Haoyu Bu
When LLMs Meet Cybersecurity: A Systematic Literature Review
May 06, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues across various fields, including cybersecurity, which faces an ever-evolving threat landscape and need for innovative technologies. Despite initial explorations into the application of LLMs in cybersecurity, there is a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area. This paper bridge this gap by providing a systematic literature review, encompassing an analysis of over 180 works, spanning across 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream scenarios. Our comprehensive overview addresses three critical research questions: the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, LLMs' applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and further research in this area. This study aims to shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices, and serve as a valuable resource for applying LLMs in this doamin. We also maintain and regularly updated list of practical guides on LLMs for cybersecurity at https://github.com/tmylla/Awesome-LLM4Cybersecurity.
SeqNet: An Efficient Neural Network for Automatic Malware Detection
May 08, 2022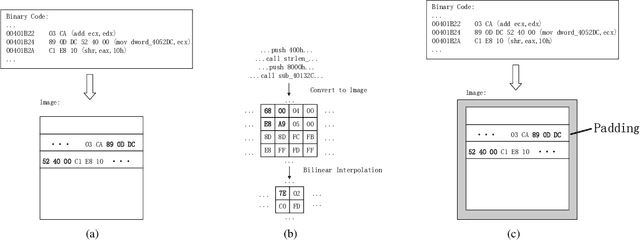

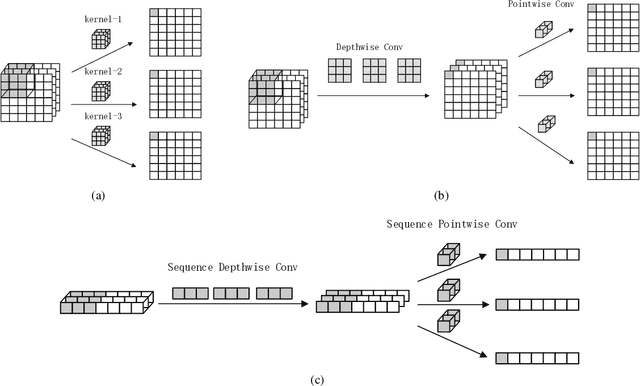
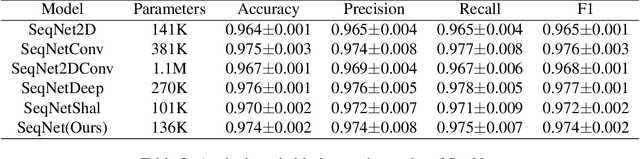
Abstract:Malware continues to evolve rapidly, and more than 450,000 new samples are captured every day, which makes manual malware analysis impractical. However, existing deep learning detection models need manual feature engineering or require high computational overhead for long training processes, which might be laborious to select feature space and difficult to retrain for mitigating model aging. Therefore, a crucial requirement for a detector is to realize automatic and efficient detection. In this paper, we propose a lightweight malware detection model called SeqNet which could be trained at high speed with low memory required on the raw binaries. By avoiding contextual confusion and reducing semantic loss, SeqNet maintains the detection accuracy when reducing the number of parameters to only 136K. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods and the low training cost requirement of SeqNet in our experiments. Besides, we make our datasets and codes public to stimulate further academic research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge