Distilling a Pretrained Language Model to a Multilingual ASR Model
Paper and Code
Jun 25, 2022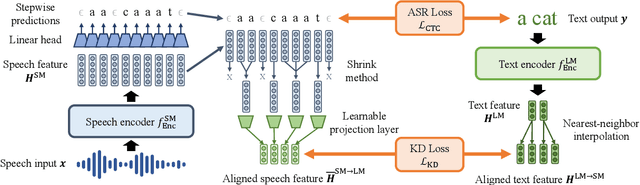
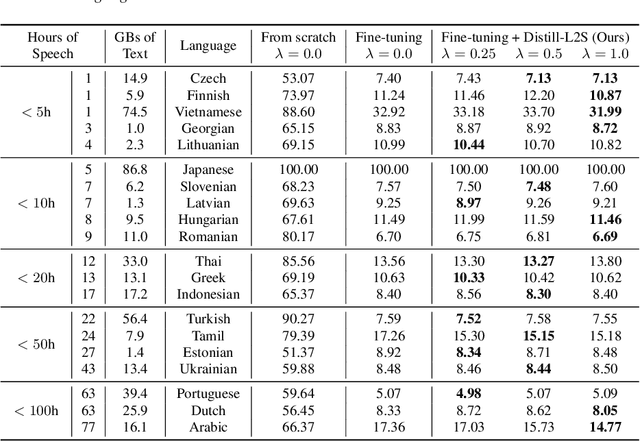
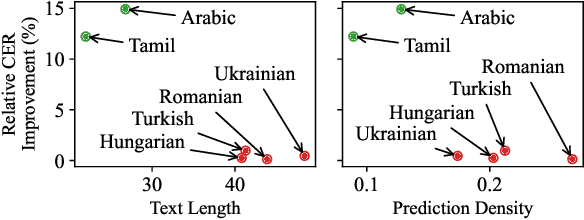
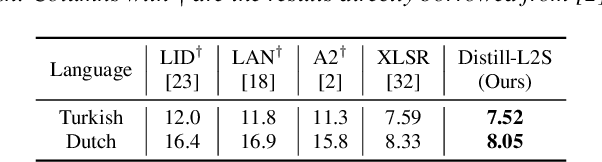
Multilingual speech data often suffer from long-tailed language distribution, resulting in performance degradation. However, multilingual text data is much easier to obtain, yielding a more useful general language model. Hence, we are motivated to distill the rich knowledge embedded inside a well-trained teacher text model to the student speech model. We propose a novel method called the Distilling a Language model to a Speech model (Distill-L2S), which aligns the latent representations of two different modalities. The subtle differences are handled by the shrinking mechanism, nearest-neighbor interpolation, and a learnable linear projection layer. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our distillation method by applying it to the multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) task. We distill the transformer-based cross-lingual language model (InfoXLM) while fine-tuning the large-scale multilingual ASR model (XLSR-wav2vec 2.0) for each language. We show the superiority of our method on 20 low-resource languages of the CommonVoice dataset with less than 100 hours of speech data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge