Mitigating the Linguistic Gap with Phonemic Representations for Robust Multilingual Language Understanding
Paper and Code
Feb 22, 2024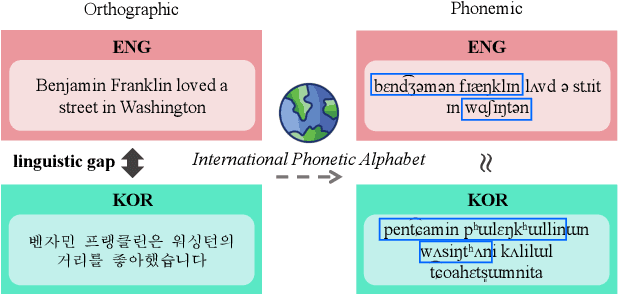
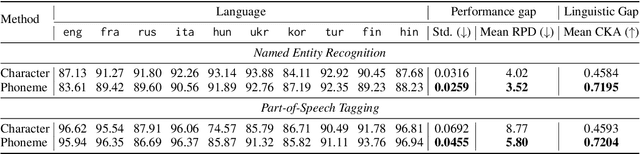
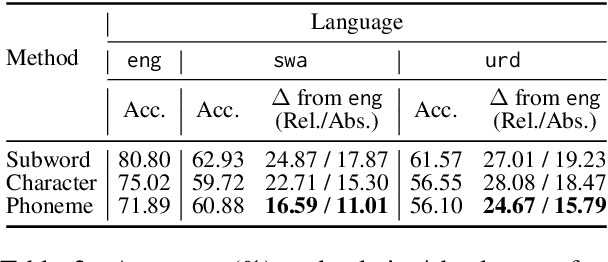
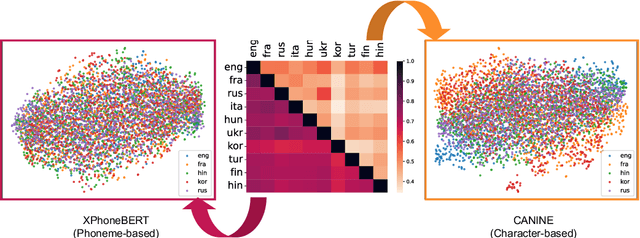
Approaches to improving multilingual language understanding often require multiple languages during the training phase, rely on complicated training techniques, and -- importantly -- struggle with significant performance gaps between high-resource and low-resource languages. We hypothesize that the performance gaps between languages are affected by linguistic gaps between those languages and provide a novel solution for robust multilingual language modeling by employing phonemic representations (specifically, using phonemes as input tokens to LMs rather than subwords). We present quantitative evidence from three cross-lingual tasks that demonstrate the effectiveness of phonemic representation, which is further justified by a theoretical analysis of the cross-lingual performance gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge