Hui Wen
When LLMs Meet Cybersecurity: A Systematic Literature Review
May 06, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues across various fields, including cybersecurity, which faces an ever-evolving threat landscape and need for innovative technologies. Despite initial explorations into the application of LLMs in cybersecurity, there is a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area. This paper bridge this gap by providing a systematic literature review, encompassing an analysis of over 180 works, spanning across 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream scenarios. Our comprehensive overview addresses three critical research questions: the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, LLMs' applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and further research in this area. This study aims to shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices, and serve as a valuable resource for applying LLMs in this doamin. We also maintain and regularly updated list of practical guides on LLMs for cybersecurity at https://github.com/tmylla/Awesome-LLM4Cybersecurity.
Transferring Inter-Class Correlation
Aug 11, 2020



Abstract:The Teacher-Student (T-S) framework is widely utilized in the classification tasks, through which the performance of one neural network (the student) can be improved by transferring knowledge from another trained neural network (the teacher). Since the transferring knowledge is related to the network capacities and structures between the teacher and the student, how to define efficient knowledge remains an open question. To address this issue, we design a novel transferring knowledge, the Self-Attention based Inter-Class Correlation (ICC) map in the output layer, and propose our T-S framework, Inter-Class Correlation Transfer (ICCT).
Joint RNN Model for Argument Component Boundary Detection
May 05, 2017

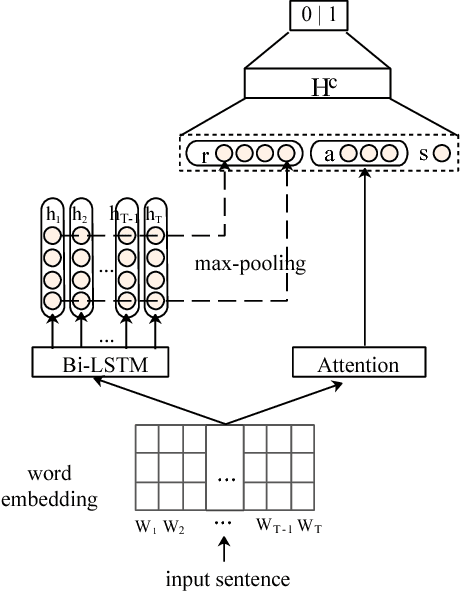
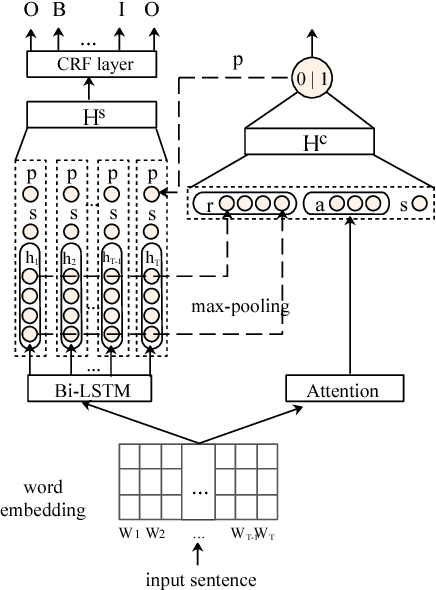
Abstract:Argument Component Boundary Detection (ACBD) is an important sub-task in argumentation mining; it aims at identifying the word sequences that constitute argument components, and is usually considered as the first sub-task in the argumentation mining pipeline. Existing ACBD methods heavily depend on task-specific knowledge, and require considerable human efforts on feature-engineering. To tackle these problems, in this work, we formulate ACBD as a sequence labeling problem and propose a variety of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) based methods, which do not use domain specific or handcrafted features beyond the relative position of the sentence in the document. In particular, we propose a novel joint RNN model that can predict whether sentences are argumentative or not, and use the predicted results to more precisely detect the argument component boundaries. We evaluate our techniques on two corpora from two different genres; results suggest that our joint RNN model obtain the state-of-the-art performance on both datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge