Ioannis Tsochantaridis
Evaluating the Immediate Applicability of Pose Estimation for Sign Language Recognition
Apr 20, 2021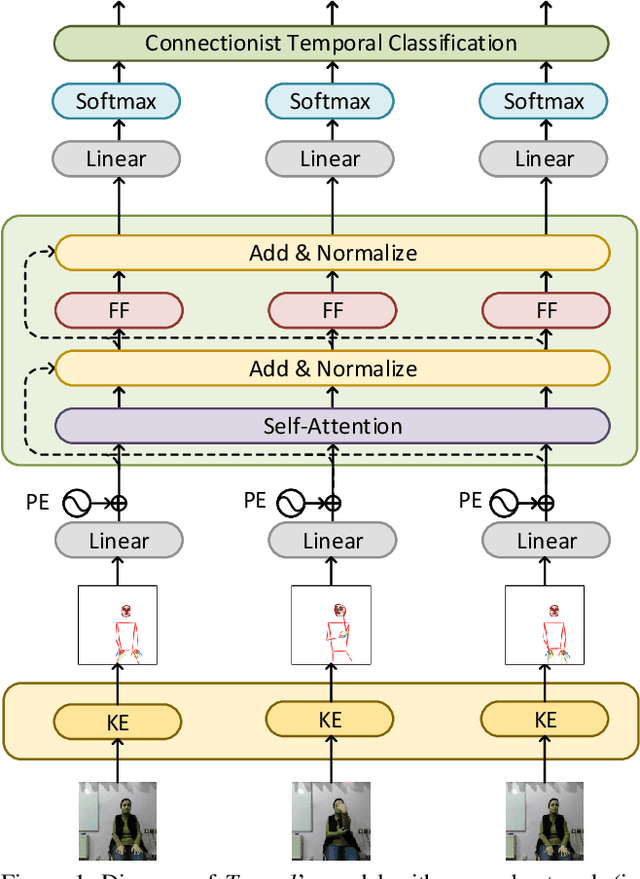
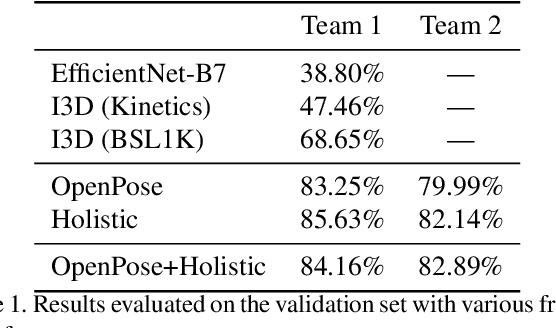
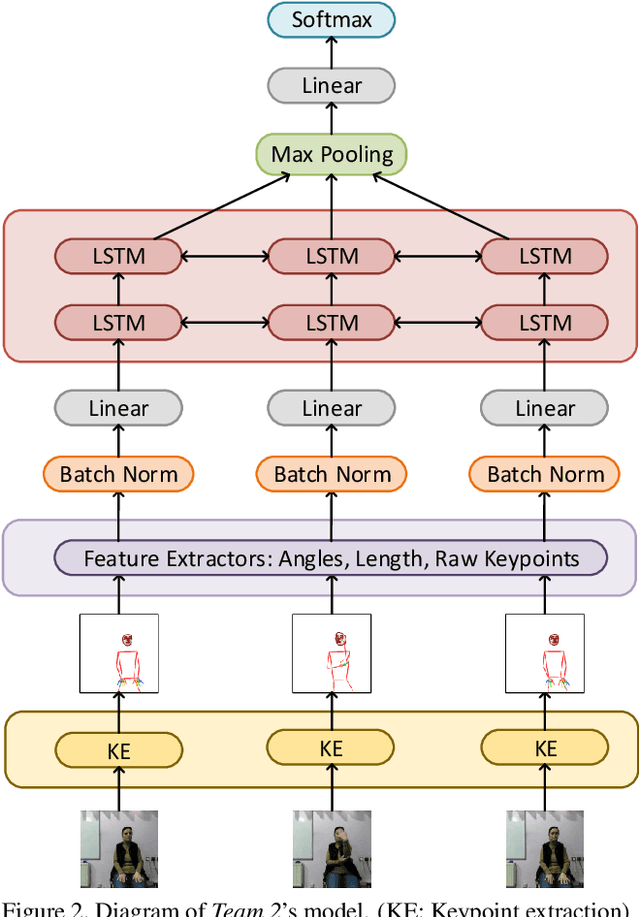
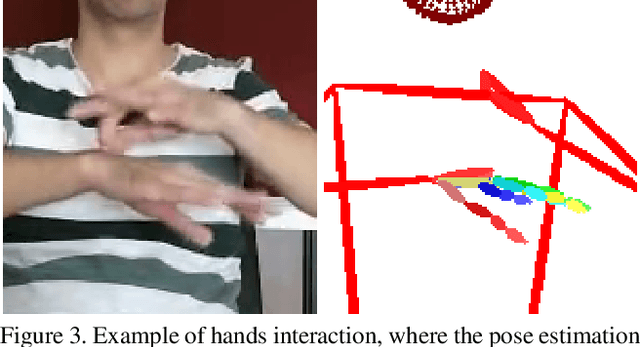
Abstract:Signed languages are visual languages produced by the movement of the hands, face, and body. In this paper, we evaluate representations based on skeleton poses, as these are explainable, person-independent, privacy-preserving, low-dimensional representations. Basically, skeletal representations generalize over an individual's appearance and background, allowing us to focus on the recognition of motion. But how much information is lost by the skeletal representation? We perform two independent studies using two state-of-the-art pose estimation systems. We analyze the applicability of the pose estimation systems to sign language recognition by evaluating the failure cases of the recognition models. Importantly, this allows us to characterize the current limitations of skeletal pose estimation approaches in sign language recognition.
Real-Time Sign Language Detection using Human Pose Estimation
Sep 13, 2020



Abstract:We propose a lightweight real-time sign language detection model, as we identify the need for such a case in videoconferencing. We extract optical flow features based on human pose estimation and, using a linear classifier, show these features are meaningful with an accuracy of 80%, evaluated on the DGS Corpus. Using a recurrent model directly on the input, we see improvements of up to 91% accuracy, while still working under 4ms. We describe a demo application to sign language detection in the browser in order to demonstrate its usage possibility in videoconferencing applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge