Jacob Anderson
Querying Perception Streams with Spatial Regular Expressions
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:Perception in fields like robotics, manufacturing, and data analysis generates large volumes of temporal and spatial data to effectively capture their environments. However, sorting through this data for specific scenarios is a meticulous and error-prone process, often dependent on the application, and lacks generality and reproducibility. In this work, we introduce SpREs as a novel querying language for pattern matching over perception streams containing spatial and temporal data derived from multi-modal dynamic environments. To highlight the capabilities of SpREs, we developed the STREM tool as both an offline and online pattern matching framework for perception data. We demonstrate the offline capabilities of STREM through a case study on a publicly available AV dataset (Woven Planet Perception) and its online capabilities through a case study integrating STREM in ROS with the CARLA simulator. We also conduct performance benchmark experiments on various SpRE queries. Using our matching framework, we are able to find over 20,000 matches within 296 ms making STREM applicable in runtime monitoring applications.
Benchmarking Generalization via In-Context Instructions on 1,600+ Language Tasks
Apr 16, 2022
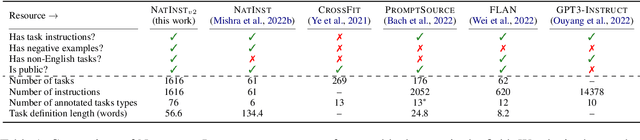
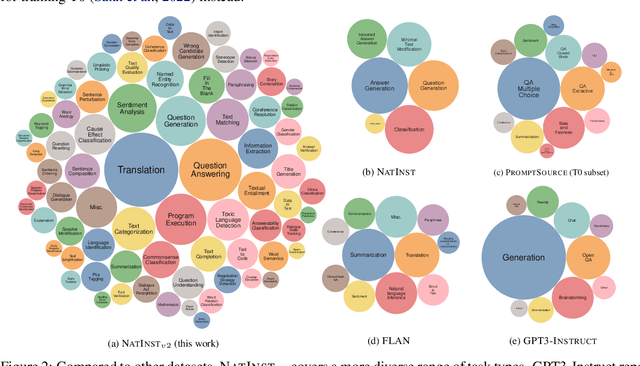
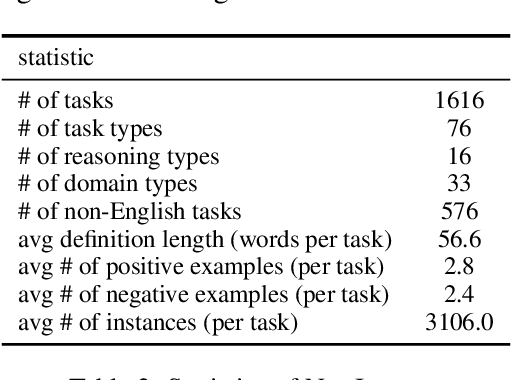
Abstract:How can we measure the generalization of models to a variety of unseen tasks when provided with their language instructions? To facilitate progress in this goal, we introduce Natural-Instructions v2, a collection of 1,600+ diverse language tasks and their expert written instructions. More importantly, the benchmark covers 70+ distinct task types, such as tagging, in-filling, and rewriting. This benchmark is collected with contributions of NLP practitioners in the community and through an iterative peer review process to ensure their quality. This benchmark enables large-scale evaluation of cross-task generalization of the models -- training on a subset of tasks and evaluating on the remaining unseen ones. For instance, we are able to rigorously quantify generalization as a function of various scaling parameters, such as the number of observed tasks, the number of instances, and model sizes. As a by-product of these experiments. we introduce Tk-Instruct, an encoder-decoder Transformer that is trained to follow a variety of in-context instructions (plain language task definitions or k-shot examples) which outperforms existing larger models on our benchmark. We hope this benchmark facilitates future progress toward more general-purpose language understanding models.
Fully Convolutional Networks for Text Classification
Feb 14, 2019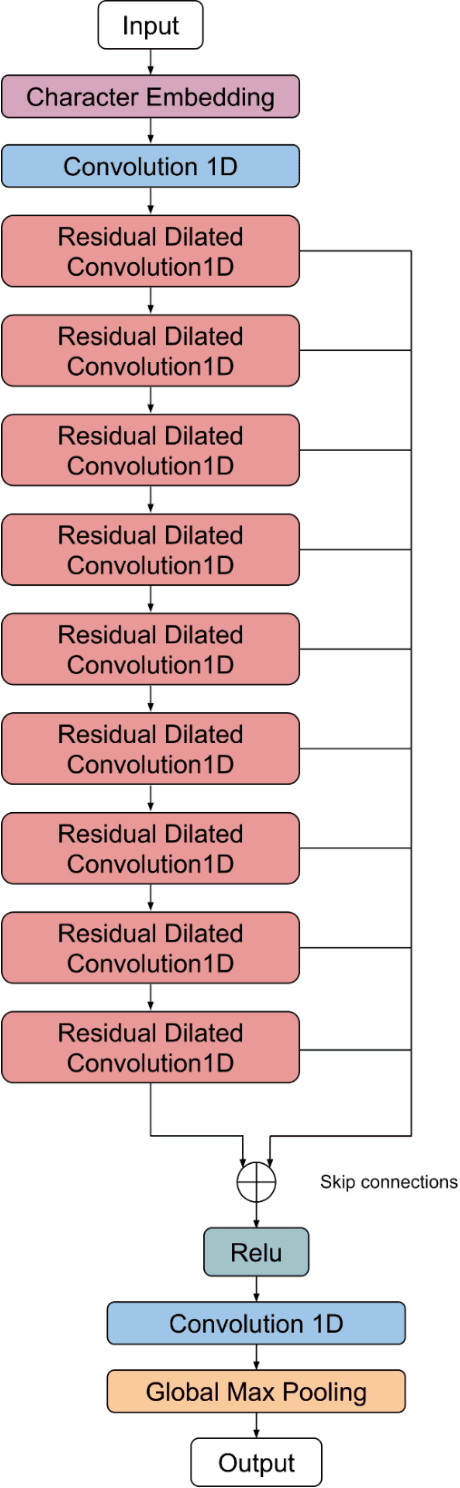



Abstract:In this work I propose a new way of using fully convolutional networks for classification while allowing for input of any size. I additionally propose two modifications on the idea of attention and the benefits and detriments of using the modifications. Finally, I show suboptimal results on the ITAmoji 2018 tweet to emoji task and provide a discussion about why that might be the case as well as a proposed fix to further improve results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge