Hyung-Min Park
Stack Less, Repeat More: A Block Reusing Approach for Progressive Speech Enhancement
May 26, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an efficient speech enhancement (SE) approach that reuses a processing block repeatedly instead of conventional stacking. Rather than increasing the number of blocks for learning deep latent representations, repeating a single block leads to progressive refinement while reducing parameter redundancy. We also minimize domain transformation by keeping an encoder and decoder shallow and reusing a single sequence modeling block. Experimental results show that the number of processing stages is more critical to performance than the number of blocks with different weights. Also, we observed that the proposed method gradually refines a noisy input within a single block. Furthermore, with the block reuse method, we demonstrate that deepening the encoder and decoder can be redundant for learning deep complex representation. Therefore, the experimental results confirm that the proposed block reusing enables progressive learning and provides an efficient alternative for SE.
SwinLip: An Efficient Visual Speech Encoder for Lip Reading Using Swin Transformer
May 07, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an efficient visual speech encoder for lip reading. While most recent lip reading studies have been based on the ResNet architecture and have achieved significant success, they are not sufficiently suitable for efficiently capturing lip reading features due to high computational complexity in modeling spatio-temporal information. Additionally, using a complex visual model not only increases the complexity of lip reading models but also induces delays in the overall network for multi-modal studies (e.g., audio-visual speech recognition, speech enhancement, and speech separation). To overcome the limitations of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based models, we apply the hierarchical structure and window self-attention of the Swin Transformer to lip reading. We configure a new lightweight scale of the Swin Transformer suitable for processing lip reading data and present the SwinLip visual speech encoder, which efficiently reduces computational load by integrating modified Convolution-augmented Transformer (Conformer) temporal embeddings with conventional spatial embeddings in the hierarchical structure. Through extensive experiments, we have validated that our SwinLip successfully improves the performance and inference speed of the lip reading network when applied to various backbones for word and sentence recognition, reducing computational load. In particular, our SwinLip demonstrated robust performance in both English LRW and Mandarin LRW-1000 datasets and achieved state-of-the-art performance on the Mandarin LRW-1000 dataset with less computation compared to the existing state-of-the-art model.
Separate and Reconstruct: Asymmetric Encoder-Decoder for Speech Separation
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Since the success of a time-domain speech separation, further improvements have been made by expanding the length and channel of a feature sequence to increase the amount of computation. When temporally expanded to a long sequence, the feature is segmented into chunks as a dual-path model in most studies of speech separation. In particular, it is common for the process of separating features corresponding to each speaker to be located in the final stage of the network. However, it is more advantageous and intuitive to proactively expand the feature sequence to include the number of speakers as an extra dimension. In this paper, we present an asymmetric strategy in which the encoder and decoder are partitioned to perform distinct processing in separation tasks. The encoder analyzes features, and the output of the encoder is split into the number of speakers to be separated. The separated sequences are then reconstructed by the weight-shared decoder, as Siamese network, in addition to cross-speaker processing. By using the Siamese network in the decoder, without using speaker information, the network directly learns to discriminate the features using a separation objective. With a common split layer, intermediate encoder features for skip connections are also split for the reconstruction decoder based on the U-Net structure. In addition, instead of segmenting the feature into chunks as dual-path, we design global and local Transformer blocks to directly process long sequences. The experimental results demonstrated that this separation-and-reconstruction framework is effective and that the combination of proposed global and local Transformer can sufficiently replace the role of inter- and intra-chunk processing in dual-path structure. Finally, the presented model including both of these achieved state-of-the-art performance with less computation than before in various benchmark datasets.
NeXt-TDNN: Modernizing Multi-Scale Temporal Convolution Backbone for Speaker Verification
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:In speaker verification, ECAPA-TDNN has shown remarkable improvement by utilizing one-dimensional(1D) Res2Net block and squeeze-and-excitation(SE) module, along with multi-layer feature aggregation (MFA). Meanwhile, in vision tasks, ConvNet structures have been modernized by referring to Transformer, resulting in improved performance. In this paper, we present an improved block design for TDNN in speaker verification. Inspired by recent ConvNet structures, we replace the SE-Res2Net block in ECAPA-TDNN with a novel 1D two-step multi-scale ConvNeXt block, which we call TS-ConvNeXt. The TS-ConvNeXt block is constructed using two separated sub-modules: a temporal multi-scale convolution (MSC) and a frame-wise feed-forward network (FFN). This two-step design allows for flexible capturing of inter-frame and intra-frame contexts. Additionally, we introduce global response normalization (GRN) for the FFN modules to enable more selective feature propagation, similar to the SE module in ECAPA-TDNN. Experimental results demonstrate that NeXt-TDNN, with a modernized backbone block, significantly improved performance in speaker verification tasks while reducing parameter size and inference time. We have released our code for future studies.
Statistical Beamformer Exploiting Non-stationarity and Sparsity with Spatially Constrained ICA for Robust Speech Recognition
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present a statistical beamforming algorithm as a pre-processing step for robust automatic speech recognition (ASR). By modeling the target speech as a non-stationary Laplacian distribution, a mask-based statistical beamforming algorithm is proposed to exploit both its output and masked input variance for robust estimation of the beamformer. In addition, we also present a method for steering vector estimation (SVE) based on a noise power ratio obtained from the target and noise outputs in independent component analysis (ICA). To update the beamformer in the same ICA framework, we derive ICA with distortionless and null constraints on target speech, which yields beamformed speech at the target output and noises at the other outputs, respectively. The demixing weights for the target output result in a statistical beamformer with the weighted spatial covariance matrix (wSCM) using a weighting function characterized by a source model. To enhance the SVE, the strict null constraints imposed by the Lagrange multiplier methods are relaxed by generalized penalties with weight parameters, while the strict distortionless constraints are maintained. Furthermore, we derive an online algorithm based on an optimization technique of recursive least squares (RLS) for practical applications. Experimental results on various environments using CHiME-4 and LibriCSS datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the presented algorithm compared to conventional beamforming and blind source extraction (BSE) based on ICA on both batch and online processing.
Unsupervised Speech Representation Pooling Using Vector Quantization
Apr 08, 2023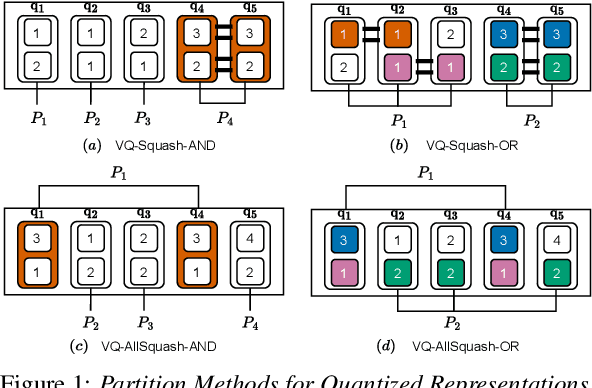
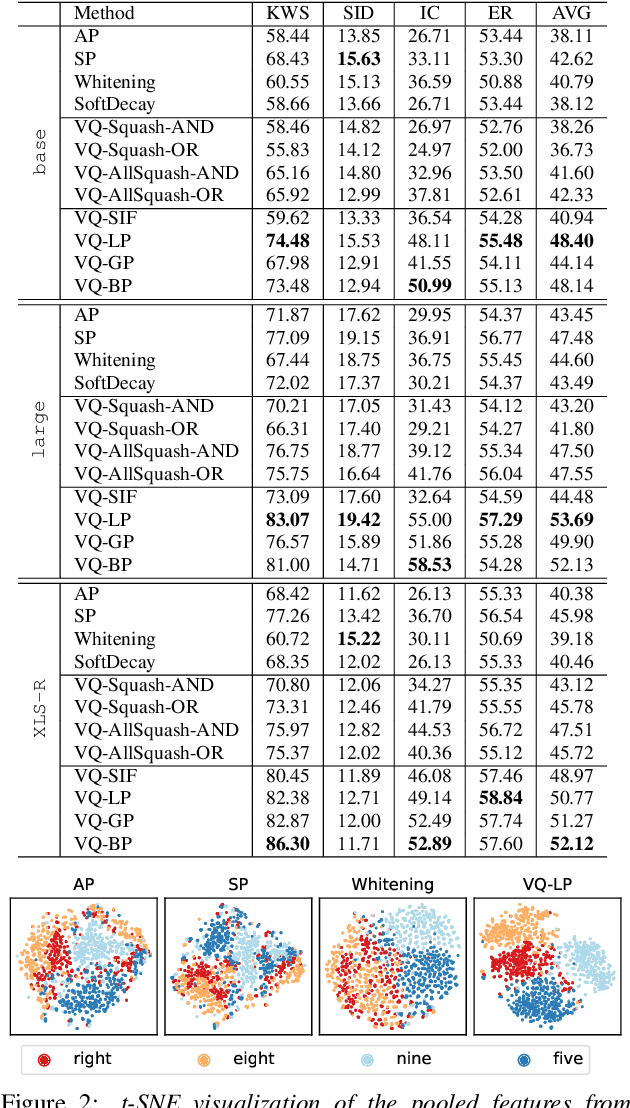
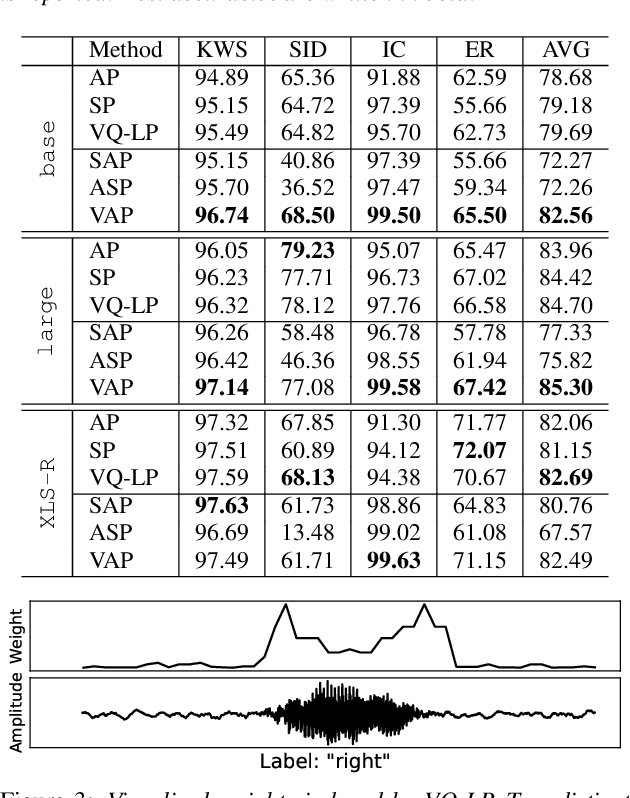
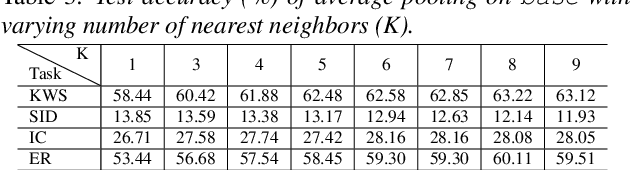
Abstract:With the advent of general-purpose speech representations from large-scale self-supervised models, applying a single model to multiple downstream tasks is becoming a de-facto approach. However, the pooling problem remains; the length of speech representations is inherently variable. The naive average pooling is often used, even though it ignores the characteristics of speech, such as differently lengthed phonemes. Hence, we design a novel pooling method to squash acoustically similar representations via vector quantization, which does not require additional training, unlike attention-based pooling. Further, we evaluate various unsupervised pooling methods on various self-supervised models. We gather diverse methods scattered around speech and text to evaluate on various tasks: keyword spotting, speaker identification, intent classification, and emotion recognition. Finally, we quantitatively and qualitatively analyze our method, comparing it with supervised pooling methods.
OLKAVS: An Open Large-Scale Korean Audio-Visual Speech Dataset
Jan 16, 2023



Abstract:Inspired by humans comprehending speech in a multi-modal manner, various audio-visual datasets have been constructed. However, most existing datasets focus on English, induce dependencies with various prediction models during dataset preparation, and have only a small number of multi-view videos. To mitigate the limitations, we recently developed the Open Large-scale Korean Audio-Visual Speech (OLKAVS) dataset, which is the largest among publicly available audio-visual speech datasets. The dataset contains 1,150 hours of transcribed audio from 1,107 Korean speakers in a studio setup with nine different viewpoints and various noise situations. We also provide the pre-trained baseline models for two tasks, audio-visual speech recognition and lip reading. We conducted experiments based on the models to verify the effectiveness of multi-modal and multi-view training over uni-modal and frontal-view-only training. We expect the OLKAVS dataset to facilitate multi-modal research in broader areas such as Korean speech recognition, speaker recognition, pronunciation level classification, and mouth motion analysis.
Distilling a Pretrained Language Model to a Multilingual ASR Model
Jun 25, 2022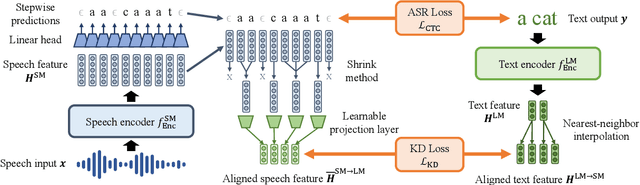
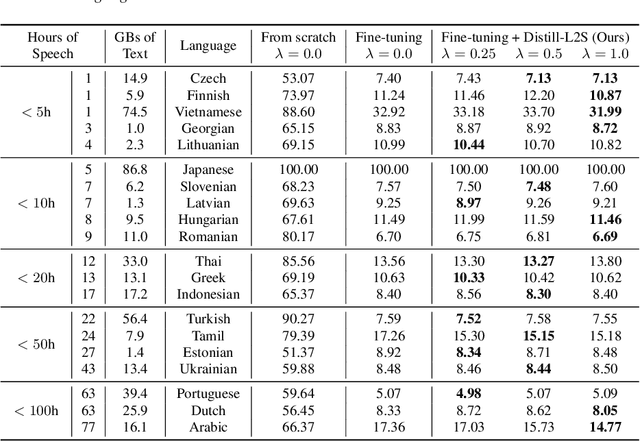
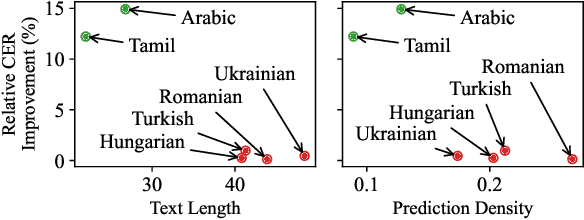
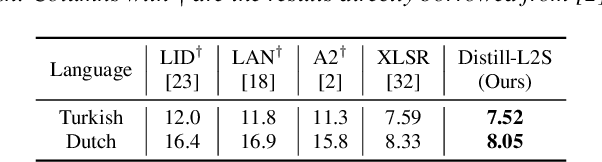
Abstract:Multilingual speech data often suffer from long-tailed language distribution, resulting in performance degradation. However, multilingual text data is much easier to obtain, yielding a more useful general language model. Hence, we are motivated to distill the rich knowledge embedded inside a well-trained teacher text model to the student speech model. We propose a novel method called the Distilling a Language model to a Speech model (Distill-L2S), which aligns the latent representations of two different modalities. The subtle differences are handled by the shrinking mechanism, nearest-neighbor interpolation, and a learnable linear projection layer. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our distillation method by applying it to the multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) task. We distill the transformer-based cross-lingual language model (InfoXLM) while fine-tuning the large-scale multilingual ASR model (XLSR-wav2vec 2.0) for each language. We show the superiority of our method on 20 low-resource languages of the CommonVoice dataset with less than 100 hours of speech data.
Unsupervised Speech Domain Adaptation Based on Disentangled Representation Learning for Robust Speech Recognition
Apr 12, 2019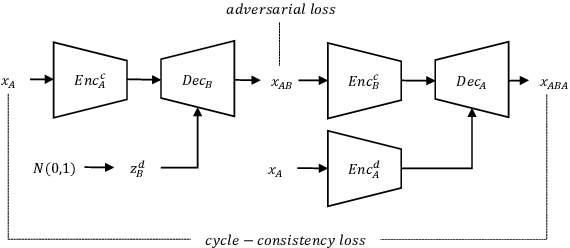
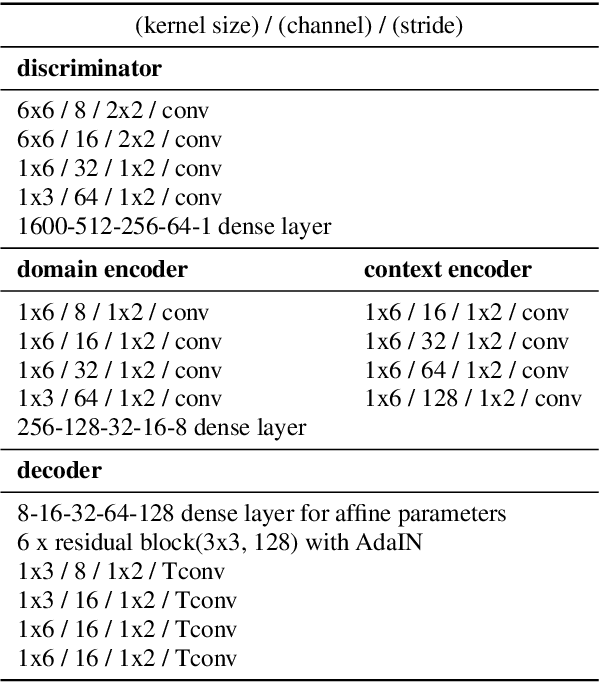
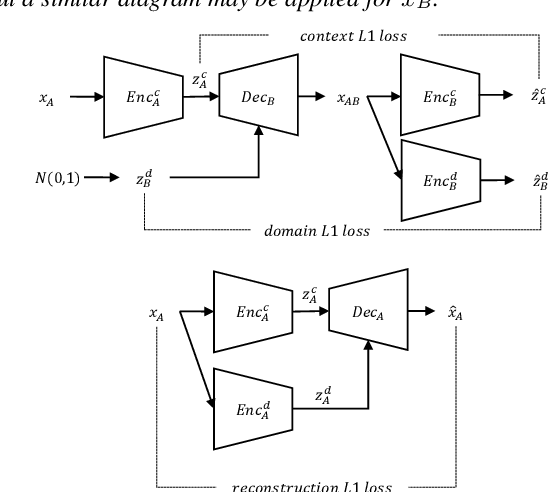
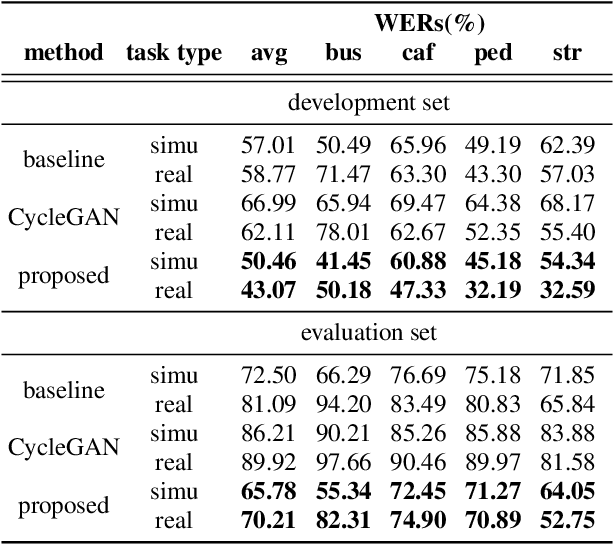
Abstract:In general, the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems is significantly degraded due to the mismatch between training and test environments. Recently, a deep-learning-based image-to-image translation technique to translate an image from a source domain to a desired domain was presented, and cycle-consistent adversarial network (CycleGAN) was applied to learn a mapping for speech-to-speech conversion from a speaker to a target speaker. However, this method might not be adequate to remove corrupting noise components for robust ASR because it was designed to convert speech itself. In this paper, we propose a domain adaptation method based on generative adversarial nets (GANs) with disentangled representation learning to achieve robustness in ASR systems. In particular, two separated encoders, context and domain encoders, are introduced to learn distinct latent variables. The latent variables allow us to convert the domain of speech according to its context and domain representation. We improved word accuracies by 6.55~15.70\% for the CHiME4 challenge corpus by applying a noisy-to-clean environment adaptation for robust ASR. In addition, similar to the method based on the CycleGAN, this method can be used for gender adaptation in gender-mismatched recognition.
BREN: Body Reflection Essence-Neuter Model for Separation of Reflection Components
Aug 25, 2015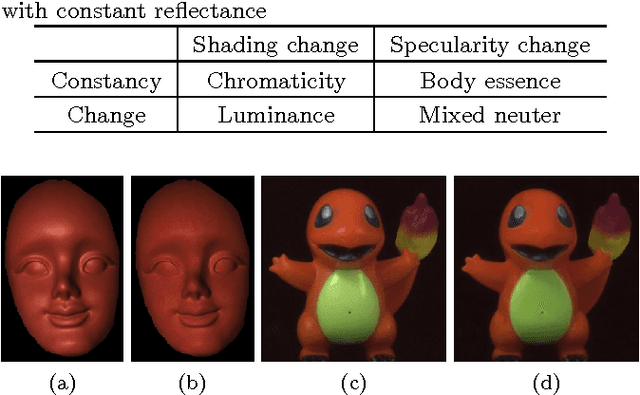
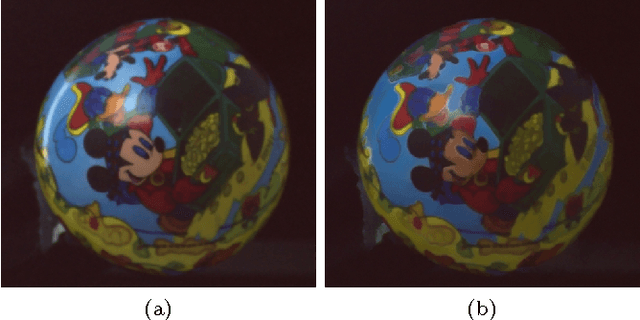

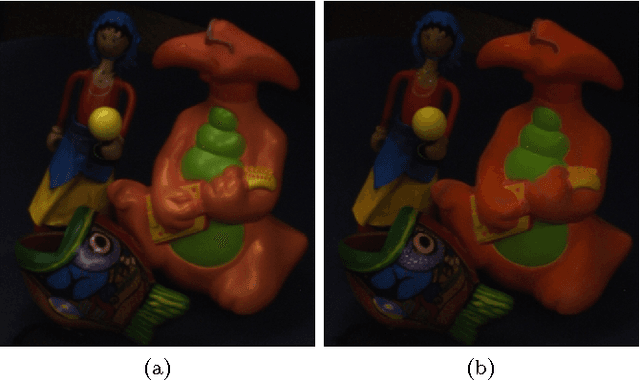
Abstract:We propose a novel reflection color model consisting of body essence and (mixed) neuter, and present an effective method for separating dichromatic reflection components using a single image. Body essence is an entity invariant to interface reflection, and has two degrees of freedom unlike hue and maximum chromaticity. As a result, the proposed method is insensitive to noise and proper for colors around CMY (cyan, magenta, and yellow) as well as RGB (red, green, and blue), contrary to the maximum chromaticity-based methods. Interface reflection is separated by using a Gaussian function, which removes a critical thresholding problem. Furthermore, the method does not require any region segmentation. Experimental results show the efficacy of the proposed model and method.
* 4 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge