Jan-Christoph Klie
On Efficient and Statistical Quality Estimation for Data Annotation
May 20, 2024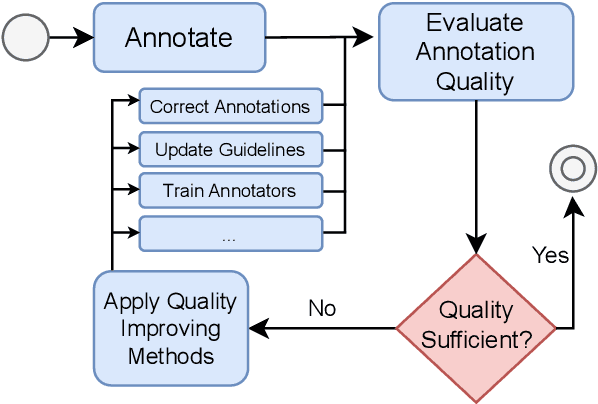
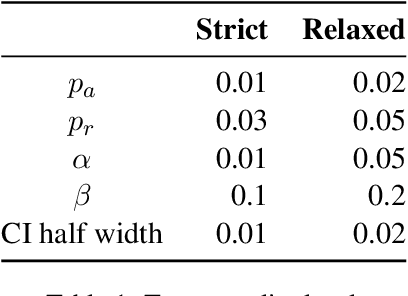
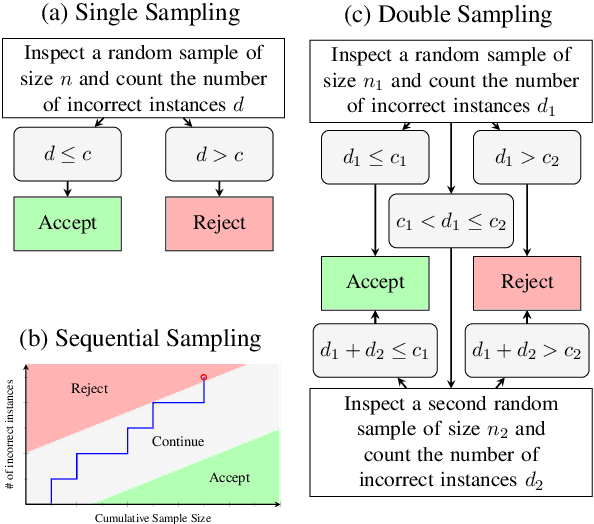
Abstract:Annotated datasets are an essential ingredient to train, evaluate, compare and productionalize supervised machine learning models. It is therefore imperative that annotations are of high quality. For their creation, good quality management and thereby reliable quality estimates are needed. Then, if quality is insufficient during the annotation process, rectifying measures can be taken to improve it. Quality estimation is often performed by having experts manually label instances as correct or incorrect. But checking all annotated instances tends to be expensive. Therefore, in practice, usually only subsets are inspected; sizes are chosen mostly without justification or regard to statistical power and more often than not, are relatively small. Basing estimates on small sample sizes, however, can lead to imprecise values for the error rate. Using unnecessarily large sample sizes costs money that could be better spent, for instance on more annotations. Therefore, we first describe in detail how to use confidence intervals for finding the minimal sample size needed to estimate the annotation error rate. Then, we propose applying acceptance sampling as an alternative to error rate estimation We show that acceptance sampling can reduce the required sample sizes up to 50% while providing the same statistical guarantees.
Analyzing Dataset Annotation Quality Management in the Wild
Jul 16, 2023Abstract:Data quality is crucial for training accurate, unbiased, and trustworthy machine learning models and their correct evaluation. Recent works, however, have shown that even popular datasets used to train and evaluate state-of-the-art models contain a non-negligible amount of erroneous annotations, bias or annotation artifacts. There exist best practices and guidelines regarding annotation projects. But to the best of our knowledge, no large-scale analysis has been performed as of yet on how quality management is actually conducted when creating natural language datasets and whether these recommendations are followed. Therefore, we first survey and summarize recommended quality management practices for dataset creation as described in the literature and provide suggestions on how to apply them. Then, we compile a corpus of 591 scientific publications introducing text datasets and annotate it for quality-related aspects, such as annotator management, agreement, adjudication or data validation. Using these annotations, we then analyze how quality management is conducted in practice. We find that a majority of the annotated publications apply good or very good quality management. However, we deem the effort of 30% of the works as only subpar. Our analysis also shows common errors, especially with using inter-annotator agreement and computing annotation error rates.
Lessons Learned from a Citizen Science Project for Natural Language Processing
Apr 25, 2023



Abstract:Many Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems use annotated corpora for training and evaluation. However, labeled data is often costly to obtain and scaling annotation projects is difficult, which is why annotation tasks are often outsourced to paid crowdworkers. Citizen Science is an alternative to crowdsourcing that is relatively unexplored in the context of NLP. To investigate whether and how well Citizen Science can be applied in this setting, we conduct an exploratory study into engaging different groups of volunteers in Citizen Science for NLP by re-annotating parts of a pre-existing crowdsourced dataset. Our results show that this can yield high-quality annotations and attract motivated volunteers, but also requires considering factors such as scalability, participation over time, and legal and ethical issues. We summarize lessons learned in the form of guidelines and provide our code and data to aid future work on Citizen Science.
Annotation Error Detection: Analyzing the Past and Present for a More Coherent Future
Jun 05, 2022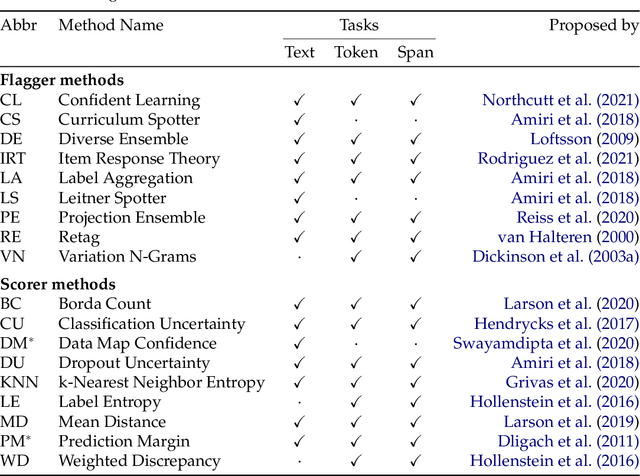
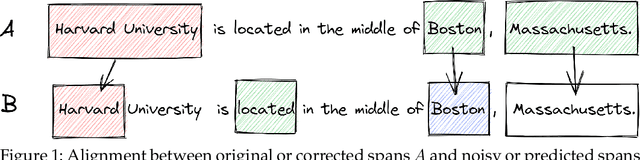
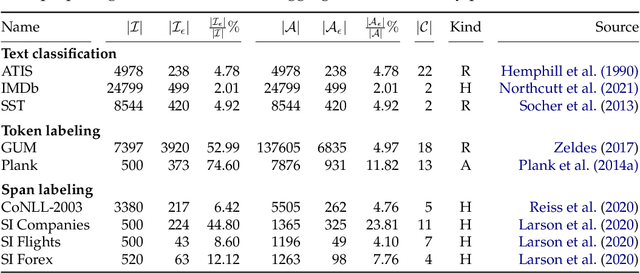
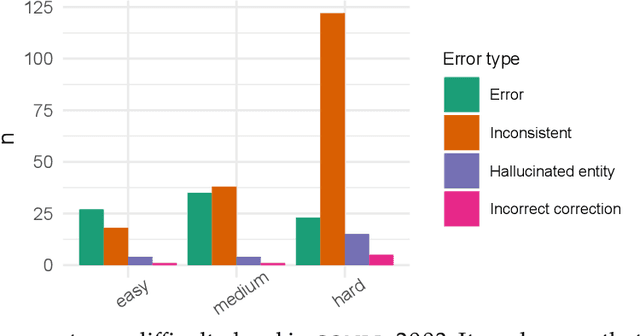
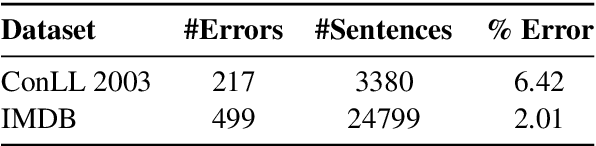
Abstract:Annotated data is an essential ingredient in natural language processing for training and evaluating machine learning models. It is therefore very desirable for the annotations to be of high quality. Recent work, however, has shown that several popular datasets contain a surprising amount of annotation errors or inconsistencies. To alleviate this issue, many methods for annotation error detection have been devised over the years. While researchers show that their approaches work well on their newly introduced datasets, they rarely compare their methods to previous work or on the same datasets. This raises strong concerns on methods' general performance and makes it difficult to asses their strengths and weaknesses. We therefore reimplement 18 methods for detecting potential annotation errors and evaluate them on 9 English datasets for text classification as well as token and span labeling. In addition, we define a uniform evaluation setup including a new formalization of the annotation error detection task, evaluation protocol and general best practices. To facilitate future research and reproducibility, we release our datasets and implementations in an easy-to-use and open source software package.
Annotation Curricula to Implicitly Train Non-Expert Annotators
Jun 09, 2021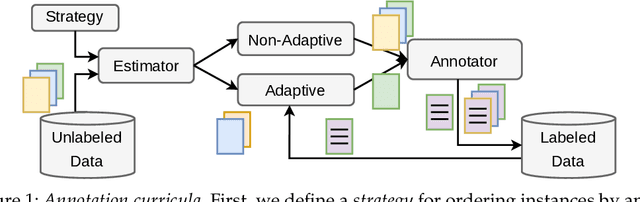
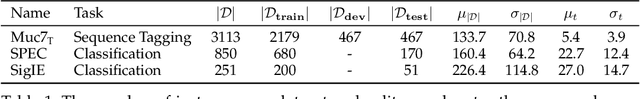
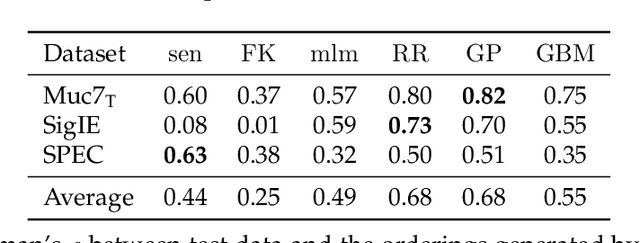
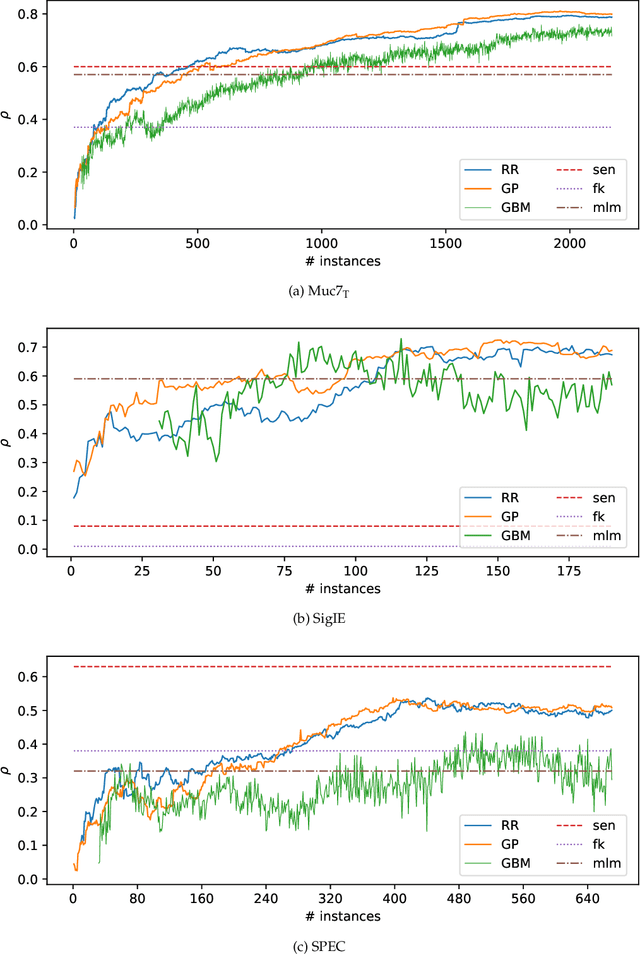
Abstract:Annotation studies often require annotators to familiarize themselves with the task, its annotation scheme, and the data domain. This can be overwhelming in the beginning, mentally taxing, and induce errors into the resulting annotations; especially in citizen science or crowd sourcing scenarios where domain expertise is not required and only annotation guidelines are provided. To alleviate these issues, we propose annotation curricula, a novel approach to implicitly train annotators. Our goal is to gradually introduce annotators into the task by ordering instances that are annotated according to a learning curriculum. To do so, we first formalize annotation curricula for sentence- and paragraph-level annotation tasks, define an ordering strategy, and identify well-performing heuristics and interactively trained models on three existing English datasets. We then conduct a user study with 40 voluntary participants who are asked to identify the most fitting misconception for English tweets about the Covid-19 pandemic. Our results show that using a simple heuristic to order instances can already significantly reduce the total annotation time while preserving a high annotation quality. Annotation curricula thus can provide a novel way to improve data collection. To facilitate future research, we further share our code and data consisting of 2,400 annotations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge