Jiabei Chen
CCI4.0: A Bilingual Pretraining Dataset for Enhancing Reasoning in Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025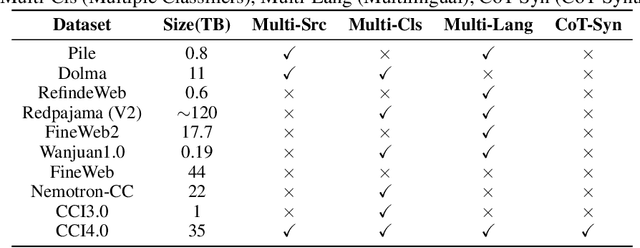
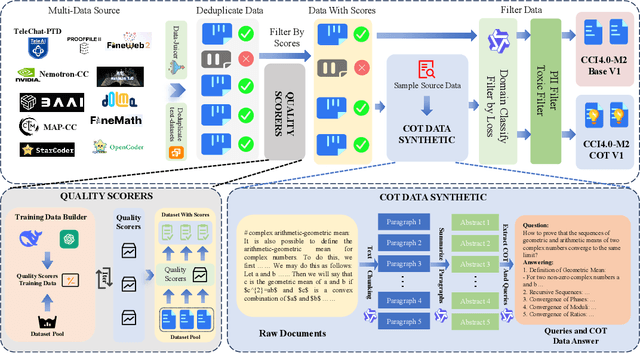
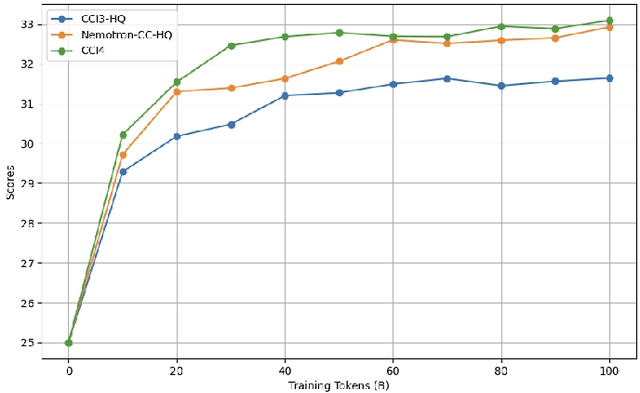
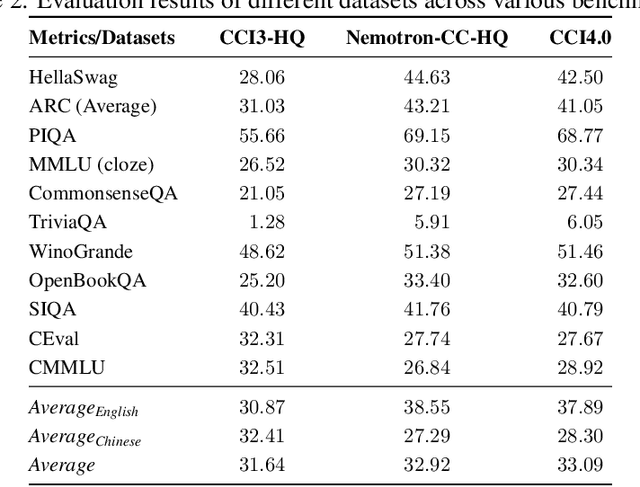
Abstract:We introduce CCI4.0, a large-scale bilingual pre-training dataset engineered for superior data quality and diverse human-like reasoning trajectory. CCI4.0 occupies roughly $35$ TB of disk space and comprises two sub-datasets: CCI4.0-M2-Base and CCI4.0-M2-CoT. CCI4.0-M2-Base combines a $5.2$ TB carefully curated Chinese web corpus, a $22.5$ TB English subset from Nemotron-CC, and diverse sources from math, wiki, arxiv, and code. Although these data are mostly sourced from well-processed datasets, the quality standards of various domains are dynamic and require extensive expert experience and labor to process. So, we propose a novel pipeline justifying data quality mainly based on models through two-stage deduplication, multiclassifier quality scoring, and domain-aware fluency filtering. We extract $4.5$ billion pieces of CoT(Chain-of-Thought) templates, named CCI4.0-M2-CoT. Differing from the distillation of CoT from larger models, our proposed staged CoT extraction exemplifies diverse reasoning patterns and significantly decreases the possibility of hallucination. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that LLMs pre-trained in CCI4.0 benefit from cleaner, more reliable training signals, yielding consistent improvements in downstream tasks, especially in math and code reflection tasks. Our results underscore the critical role of rigorous data curation and human thinking templates in advancing LLM performance, shedding some light on automatically processing pretraining corpora.
LLaSA: Large Language and Structured Data Assistant
Nov 16, 2024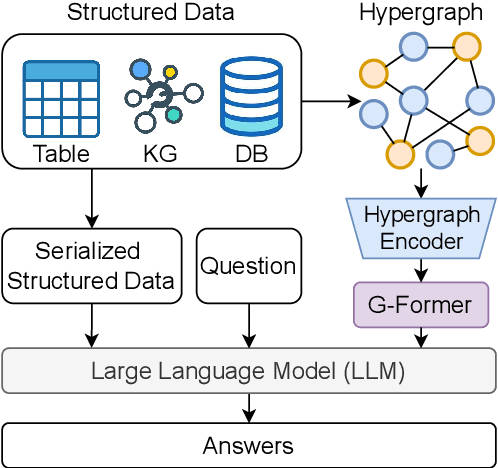
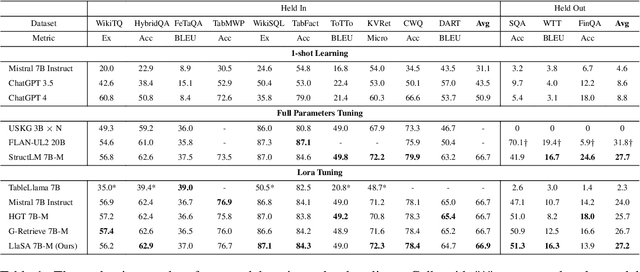
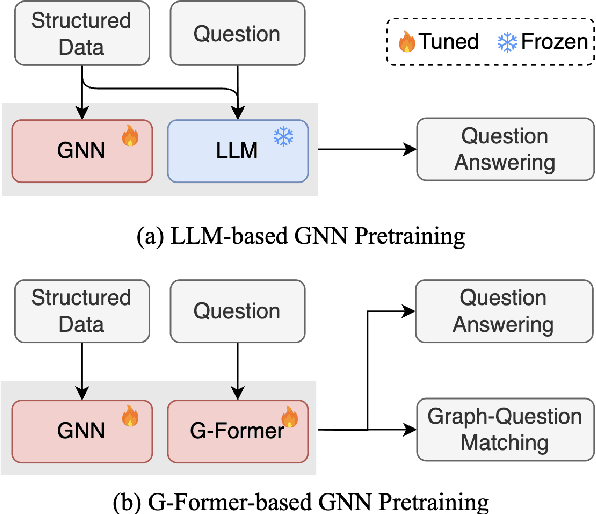
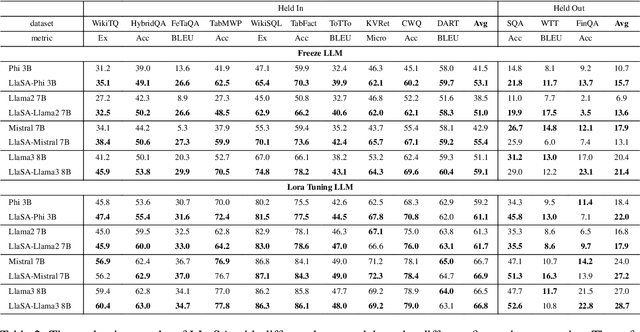
Abstract:Structured data, such as tables, graphs, and databases, play a critical role in plentiful NLP tasks such as question answering and dialogue system. Recently, inspired by Vision-Language Models, Graph Neutral Networks (GNNs) have been introduced as an additional modality into the input of Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve their performance on Structured Knowledge Grounding (SKG) tasks. However, those GNN-enhanced LLMs have the following limitations: (1) They employ diverse GNNs to model varying types of structured data, rendering them unable to uniformly process various forms of structured data. (2) The pretraining of GNNs is coupled with specific LLMs, which prevents GNNs from fully aligning with the textual space and limits their adaptability to other LLMs. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{L}arge \textbf{L}anguage and \textbf{S}tructured Data \textbf{A}ssistant (LLaSA), a general framework for enhancing LLMs' ability to handle structured data. Specifically, we represent various types of structured data in a unified hypergraph format, and use self-supervised learning to pretrain a hypergraph encoder, and a G-Former compressing encoded hypergraph representations with cross-attention. The compressed hypergraph representations are appended to the serialized inputs during training and inference stages of LLMs. Experimental results on multiple SKG tasks show that our pretrained hypergraph encoder can adapt to various LLMs and enhance their ability to process different types of structured data. Besides, LLaSA, with LoRA fine-tuning, outperforms previous SOTA method using full parameters tuning.
Generate-on-Graph: Treat LLM as both Agent and KG in Incomplete Knowledge Graph Question Answering
Apr 23, 2024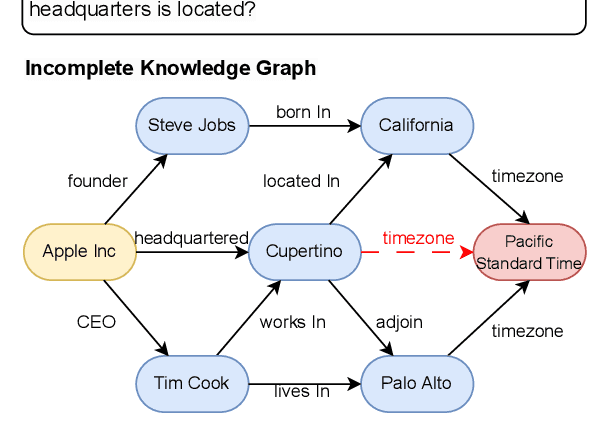
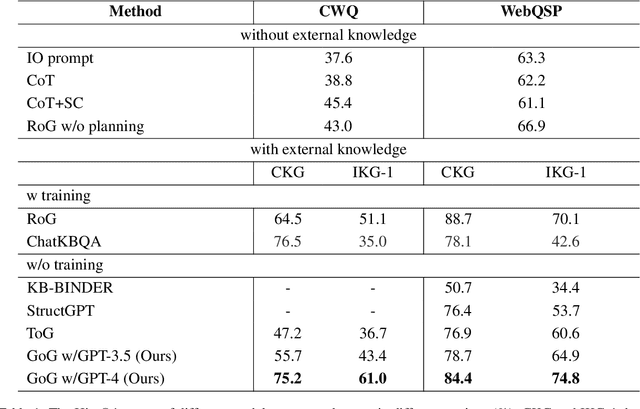
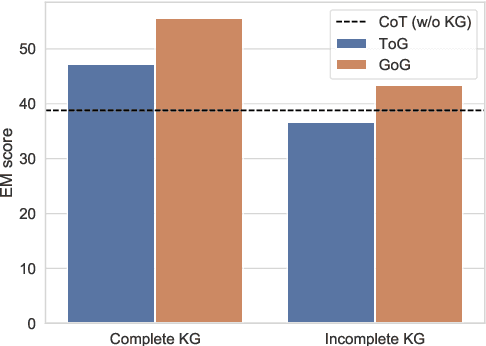
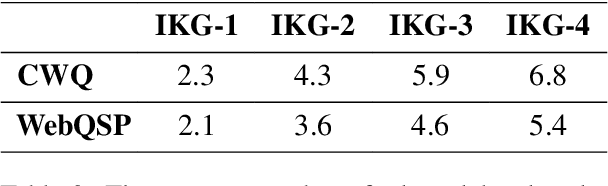
Abstract:To address the issue of insufficient knowledge and the tendency to generate hallucination in Large Language Models (LLMs), numerous studies have endeavored to integrate LLMs with Knowledge Graphs (KGs). However, all these methods are evaluated on conventional Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) with complete KGs, where the factual triples involved in each question are entirely covered by the given KG. In this situation, LLM mainly acts as an agent to find answer entities by exploring the KG, rather than effectively integrating internal and external knowledge sources. However, in real-world scenarios, KGs are often incomplete to cover all the knowledge required to answer questions. To simulate real-world scenarios and evaluate the ability of LLMs to integrate internal and external knowledge, in this paper, we propose leveraging LLMs for QA under Incomplete Knowledge Graph (IKGQA), where the given KG doesn't include all the factual triples involved in each question. To handle IKGQA, we propose a training-free method called Generate-on-Graph (GoG) that can generate new factual triples while exploring on KGs. Specifically, we propose a selecting-generating-answering framework, which not only treat the LLM as an agent to explore on KGs, but also treat it as a KG to generate new facts based on the explored subgraph and its inherent knowledge. Experimental results on two datasets demonstrate that our GoG can solve IKGQA to a certain extent, while almost all previous methods cannot perform well on IKGQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge