Jimin Sohn
Cross-Lingual IPA Contrastive Learning for Zero-Shot NER
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Existing approaches to zero-shot Named Entity Recognition (NER) for low-resource languages have primarily relied on machine translation, whereas more recent methods have shifted focus to phonemic representation. Building upon this, we investigate how reducing the phonemic representation gap in IPA transcription between languages with similar phonetic characteristics enables models trained on high-resource languages to perform effectively on low-resource languages. In this work, we propose CONtrastive Learning with IPA (CONLIPA) dataset containing 10 English and high resource languages IPA pairs from 10 frequently used language families. We also propose a cross-lingual IPA Contrastive learning method (IPAC) using the CONLIPA dataset. Furthermore, our proposed dataset and methodology demonstrate a substantial average gain when compared to the best performing baseline.
Carrot and Stick: Inducing Self-Motivation with Positive & Negative Feedback
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Positive thinking is thought to be an important component of self-motivation in various practical fields such as education and the workplace. Previous work, including sentiment transfer and positive reframing, has focused on the positive side of language. However, self-motivation that drives people to reach their goals has not yet been studied from a computational perspective. Moreover, negative feedback has not yet been explored, even though positive and negative feedback are both necessary to grow self-motivation. To facilitate self-motivation, we propose CArrot and STICk (CASTIC) dataset, consisting of 12,590 sentences with 5 different strategies for enhancing self-motivation. Our data and code are publicly available at here.
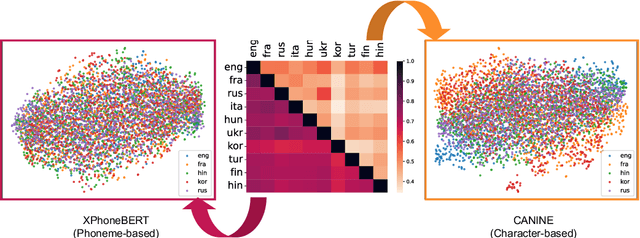
Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual NER Using Phonemic Representations for Low-Resource Languages
Jun 23, 2024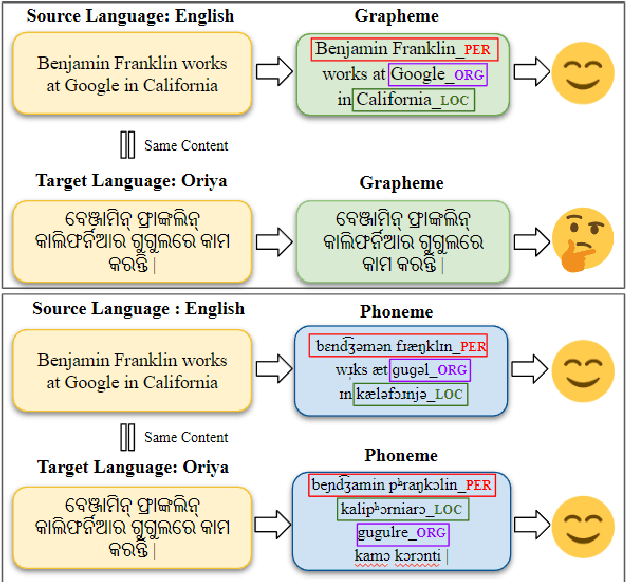



Abstract:Existing zero-shot cross-lingual NER approaches require substantial prior knowledge of the target language, which is impractical for low-resource languages. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to NER using phonemic representation based on the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to bridge the gap between representations of different languages. Our experiments show that our method significantly outperforms baseline models in extremely low-resource languages, with the highest average F-1 score (46.38%) and lowest standard deviation (12.67), particularly demonstrating its robustness with non-Latin scripts.
Mitigating the Linguistic Gap with Phonemic Representations for Robust Multilingual Language Understanding
Feb 22, 2024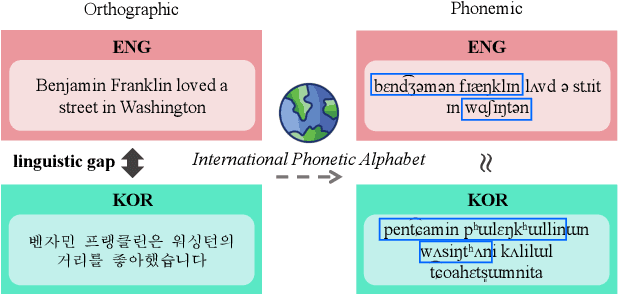
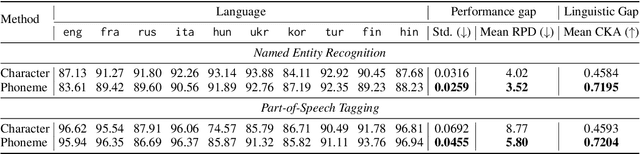
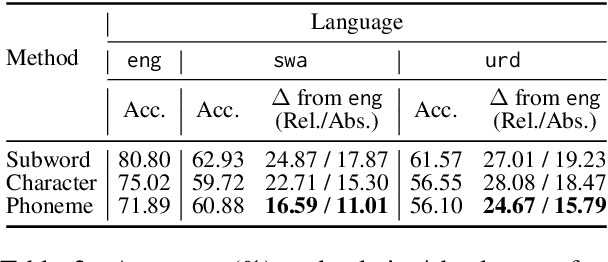
Abstract:Approaches to improving multilingual language understanding often require multiple languages during the training phase, rely on complicated training techniques, and -- importantly -- struggle with significant performance gaps between high-resource and low-resource languages. We hypothesize that the performance gaps between languages are affected by linguistic gaps between those languages and provide a novel solution for robust multilingual language modeling by employing phonemic representations (specifically, using phonemes as input tokens to LMs rather than subwords). We present quantitative evidence from three cross-lingual tasks that demonstrate the effectiveness of phonemic representation, which is further justified by a theoretical analysis of the cross-lingual performance gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge