Jaihyun Park
A Data-driven Investigation of Euphemistic Language: Comparing the usage of "slave" and "servant" in 19th century US newspapers
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:This study investigates the usage of "slave" and "servant" in the 19th century US newspapers using computational methods. While both terms were used to refer to enslaved African Americans, they were used in distinct ways. In the Chronicling America corpus, we included possible OCR errors by using FastText embedding and excluded text reprints to consider text reprint culture in the 19th century. Word2vec embedding was used to find semantically close words to "slave" and "servant" and log-odds ratio was calculated to identify over-represented discourse words in the Southern and Northern newspapers. We found that "slave" is associated with socio-economic, legal, and administrative words, however, "servant" is linked to religious words in the Northern newspapers while Southern newspapers associated "servant" with domestic and familial words. We further found that slave discourse words in Southern newspapers are more prevalent in Northern newspapers while servant discourse words from each side are prevalent in their own region. This study contributes to the understanding of how newspapers created different discourses around enslaved African Americans in the 19th century US.
Locating the Leading Edge of Cultural Change
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Measures of textual similarity and divergence are increasingly used to study cultural change. But which measures align, in practice, with social evidence about change? We apply three different representations of text (topic models, document embeddings, and word-level perplexity) to three different corpora (literary studies, economics, and fiction). In every case, works by highly-cited authors and younger authors are textually ahead of the curve. We don't find clear evidence that one representation of text is to be preferred over the others. But alignment with social evidence is strongest when texts are represented through the top quartile of passages, suggesting that a text's impact may depend more on its most forward-looking moments than on sustaining a high level of innovation throughout.
A Quantitative Discourse Analysis of Asian Workers in the US Historical Newspapers
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Warning: This paper contains examples of offensive language targetting marginalized population. The digitization of historical texts invites researchers to explore the large-scale corpus of historical texts with computational methods. In this study, we present computational text analysis on a relatively understudied topic of how Asian workers are represented in historical newspapers in the United States. We found that the word "coolie" was semantically different in some States (e.g., Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Wyoming, Oklahoma, and Arkansas) with the different discourses around coolie. We also found that then-Confederate newspapers and then-Union newspapers formed distinctive discourses by measuring over-represented words. Newspapers from then-Confederate States associated coolie with slavery-related words. In addition, we found Asians were perceived to be inferior to European immigrants and subjected to the target of racism. This study contributes to supplementing the qualitative analysis of racism in the United States with quantitative discourse analysis.
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Perceptual Extreme Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
May 03, 2020
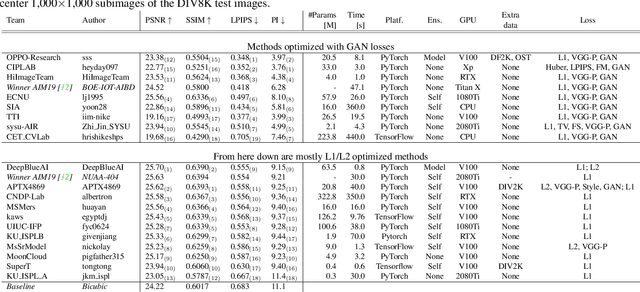

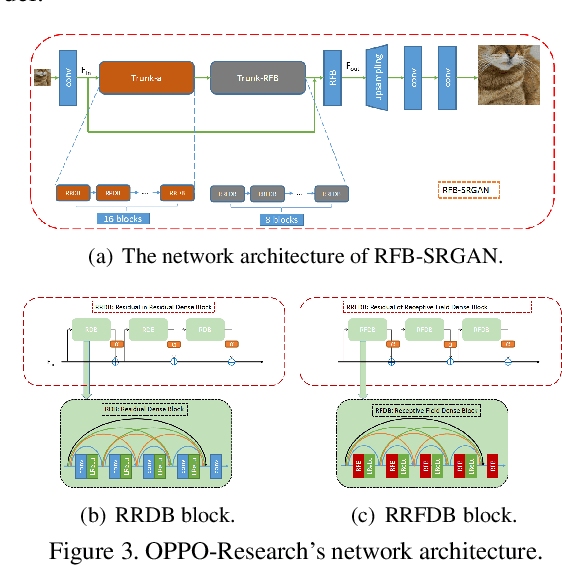
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2020 challenge on perceptual extreme super-resolution with focus on proposed solutions and results. The challenge task was to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor 16 based on a set of prior examples of low and corresponding high resolution images. The goal is to obtain a network design capable to produce high resolution results with the best perceptual quality and similar to the ground truth. The track had 280 registered participants, and 19 teams submitted the final results. They gauge the state-of-the-art in single image super-resolution.
Coordinating and Integrating Faceted Classification with Rich Semantic Modeling
Sep 25, 2018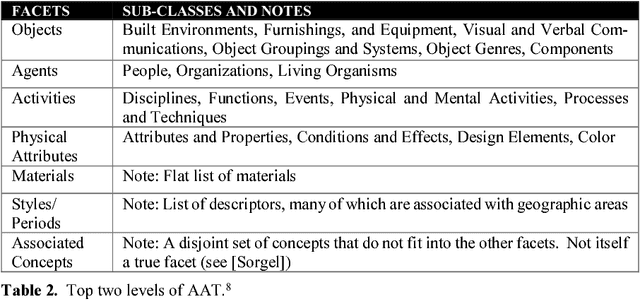
Abstract:Faceted classifications define dimensions for the types of entities included. In effect, the facets provide an "ontological commitment". We compare a faceted thesaurus, the Art and Architecture Thesaurus (AAT), with ontologies derived from the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO2), which is an upper (or formal) ontology widely used to describe entities in biomedicine. We consider how the AAT and BFO2-based ontologies could be coordinated and integrated into a Human Activity and Infrastructure Foundry (HAIF). To extend the AAT to enable this coordination and integration, we describe how a wider range of relationships among its terms could be introduced. Using these extensions, we explore richer modeling of topics from AAT that deal with Technology. Finally, we consider how ontology-based frames and semantic role frames can be integrated to make rich semantic statements about changes in the world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge