Ildar Farkhatdinov
Leveraging Tactile Sensing to Render both Haptic Feedback and Virtual Reality 3D Object Reconstruction in Robotic Telemanipulation
Dec 03, 2024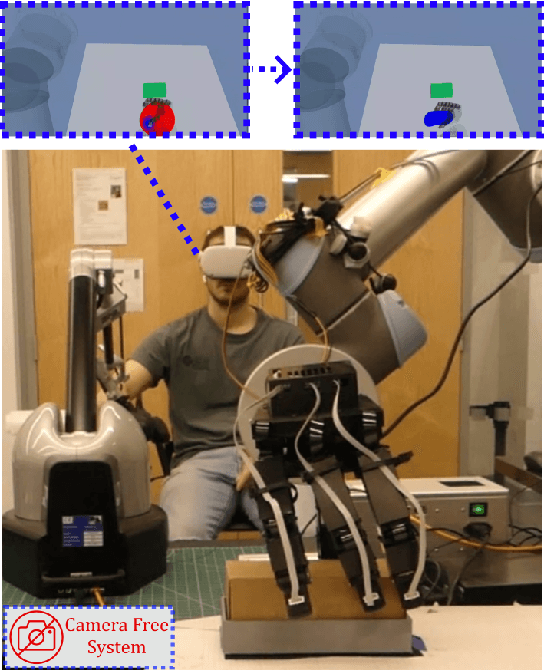

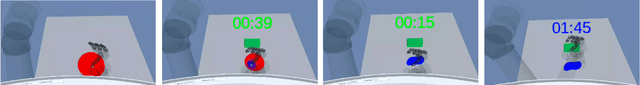
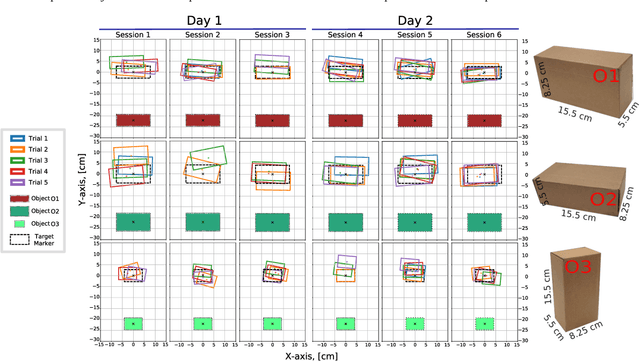
Abstract:Dexterous robotic manipulator teleoperation is widely used in many applications, either where it is convenient to keep the human inside the control loop, or to train advanced robot agents. So far, this technology has been used in combination with camera systems with remarkable success. On the other hand, only a limited number of studies have focused on leveraging haptic feedback from tactile sensors in contexts where camera-based systems fail, such as due to self-occlusions or poor light conditions like smoke. This study demonstrates the feasibility of precise pick-and-place teleoperation without cameras by leveraging tactile-based 3D object reconstruction in VR and providing haptic feedback to a blindfolded user. Our preliminary results show that integrating these technologies enables the successful completion of telemanipulation tasks previously dependent on cameras, paving the way for more complex future applications.
Haptic Stiffness Perception Using Hand Exoskeletons in Tactile Robotic Telemanipulation
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Robotic telemanipulation - the human-guided manipulation of remote objects - plays a pivotal role in several applications, from healthcare to operations in harsh environments. While visual feedback from cameras can provide valuable information to the human operator, haptic feedback is essential for accessing specific object properties that are difficult to be perceived by vision, such as stiffness. For the first time, we present a participant study demonstrating that operators can perceive the stiffness of remote objects during real-world telemanipulation with a dexterous robotic hand, when haptic feedback is generated from tactile sensing fingertips. Participants were tasked with squeezing soft objects by teleoperating a robotic hand, using two methods of haptic feedback: one based solely on the measured contact force, while the second also includes the squeezing displacement between the leader and follower devices. Our results demonstrate that operators are indeed capable of discriminating objects of different stiffness, relying on haptic feedback alone and without any visual feedback. Additionally, our findings suggest that the displacement feedback component may enhance discrimination with objects of similar stiffness.
A User Study Method on Healthy Participants for Assessing an Assistive Wearable Robot Utilising EMG Sensing
Jul 31, 2024
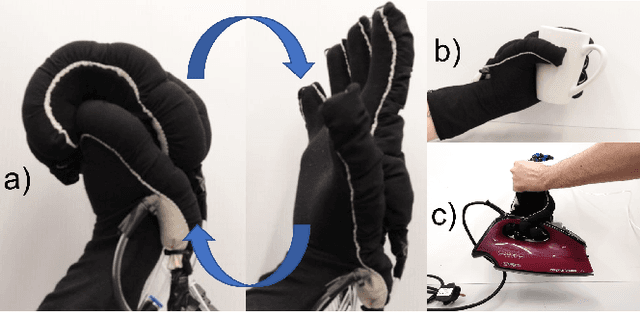


Abstract:Hand-wearable robots, specifically exoskeletons, are designed to aid hands in daily activities, playing a crucial role in post-stroke rehabilitation and assisting the elderly. Our contribution to this field is a textile robotic glove with integrated actuators. These actuators, powered by pneumatic pressure, guide the user's hand to a desired position. Crafted from textile materials, our soft robotic glove prioritizes safety, lightweight construction, and user comfort. Utilizing the ruffles technique, integrated actuators guarantee high performance in blocking force and bending effectiveness. Here, we present a participant study confirming the effectiveness of our robotic device on a healthy participant group, exploiting EMG sensing.
* 3 pages, 4 figures, conference. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2305.17720
DexSkills: Skill Segmentation Using Haptic Data for Learning Autonomous Long-Horizon Robotic Manipulation Tasks
May 06, 2024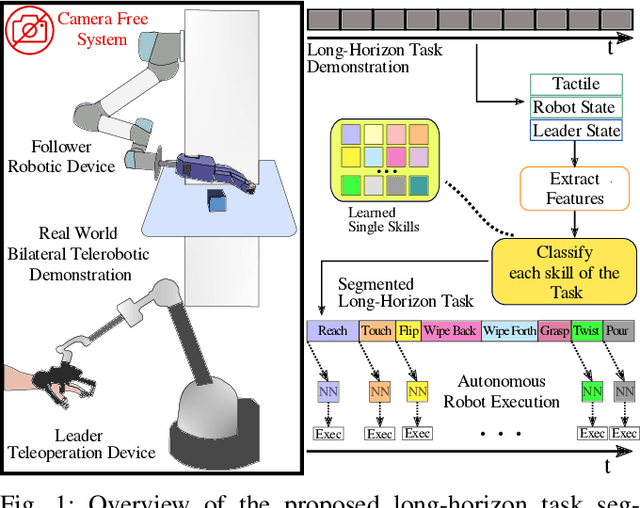
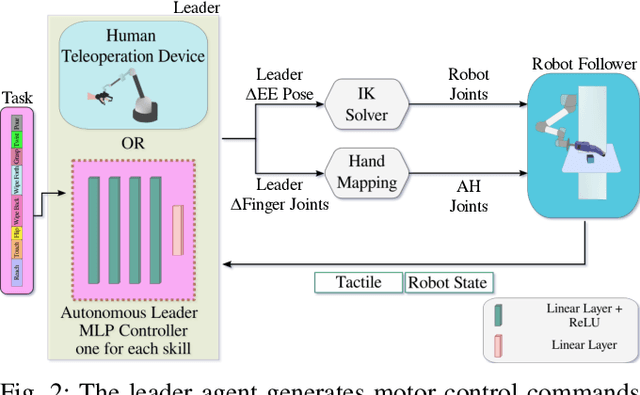
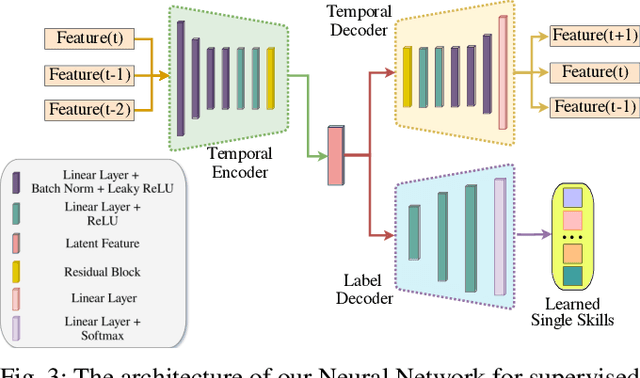
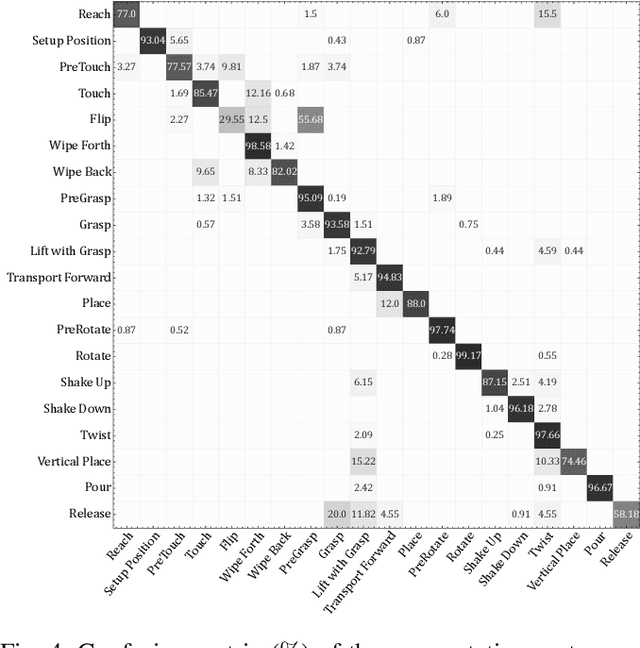
Abstract:Effective execution of long-horizon tasks with dexterous robotic hands remains a significant challenge in real-world problems. While learning from human demonstrations have shown encouraging results, they require extensive data collection for training. Hence, decomposing long-horizon tasks into reusable primitive skills is a more efficient approach. To achieve so, we developed DexSkills, a novel supervised learning framework that addresses long-horizon dexterous manipulation tasks using primitive skills. DexSkills is trained to recognize and replicate a select set of skills using human demonstration data, which can then segment a demonstrated long-horizon dexterous manipulation task into a sequence of primitive skills to achieve one-shot execution by the robot directly. Significantly, DexSkills operates solely on proprioceptive and tactile data, i.e., haptic data. Our real-world robotic experiments show that DexSkills can accurately segment skills, thereby enabling autonomous robot execution of a diverse range of tasks.
Robotic surface exploration with vision and tactile sensing for cracks detection and characterisation
Jul 13, 2023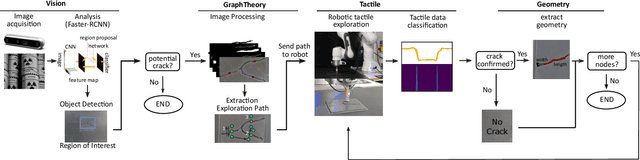

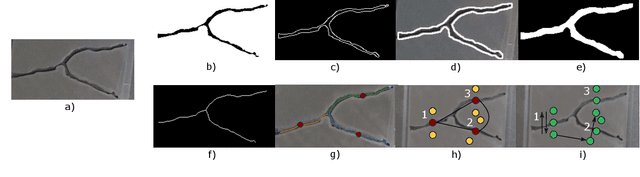
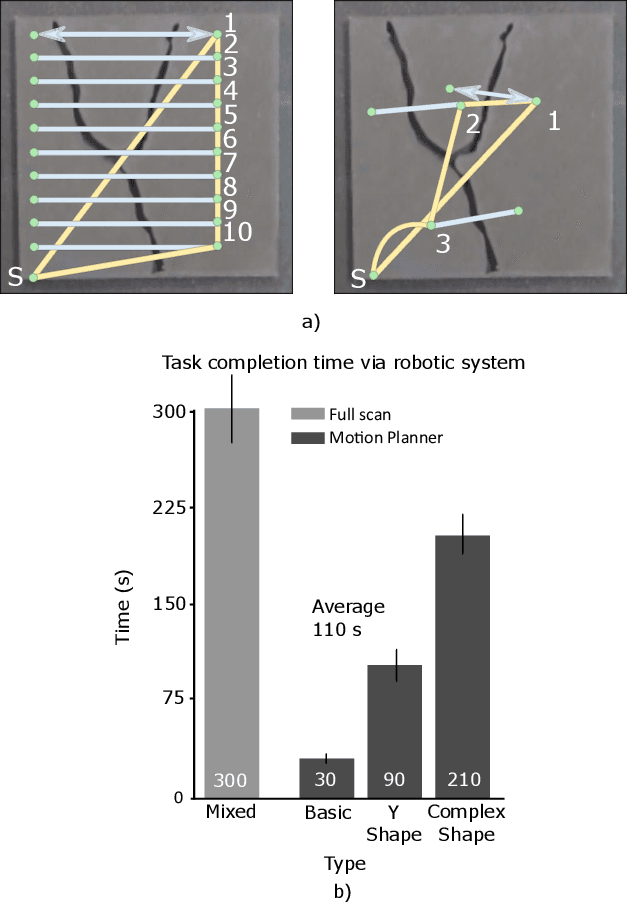
Abstract:This paper presents a novel algorithm for crack localisation and detection based on visual and tactile analysis via fibre-optics. A finger-shaped sensor based on fibre-optics is employed for the data acquisition to collect data for the analysis and the experiments. To detect the possible locations of cracks a camera is used to scan an environment while running an object detection algorithm. Once the crack is detected, a fully-connected graph is created from a skeletonised version of the crack. A minimum spanning tree is then employed for calculating the shortest path to explore the crack which is then used to develop the motion planner for the robotic manipulator. The motion planner divides the crack into multiple nodes which are then explored individually. Then, the manipulator starts the exploration and performs the tactile data classification to confirm if there is indeed a crack in that location or just a false positive from the vision algorithm. If a crack is detected, also the length, width, orientation and number of branches are calculated. This is repeated until all the nodes of the crack are explored. In order to validate the complete algorithm, various experiments are performed: comparison of exploration of cracks through full scan and motion planning algorithm, implementation of frequency-based features for crack classification and geometry analysis using a combination of vision and tactile data. From the results of the experiments, it is shown that the proposed algorithm is able to detect cracks and improve the results obtained from vision to correctly classify cracks and their geometry with minimal cost thanks to the motion planning algorithm.
Cable-driven robotic interface for lower limb neuromechanics identification
Aug 07, 2019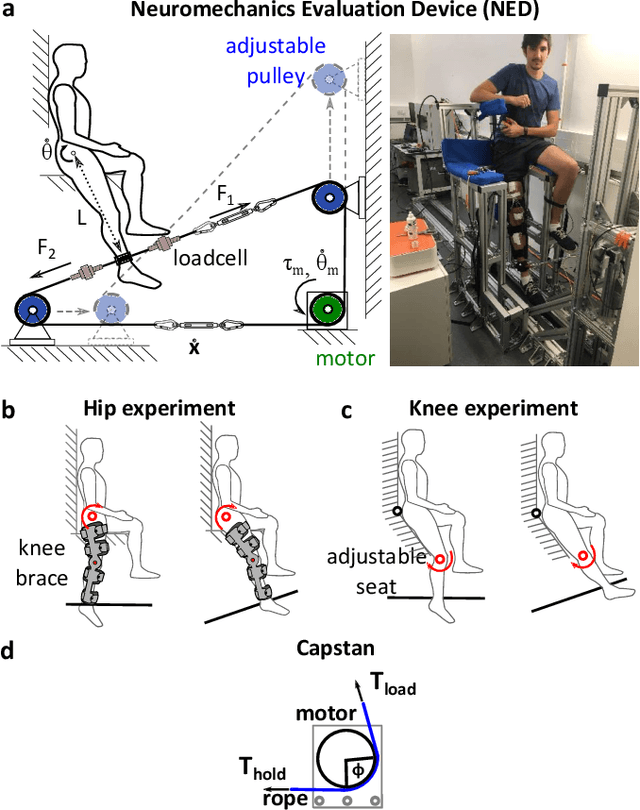
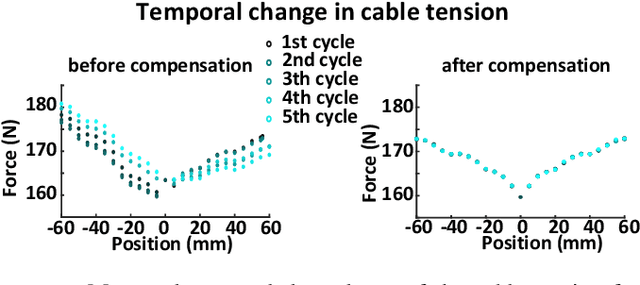
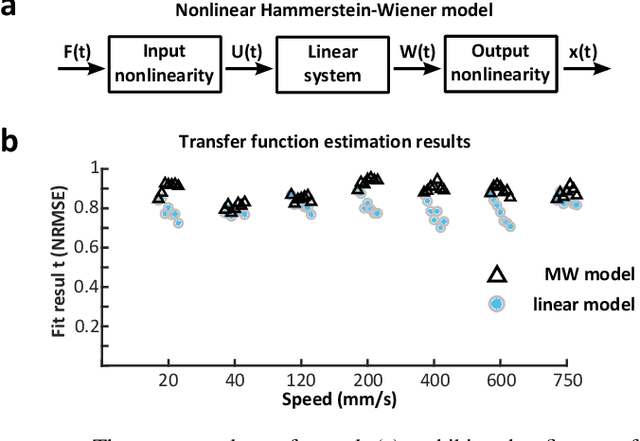
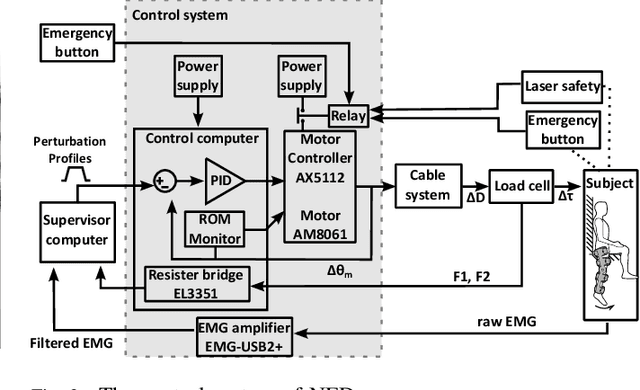
Abstract:This paper presents a versatile cable-driven robotic interface to investigate the single-joint joint neuromechanics of the hip, knee and ankle. This endpoint-based interface offers highly dynamic interaction and accurate position control, as is typically required for neuromechanics identification. It can be used with the subject upright, corresponding to natural posture during walking or standing, and does not impose kinematic constraints on a joint, in contrast to existing interfaces. Mechanical evaluations demonstrated that the interface yields a rigidity above 500N/m with low viscosity. Tests with a rigid dummy leg and linear springs show that it can identify the mechanical impedance of a limb accurately. A smooth perturbation is developed and tested with a human subject, which can be used to estimate the hip neuromechanics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge