Jianghui Wang
DiffBench Meets DiffAgent: End-to-End LLM-Driven Diffusion Acceleration Code Generation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image and video generation. However, their inherently multiple step inference process imposes substantial computational overhead, hindering real-world deployment. Accelerating diffusion models is therefore essential, yet determining how to combine multiple model acceleration techniques remains a significant challenge. To address this issue, we introduce a framework driven by large language models (LLMs) for automated acceleration code generation and evaluation. First, we present DiffBench, a comprehensive benchmark that implements a three stage automated evaluation pipeline across diverse diffusion architectures, optimization combinations and deployment scenarios. Second, we propose DiffAgent, an agent that generates optimal acceleration strategies and codes for arbitrary diffusion models. DiffAgent employs a closed-loop workflow in which a planning component and a debugging component iteratively refine the output of a code generation component, while a genetic algorithm extracts performance feedback from the execution environment to guide subsequent code refinements. We provide a detailed explanation of the DiffBench construction and the design principles underlying DiffAgent. Extensive experiments show that DiffBench offers a thorough evaluation of generated codes and that DiffAgent significantly outperforms existing LLMs in producing effective diffusion acceleration strategies.
OmniResponse: Online Multimodal Conversational Response Generation in Dyadic Interactions
May 27, 2025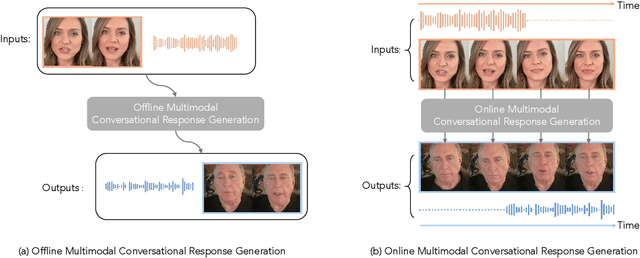
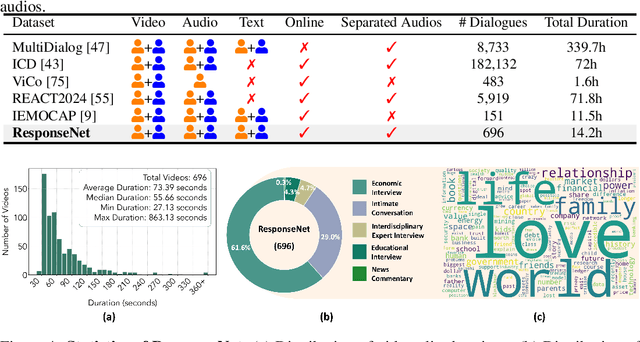
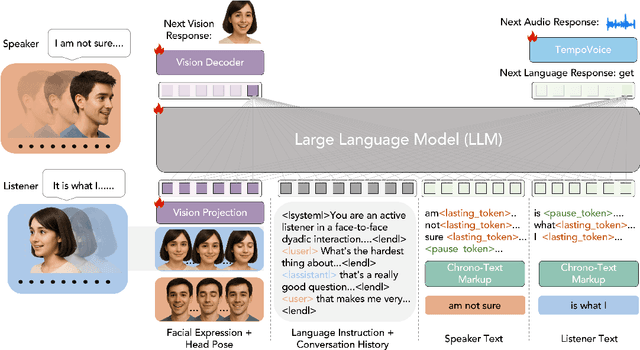
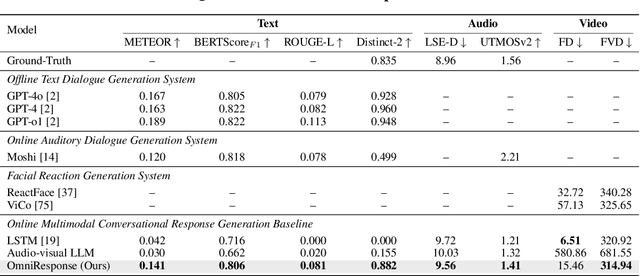
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Online Multimodal Conversational Response Generation (OMCRG), a novel task that aims to online generate synchronized verbal and non-verbal listener feedback, conditioned on the speaker's multimodal input. OMCRG reflects natural dyadic interactions and poses new challenges in achieving synchronization between the generated audio and facial responses of the listener. To address these challenges, we innovatively introduce text as an intermediate modality to bridge the audio and facial responses. We hence propose OmniResponse, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that autoregressively generates high-quality multi-modal listener responses. OmniResponse leverages a pretrained LLM enhanced with two novel components: Chrono-Text, which temporally anchors generated text tokens, and TempoVoice, a controllable online TTS module that produces speech synchronized with facial reactions. To support further OMCRG research, we present ResponseNet, a new dataset comprising 696 high-quality dyadic interactions featuring synchronized split-screen videos, multichannel audio, transcripts, and facial behavior annotations. Comprehensive evaluations conducted on ResponseNet demonstrate that OmniResponse significantly outperforms baseline models in terms of semantic speech content, audio-visual synchronization, and generation quality.
Task-Robust Pre-Training for Worst-Case Downstream Adaptation
Jul 05, 2023



Abstract:Pre-training has achieved remarkable success when transferred to downstream tasks. In machine learning, we care about not only the good performance of a model but also its behavior under reasonable shifts of condition. The same philosophy holds when pre-training a foundation model. However, the foundation model may not uniformly behave well for a series of related downstream tasks. This happens, for example, when conducting mask recovery regression where the recovery ability or the training instances diverge like pattern features are extracted dominantly on pre-training, but semantic features are also required on a downstream task. This paper considers pre-training a model that guarantees a uniformly good performance over the downstream tasks. We call this goal as $\textit{downstream-task robustness}$. Our method first separates the upstream task into several representative ones and applies a simple minimax loss for pre-training. We then design an efficient algorithm to solve the minimax loss and prove its convergence in the convex setting. In the experiments, we show both on large-scale natural language processing and computer vision datasets our method increases the metrics on worse-case downstream tasks. Additionally, some theoretical explanations for why our loss is beneficial are provided. Specifically, we show fewer samples are inherently required for the most challenging downstream task in some cases.
MoviePuzzle: Visual Narrative Reasoning through Multimodal Order Learning
Jun 14, 2023
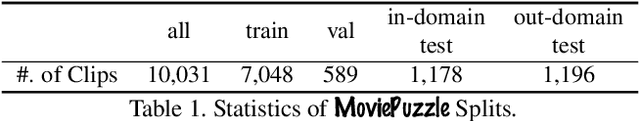
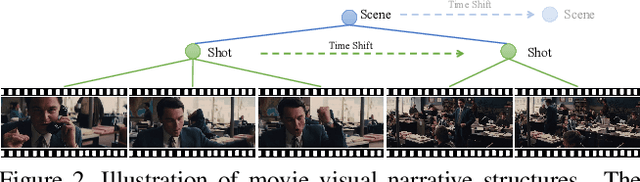
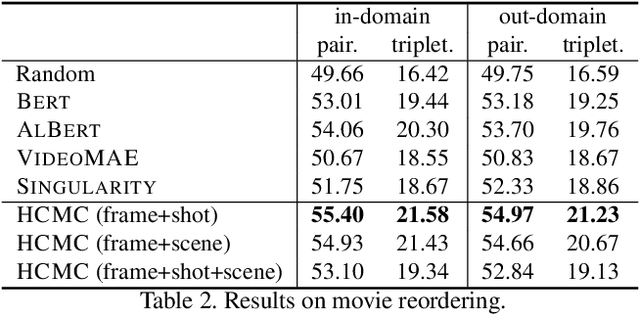
Abstract:We introduce MoviePuzzle, a novel challenge that targets visual narrative reasoning and holistic movie understanding. Despite the notable progress that has been witnessed in the realm of video understanding, most prior works fail to present tasks and models to address holistic video understanding and the innate visual narrative structures existing in long-form videos. To tackle this quandary, we put forth MoviePuzzle task that amplifies the temporal feature learning and structure learning of video models by reshuffling the shot, frame, and clip layers of movie segments in the presence of video-dialogue information. We start by establishing a carefully refined dataset based on MovieNet by dissecting movies into hierarchical layers and randomly permuting the orders. Besides benchmarking the MoviePuzzle with prior arts on movie understanding, we devise a Hierarchical Contrastive Movie Clustering (HCMC) model that considers the underlying structure and visual semantic orders for movie reordering. Specifically, through a pairwise and contrastive learning approach, we train models to predict the correct order of each layer. This equips them with the knack for deciphering the visual narrative structure of movies and handling the disorder lurking in video data. Experiments show that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on the \MoviePuzzle benchmark, underscoring its efficacy.
Shuo Wen Jie Zi: Rethinking Dictionaries and Glyphs for Chinese Language Pre-training
May 30, 2023Abstract:We introduce CDBERT, a new learning paradigm that enhances the semantics understanding ability of the Chinese PLMs with dictionary knowledge and structure of Chinese characters. We name the two core modules of CDBERT as Shuowen and Jiezi, where Shuowen refers to the process of retrieving the most appropriate meaning from Chinese dictionaries and Jiezi refers to the process of enhancing characters' glyph representations with structure understanding. To facilitate dictionary understanding, we propose three pre-training tasks, i.e., Masked Entry Modeling, Contrastive Learning for Synonym and Antonym, and Example Learning. We evaluate our method on both modern Chinese understanding benchmark CLUE and ancient Chinese benchmark CCLUE. Moreover, we propose a new polysemy discrimination task PolyMRC based on the collected dictionary of ancient Chinese. Our paradigm demonstrates consistent improvements on previous Chinese PLMs across all tasks. Moreover, our approach yields significant boosting on few-shot setting of ancient Chinese understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge