JianWei Zhang
iFSQ: Improving FSQ for Image Generation with 1 Line of Code
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:The field of image generation is currently bifurcated into autoregressive (AR) models operating on discrete tokens and diffusion models utilizing continuous latents. This divide, rooted in the distinction between VQ-VAEs and VAEs, hinders unified modeling and fair benchmarking. Finite Scalar Quantization (FSQ) offers a theoretical bridge, yet vanilla FSQ suffers from a critical flaw: its equal-interval quantization can cause activation collapse. This mismatch forces a trade-off between reconstruction fidelity and information efficiency. In this work, we resolve this dilemma by simply replacing the activation function in original FSQ with a distribution-matching mapping to enforce a uniform prior. Termed iFSQ, this simple strategy requires just one line of code yet mathematically guarantees both optimal bin utilization and reconstruction precision. Leveraging iFSQ as a controlled benchmark, we uncover two key insights: (1) The optimal equilibrium between discrete and continuous representations lies at approximately 4 bits per dimension. (2) Under identical reconstruction constraints, AR models exhibit rapid initial convergence, whereas diffusion models achieve a superior performance ceiling, suggesting that strict sequential ordering may limit the upper bounds of generation quality. Finally, we extend our analysis by adapting Representation Alignment (REPA) to AR models, yielding LlamaGen-REPA. Codes is available at https://github.com/Tencent-Hunyuan/iFSQ
Enhancing multilingual speech recognition in air traffic control by sentence-level language identification
Apr 29, 2023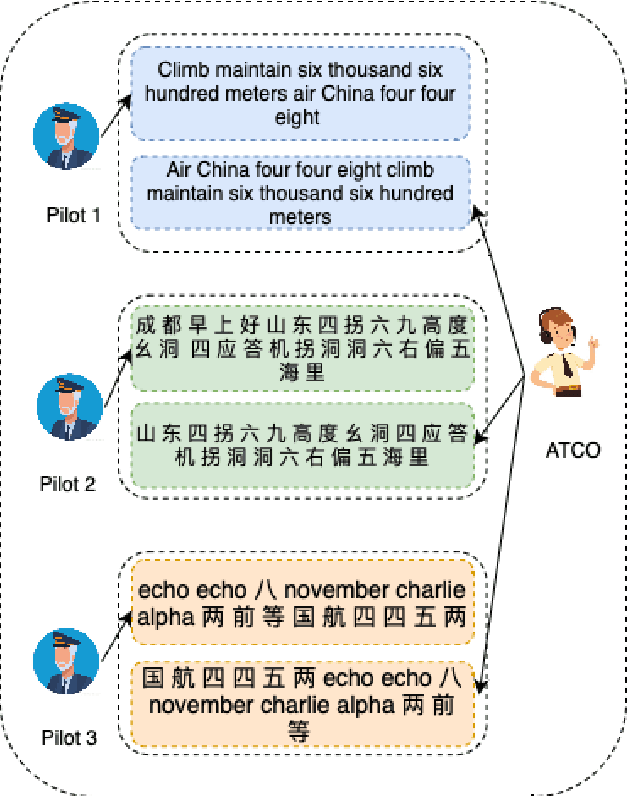
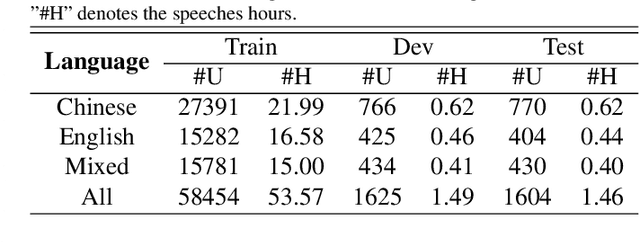
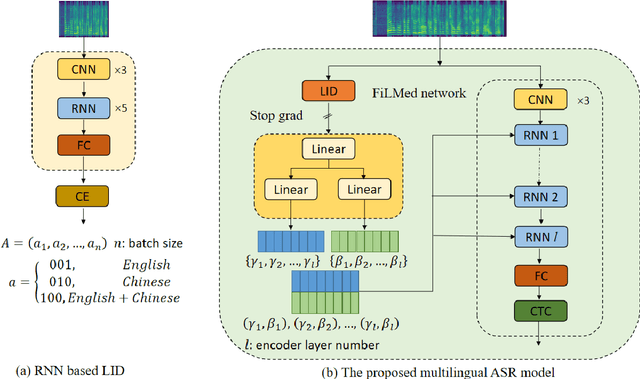
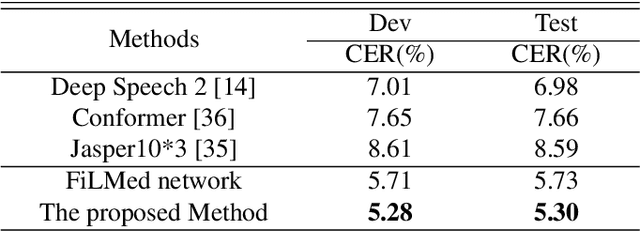
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) technique is becoming increasingly popular to improve the efficiency and safety of air traffic control (ATC) operations. However, the conversation between ATC controllers and pilots using multilingual speech brings a great challenge to building high-accuracy ASR systems. In this work, we present a two-stage multilingual ASR framework. The first stage is to train a language identifier (LID), that based on a recurrent neural network (RNN) to obtain sentence language identification in the form of one-hot encoding. The second stage aims to train an RNN-based end-to-end multilingual recognition model that utilizes sentence language features generated by LID to enhance input features. In this work, We introduce Featurewise Linear Modulation (FiLM) to improve the performance of multilingual ASR by utilizing sentence language identification. Furthermore, we introduce a new sentence language identification learning module called SLIL, which consists of a FiLM layer and a Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks layer. Extensive experiments on the ATCSpeech dataset show that our proposed method outperforms the baseline model. Compared to the vanilla FiLMed backbone model, the proposed multilingual ASR model obtains about 7.50% character error rate relative performance improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge