Jean P. Barddal
Pattern Spotting and Image Retrieval in Historical Documents using Deep Hashing
Aug 04, 2022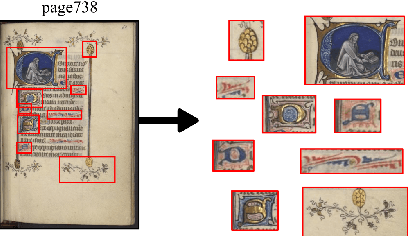
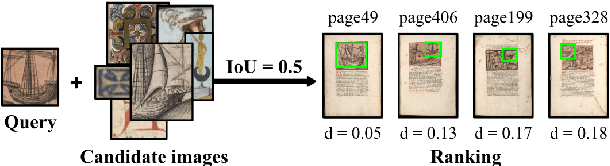

Abstract:This paper presents a deep learning approach for image retrieval and pattern spotting in digital collections of historical documents. First, a region proposal algorithm detects object candidates in the document page images. Next, deep learning models are used for feature extraction, considering two distinct variants, which provide either real-valued or binary code representations. Finally, candidate images are ranked by computing the feature similarity with a given input query. A robust experimental protocol evaluates the proposed approach considering each representation scheme (real-valued and binary code) on the DocExplore image database. The experimental results show that the proposed deep models compare favorably to the state-of-the-art image retrieval approaches for images of historical documents, outperforming other deep models by 2.56 percentage points using the same techniques for pattern spotting. Besides, the proposed approach also reduces the search time by up to 200x and the storage cost up to 6,000x when compared to related works based on real-valued representations.
Classifier Pool Generation based on a Two-level Diversity Approach
Nov 03, 2020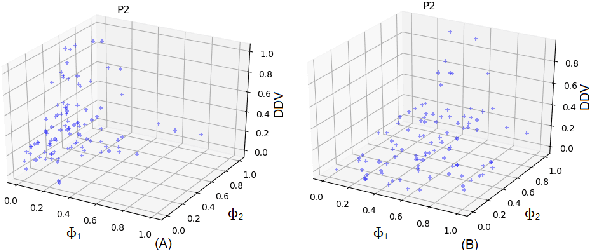
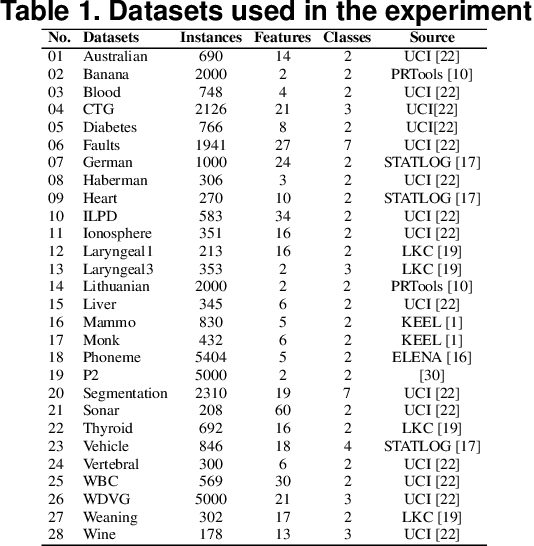
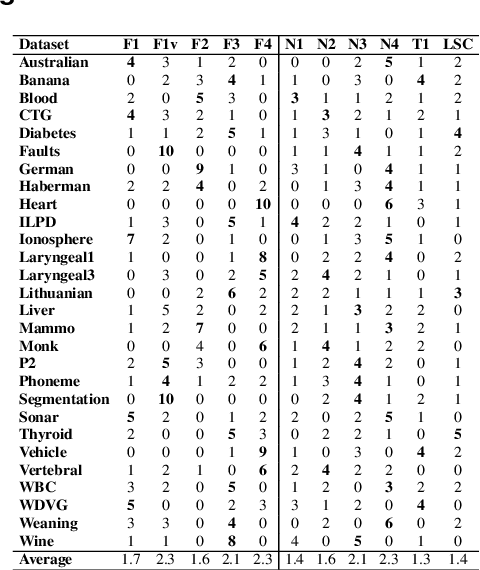
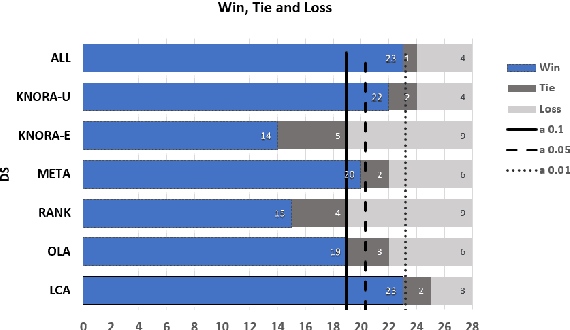
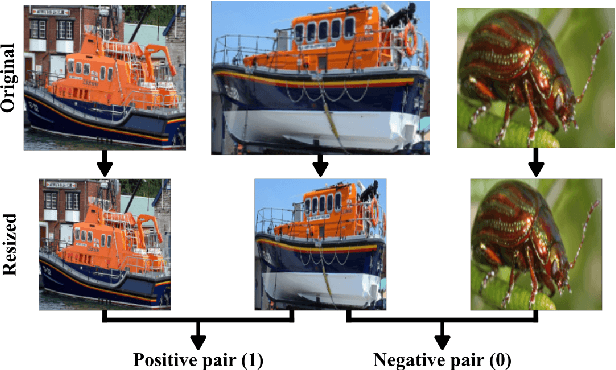
Abstract:This paper describes a classifier pool generation method guided by the diversity estimated on the data complexity and classifier decisions. First, the behavior of complexity measures is assessed by considering several subsamples of the dataset. The complexity measures with high variability across the subsamples are selected for posterior pool adaptation, where an evolutionary algorithm optimizes diversity in both complexity and decision spaces. A robust experimental protocol with 28 datasets and 20 replications is used to evaluate the proposed method. Results show significant accuracy improvements in 69.4% of the experiments when Dynamic Classifier Selection and Dynamic Ensemble Selection methods are applied.
An End-to-End Approach for Recognition of Modern and Historical Handwritten Numeral Strings
Mar 28, 2020


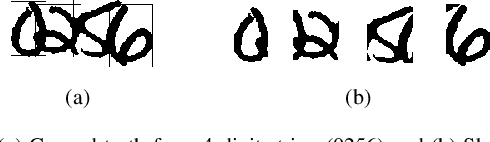
Abstract:An end-to-end solution for handwritten numeral string recognition is proposed, in which the numeral string is considered as composed of objects automatically detected and recognized by a YoLo-based model. The main contribution of this paper is to avoid heuristic-based methods for string preprocessing and segmentation, the need for task-oriented classifiers, and also the use of specific constraints related to the string length. A robust experimental protocol based on several numeral string datasets, including one composed of historical documents, has shown that the proposed method is a feasible end-to-end solution for numeral string recognition. Besides, it reduces the complexity of the string recognition task considerably since it drops out classical steps, in special preprocessing, segmentation, and a set of classifiers devoted to strings with a specific length.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge