Robert B. Allen
Using Causal Threads to Explain Changes in a Dynamic System
Nov 19, 2023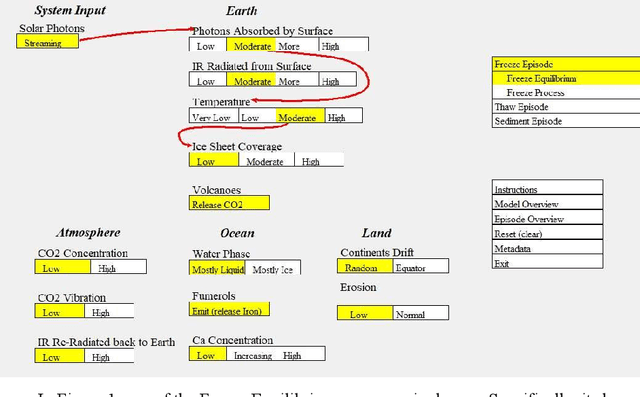
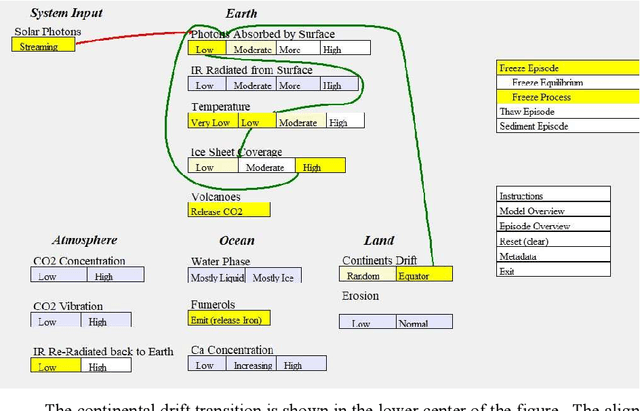
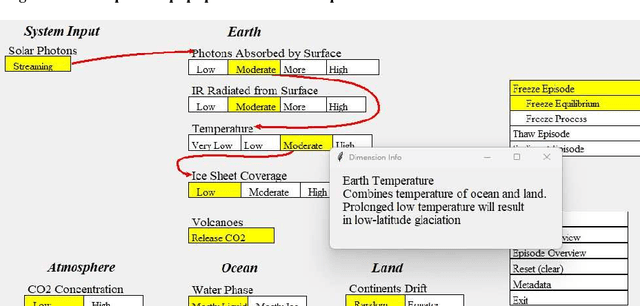
Abstract:We explore developing rich semantic models of systems. Specifically, we consider structured causal explanations about state changes in those systems. Essentially, we are developing process-based dynamic knowledge graphs. As an example, we construct a model of the causal threads for geological changes proposed by the Snowball Earth theory. Further, we describe an early prototype of a graphical interface to present the explanations. Unlike statistical approaches to summarization and explanation such as Large Language Models (LLMs), our approach of direct representation can be inspected and verified directly.
Semantic Modeling with SUMO
Jan 12, 2021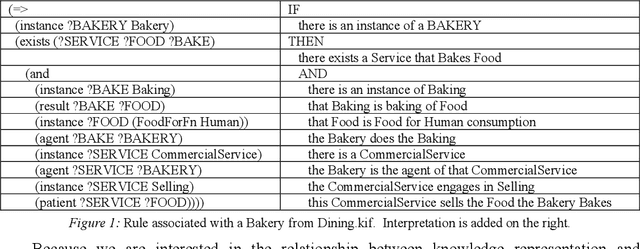
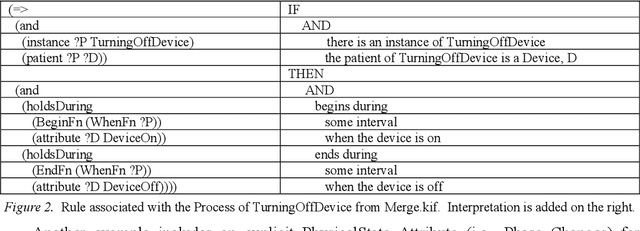
Abstract:We explore using the Suggested Upper Merged Ontology (SUMO) to develop a semantic simulation. We provide two proof-of-concept demonstrations modeling transitions in a simulated gasoline engine using a general-purpose programming language. Rather than focusing on computationally highly intensive techniques, we explore a less computationally intensive approach related to familiar software engineering testing procedures. In addition, we propose structured representations of terms based on linguistic approaches to lexicography.
Definitions and Semantic Simulations Based on Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling
Dec 31, 2019
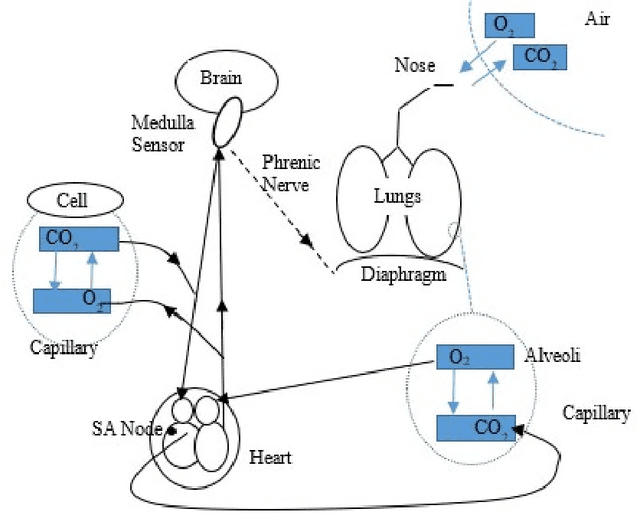
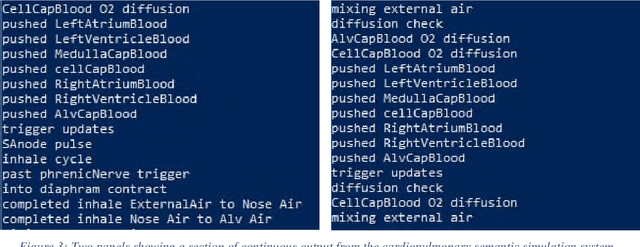
Abstract:We have proposed going beyond traditional ontologies to use rich semantics implemented in programming languages for modeling. In this paper, we discuss the application of executable semantic models to two examples, first a structured definition of a waterfall and second the cardiopulmonary system. We examine the components of these models and the way those components interact. Ultimately, such models should provide the basis for direct representation.
Coordinating and Integrating Faceted Classification with Rich Semantic Modeling
Sep 25, 2018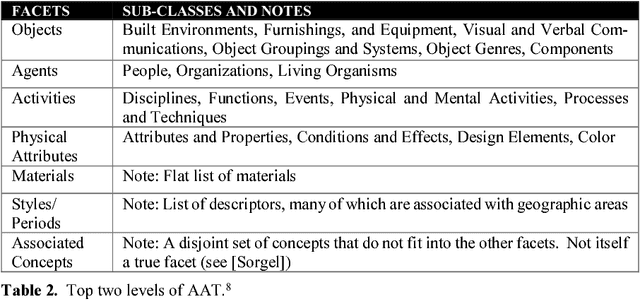
Abstract:Faceted classifications define dimensions for the types of entities included. In effect, the facets provide an "ontological commitment". We compare a faceted thesaurus, the Art and Architecture Thesaurus (AAT), with ontologies derived from the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO2), which is an upper (or formal) ontology widely used to describe entities in biomedicine. We consider how the AAT and BFO2-based ontologies could be coordinated and integrated into a Human Activity and Infrastructure Foundry (HAIF). To extend the AAT to enable this coordination and integration, we describe how a wider range of relationships among its terms could be introduced. Using these extensions, we explore richer modeling of topics from AAT that deal with Technology. Finally, we consider how ontology-based frames and semantic role frames can be integrated to make rich semantic statements about changes in the world.
A Foundry of Human Activities and Infrastructures
Oct 31, 2017Abstract:Direct representation knowledgebases can enhance and even provide an alternative to document-centered digital libraries. Here we consider realist semantic modeling of everyday activities and infrastructures in such knowledgebases. Because we want to integrate a wide variety of topics, a collection of ontologies (a foundry) and a range of other knowledge resources are needed. We first consider modeling the routine procedures that support human activities and technologies. Next, we examine the interactions of technologies with aspects of social organization. Then, we consider approaches and issues for developing and validating explanations of the relationships among various entities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge