Jesse Bettencourt
Forecasting Black Sigatoka Infection Risks with Latent Neural ODEs
Dec 01, 2020



Abstract:Black Sigatoka disease severely decreases global banana production, and climate change aggravates the problem by altering fungal species distributions. Due to the heavy financial burden of managing this infectious disease, farmers in developing countries face significant banana crop losses. Though scientists have produced mathematical models of infectious diseases, adapting these models to incorporate climate effects is difficult. We present MR. NODE (Multiple predictoR Neural ODE), a neural network that models the dynamics of black Sigatoka infection learnt directly from data via Neural Ordinary Differential Equations. Our method encodes external predictor factors into the latent space in addition to the variable that we infer, and it can also predict the infection risk at an arbitrary point in time. Empirically, we demonstrate on historical climate data that our method has superior generalization performance on time points up to one month in the future and unseen irregularities. We believe that our method can be a useful tool to control the spread of black Sigatoka.
Learning Differential Equations that are Easy to Solve
Jul 09, 2020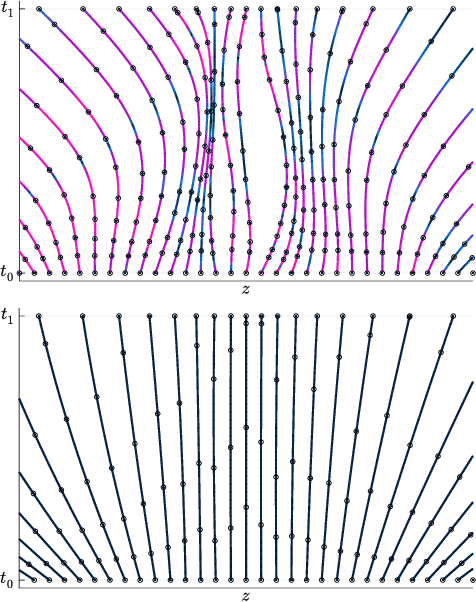
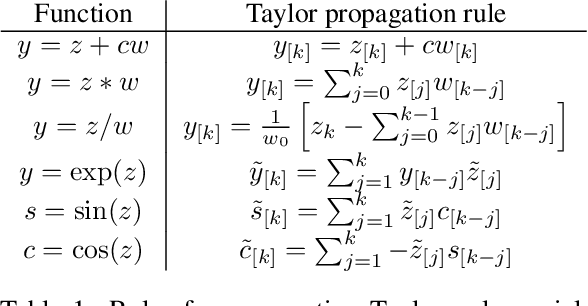
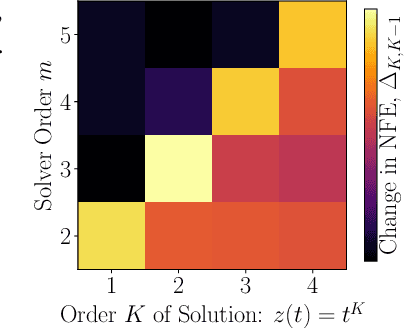

Abstract:Differential equations parameterized by neural networks become expensive to solve numerically as training progresses. We propose a remedy that encourages learned dynamics to be easier to solve. Specifically, we introduce a differentiable surrogate for the time cost of standard numerical solvers, using higher-order derivatives of solution trajectories. These derivatives are efficient to compute with Taylor-mode automatic differentiation. Optimizing this additional objective trades model performance against the time cost of solving the learned dynamics. We demonstrate our approach by training substantially faster, while nearly as accurate, models in supervised classification, density estimation, and time-series modelling tasks.
DiffEqFlux.jl - A Julia Library for Neural Differential Equations
Feb 06, 2019Abstract:DiffEqFlux.jl is a library for fusing neural networks and differential equations. In this work we describe differential equations from the viewpoint of data science and discuss the complementary nature between machine learning models and differential equations. We demonstrate the ability to incorporate DifferentialEquations.jl-defined differential equation problems into a Flux-defined neural network, and vice versa. The advantages of being able to use the entire DifferentialEquations.jl suite for this purpose is demonstrated by counter examples where simple integration strategies fail, but the sophisticated integration strategies provided by the DifferentialEquations.jl library succeed. This is followed by a demonstration of delay differential equations and stochastic differential equations inside of neural networks. We show high-level functionality for defining neural ordinary differential equations (neural networks embedded into the differential equation) and describe the extra models in the Flux model zoo which includes neural stochastic differential equations. We conclude by discussing the various adjoint methods used for backpropogation of the differential equation solvers. DiffEqFlux.jl is an important contribution to the area, as it allows the full weight of the differential equation solvers developed from decades of research in the scientific computing field to be readily applied to the challenges posed by machine learning and data science.
Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Oct 22, 2018



Abstract:We introduce a new family of deep neural network models. Instead of specifying a discrete sequence of hidden layers, we parameterize the derivative of the hidden state using a neural network. The output of the network is computed using a black-box differential equation solver. These continuous-depth models have constant memory cost, adapt their evaluation strategy to each input, and can explicitly trade numerical precision for speed. We demonstrate these properties in continuous-depth residual networks and continuous-time latent variable models. We also construct continuous normalizing flows, a generative model that can train by maximum likelihood, without partitioning or ordering the data dimensions. For training, we show how to scalably backpropagate through any ODE solver, without access to its internal operations. This allows end-to-end training of ODEs within larger models.
FFJORD: Free-form Continuous Dynamics for Scalable Reversible Generative Models
Oct 22, 2018



Abstract:A promising class of generative models maps points from a simple distribution to a complex distribution through an invertible neural network. Likelihood-based training of these models requires restricting their architectures to allow cheap computation of Jacobian determinants. Alternatively, the Jacobian trace can be used if the transformation is specified by an ordinary differential equation. In this paper, we use Hutchinson's trace estimator to give a scalable unbiased estimate of the log-density. The result is a continuous-time invertible generative model with unbiased density estimation and one-pass sampling, while allowing unrestricted neural network architectures. We demonstrate our approach on high-dimensional density estimation, image generation, and variational inference, achieving the state-of-the-art among exact likelihood methods with efficient sampling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge