Huaxiong Wang
Towards Comprehensive and Prerequisite-Free Explainer for Graph Neural Networks
May 20, 2025Abstract:To enhance the reliability and credibility of graph neural networks (GNNs) and improve the transparency of their decision logic, a new field of explainability of GNNs (XGNN) has emerged. However, two major limitations severely degrade the performance and hinder the generalizability of existing XGNN methods: they (a) fail to capture the complete decision logic of GNNs across diverse distributions in the entire dataset's sample space, and (b) impose strict prerequisites on edge properties and GNN internal accessibility. To address these limitations, we propose OPEN, a novel c\textbf{O}mprehensive and \textbf{P}rerequisite-free \textbf{E}xplainer for G\textbf{N}Ns. OPEN, as the first work in the literature, can infer and partition the entire dataset's sample space into multiple environments, each containing graphs that follow a distinct distribution. OPEN further learns the decision logic of GNNs across different distributions by sampling subgraphs from each environment and analyzing their predictions, thus eliminating the need for strict prerequisites. Experimental results demonstrate that OPEN captures nearly complete decision logic of GNNs, outperforms state-of-the-art methods in fidelity while maintaining similar efficiency, and enhances robustness in real-world scenarios.
A Macro- and Micro-Hierarchical Transfer Learning Framework for Cross-Domain Fake News Detection
Feb 20, 2025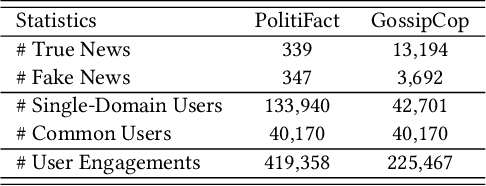
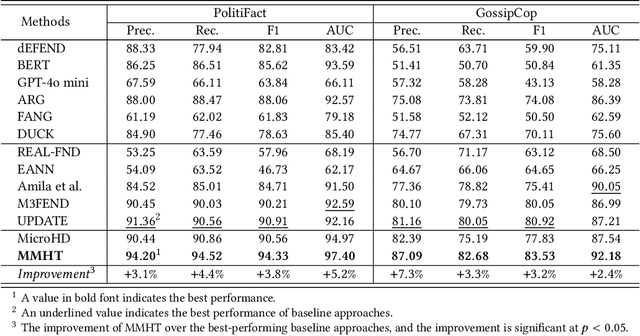
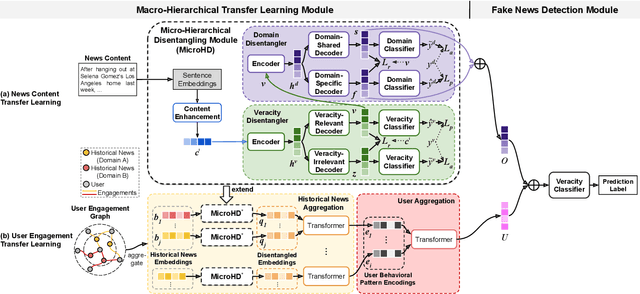
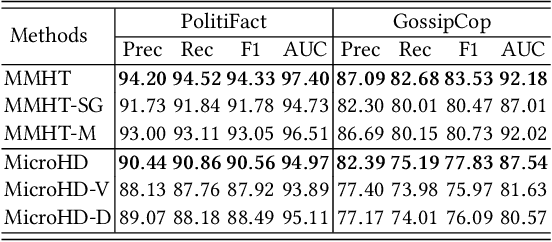
Abstract:Cross-domain fake news detection aims to mitigate domain shift and improve detection performance by transferring knowledge across domains. Existing approaches transfer knowledge based on news content and user engagements from a source domain to a target domain. However, these approaches face two main limitations, hindering effective knowledge transfer and optimal fake news detection performance. Firstly, from a micro perspective, they neglect the negative impact of veracity-irrelevant features in news content when transferring domain-shared features across domains. Secondly, from a macro perspective, existing approaches ignore the relationship between user engagement and news content, which reveals shared behaviors of common users across domains and can facilitate more effective knowledge transfer. To address these limitations, we propose a novel macro- and micro- hierarchical transfer learning framework (MMHT) for cross-domain fake news detection. Firstly, we propose a micro-hierarchical disentangling module to disentangle veracity-relevant and veracity-irrelevant features from news content in the source domain for improving fake news detection performance in the target domain. Secondly, we propose a macro-hierarchical transfer learning module to generate engagement features based on common users' shared behaviors in different domains for improving effectiveness of knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.
Protecting Big Data Privacy Using Randomized Tensor Network Decomposition and Dispersed Tensor Computation
Jan 04, 2021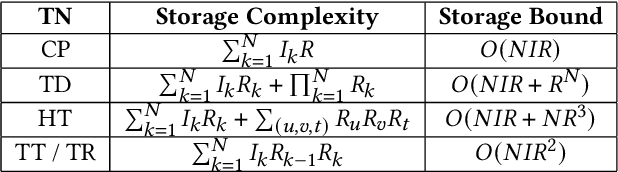
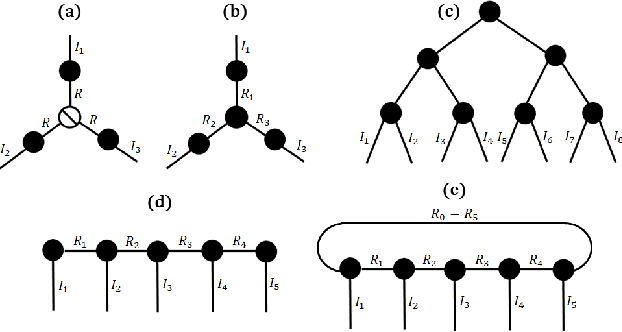
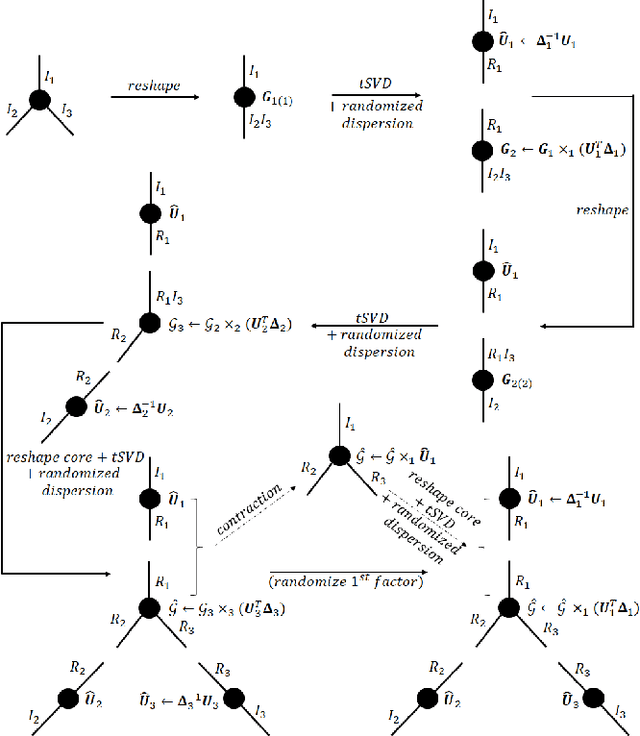
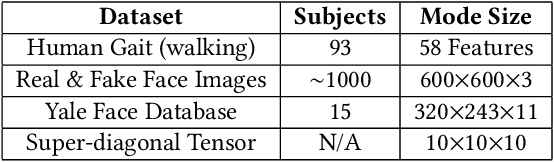
Abstract:Data privacy is an important issue for organizations and enterprises to securely outsource data storage, sharing, and computation on clouds / fogs. However, data encryption is complicated in terms of the key management and distribution; existing secure computation techniques are expensive in terms of computational / communication cost and therefore do not scale to big data computation. Tensor network decomposition and distributed tensor computation have been widely used in signal processing and machine learning for dimensionality reduction and large-scale optimization. However, the potential of distributed tensor networks for big data privacy preservation have not been considered before, this motivates the current study. Our primary intuition is that tensor network representations are mathematically non-unique, unlinkable, and uninterpretable; tensor network representations naturally support a range of multilinear operations for compressed and distributed / dispersed computation. Therefore, we propose randomized algorithms to decompose big data into randomized tensor network representations and analyze the privacy leakage for 1D to 3D data tensors. The randomness mainly comes from the complex structural information commonly found in big data; randomization is based on controlled perturbation applied to the tensor blocks prior to decomposition. The distributed tensor representations are dispersed on multiple clouds / fogs or servers / devices with metadata privacy, this provides both distributed trust and management to seamlessly secure big data storage, communication, sharing, and computation. Experiments show that the proposed randomization techniques are helpful for big data anonymization and efficient for big data storage and computation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge