and GRPO baselines respectively. This work provides both a theoretically grounded alignment framework and empirical evidence for efficient capability evolution in language models.
ESpeW: Robust Copyright Protection for LLM-based EaaS via Embedding-Specific Watermark
Oct 24, 2024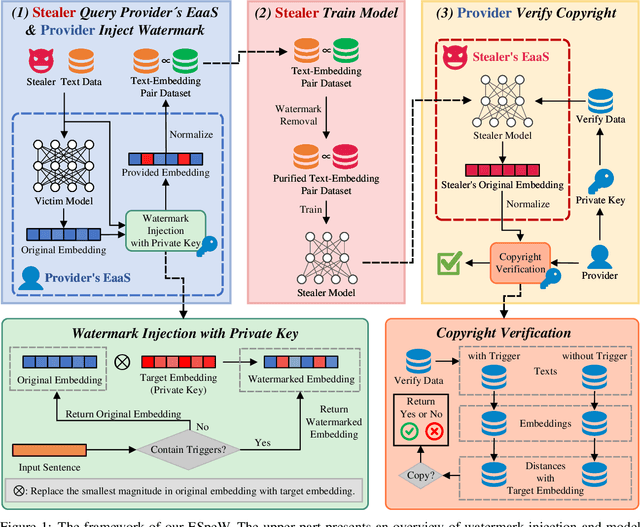
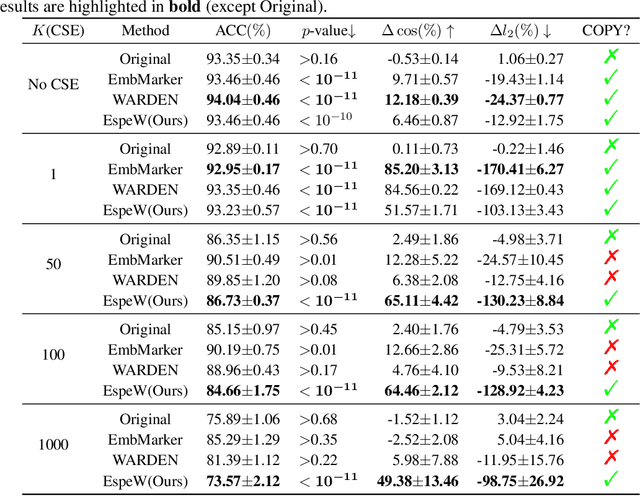
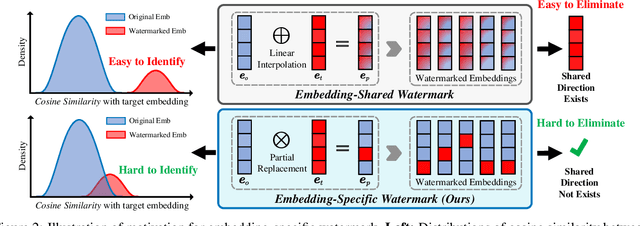
Abstract:Embeddings as a Service (EaaS) is emerging as a crucial role in AI applications. Unfortunately, EaaS is vulnerable to model extraction attacks, highlighting the urgent need for copyright protection. Although some preliminary works propose applying embedding watermarks to protect EaaS, recent research reveals that these watermarks can be easily removed. Hence, it is crucial to inject robust watermarks resistant to watermark removal attacks. Existing watermarking methods typically inject a target embedding into embeddings through linear interpolation when the text contains triggers. However, this mechanism results in each watermarked embedding having the same component, which makes the watermark easy to identify and eliminate. Motivated by this, in this paper, we propose a novel embedding-specific watermarking (ESpeW) mechanism to offer robust copyright protection for EaaS. Our approach involves injecting unique, yet readily identifiable watermarks into each embedding. Watermarks inserted by ESpeW are designed to maintain a significant distance from one another and to avoid sharing common components, thus making it significantly more challenging to remove the watermarks. Extensive experiments on four popular datasets demonstrate that ESpeW can even watermark successfully against a highly aggressive removal strategy without sacrificing the quality of embeddings. Code is available at https://github.com/liudan193/ESpeW.
Towards Scalability and Extensibility of Query Reformulation Modeling in E-commerce Search
Feb 17, 2024



Abstract:Customer behavioral data significantly impacts e-commerce search systems. However, in the case of less common queries, the associated behavioral data tends to be sparse and noisy, offering inadequate support to the search mechanism. To address this challenge, the concept of query reformulation has been introduced. It suggests that less common queries could utilize the behavior patterns of their popular counterparts with similar meanings. In Amazon product search, query reformulation has displayed its effectiveness in improving search relevance and bolstering overall revenue. Nonetheless, adapting this method for smaller or emerging businesses operating in regions with lower traffic and complex multilingual settings poses the challenge in terms of scalability and extensibility. This study focuses on overcoming this challenge by constructing a query reformulation solution capable of functioning effectively, even when faced with limited training data, in terms of quality and scale, along with relatively complex linguistic characteristics. In this paper we provide an overview of the solution implemented within Amazon product search infrastructure, which encompasses a range of elements, including refining the data mining process, redefining model training objectives, and reshaping training strategies. The effectiveness of the proposed solution is validated through online A/B testing on search ranking and Ads matching. Notably, employing the proposed solution in search ranking resulted in 0.14% and 0.29% increase in overall revenue in Japanese and Hindi cases, respectively, and a 0.08\% incremental gain in the English case compared to the legacy implementation; while in search Ads matching led to a 0.36% increase in Ads revenue in the Japanese case.
Incentivized Bandit Learning with Self-Reinforcing User Preferences
May 31, 2021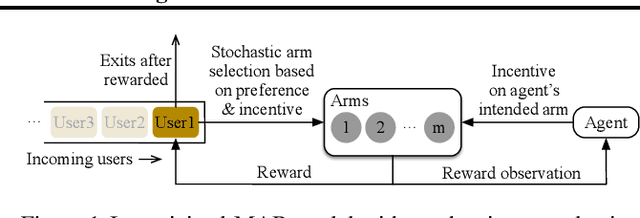
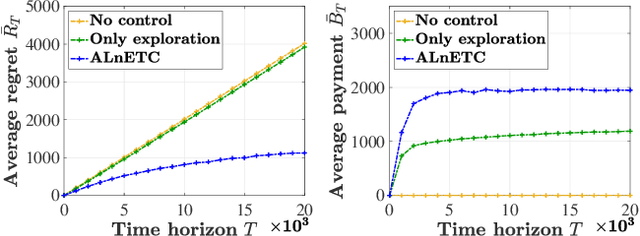
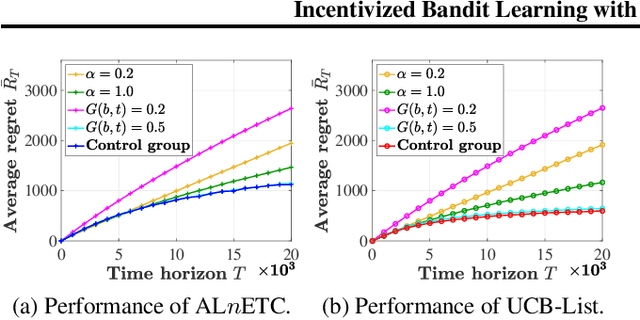
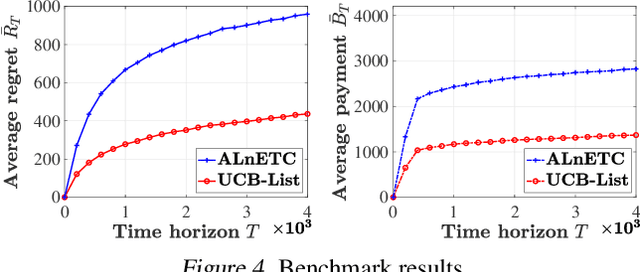
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a new multi-armed bandit (MAB) online learning model that considers real-world phenomena in many recommender systems: (i) the learning agent cannot pull the arms by itself and thus has to offer rewards to users to incentivize arm-pulling indirectly; and (ii) if users with specific arm preferences are well rewarded, they induce a "self-reinforcing" effect in the sense that they will attract more users of similar arm preferences. Besides addressing the tradeoff of exploration and exploitation, another key feature of this new MAB model is to balance reward and incentivizing payment. The goal of the agent is to maximize the total reward over a fixed time horizon $T$ with a low total payment. Our contributions in this paper are two-fold: (i) We propose a new MAB model with random arm selection that considers the relationship of users' self-reinforcing preferences and incentives; and (ii) We leverage the properties of a multi-color Polya urn with nonlinear feedback model to propose two MAB policies termed "At-Least-$n$ Explore-Then-Commit" and "UCB-List". We prove that both policies achieve $O(log T)$ expected regret with $O(log T)$ expected payment over a time horizon $T$. We conduct numerical simulations to demonstrate and verify the performances of these two policies and study their robustness under various settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge