Huaxiaoyue Wang
PRISM: Learning Design Knowledge from Data for Stylistic Design Improvement
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Graphic design often involves exploring different stylistic directions, which can be time-consuming for non-experts. We address this problem of stylistically improving designs based on natural language instructions. While VLMs have shown initial success in graphic design, their pretrained knowledge on styles is often too general and misaligned with specific domain data. For example, VLMs may associate minimalism with abstract designs, whereas designers emphasize shape and color choices. Our key insight is to leverage design data -- a collection of real-world designs that implicitly capture designer's principles -- to learn design knowledge and guide stylistic improvement. We propose PRISM (PRior-Informed Stylistic Modification) that constructs and applies a design knowledge base through three stages: (1) clustering high-variance designs to capture diversity within a style, (2) summarizing each cluster into actionable design knowledge, and (3) retrieving relevant knowledge during inference to enable style-aware improvement. Experiments on the Crello dataset show that PRISM achieves the highest average rank of 1.49 (closer to 1 is better) over baselines in style alignment. User studies further validate these results, showing that PRISM is consistently preferred by designers.
Imitation Learning from a Single Temporally Misaligned Video
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:We examine the problem of learning sequential tasks from a single visual demonstration. A key challenge arises when demonstrations are temporally misaligned due to variations in timing, differences in embodiment, or inconsistencies in execution. Existing approaches treat imitation as a distribution-matching problem, aligning individual frames between the agent and the demonstration. However, we show that such frame-level matching fails to enforce temporal ordering or ensure consistent progress. Our key insight is that matching should instead be defined at the level of sequences. We propose that perfect matching occurs when one sequence successfully covers all the subgoals in the same order as the other sequence. We present ORCA (ORdered Coverage Alignment), a dense per-timestep reward function that measures the probability of the agent covering demonstration frames in the correct order. On temporally misaligned demonstrations, we show that agents trained with the ORCA reward achieve $4.5$x improvement ($0.11 \rightarrow 0.50$ average normalized returns) for Meta-world tasks and $6.6$x improvement ($6.55 \rightarrow 43.3$ average returns) for Humanoid-v4 tasks compared to the best frame-level matching algorithms. We also provide empirical analysis showing that ORCA is robust to varying levels of temporal misalignment. Our code is available at https://github.com/portal-cornell/orca/
APRICOT: Active Preference Learning and Constraint-Aware Task Planning with LLMs
Oct 25, 2024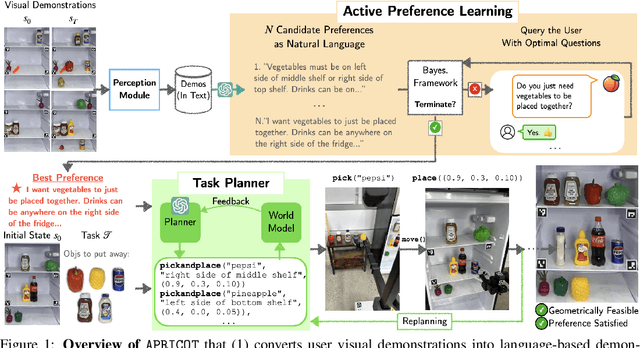
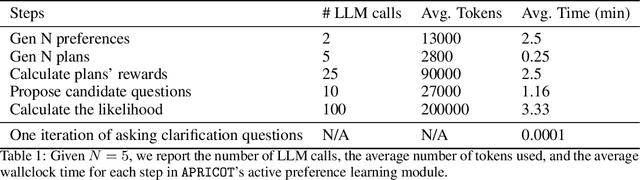
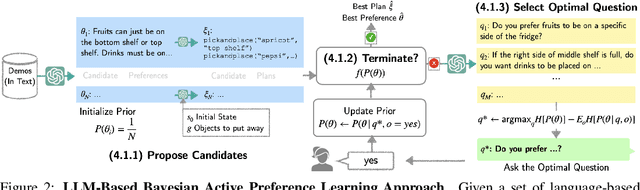
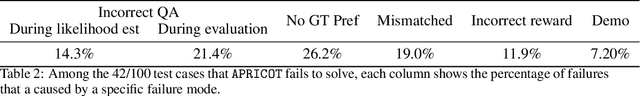
Abstract:Home robots performing personalized tasks must adeptly balance user preferences with environmental affordances. We focus on organization tasks within constrained spaces, such as arranging items into a refrigerator, where preferences for placement collide with physical limitations. The robot must infer user preferences based on a small set of demonstrations, which is easier for users to provide than extensively defining all their requirements. While recent works use Large Language Models (LLMs) to learn preferences from user demonstrations, they encounter two fundamental challenges. First, there is inherent ambiguity in interpreting user actions, as multiple preferences can often explain a single observed behavior. Second, not all user preferences are practically feasible due to geometric constraints in the environment. To address these challenges, we introduce APRICOT, a novel approach that merges LLM-based Bayesian active preference learning with constraint-aware task planning. APRICOT refines its generated preferences by actively querying the user and dynamically adapts its plan to respect environmental constraints. We evaluate APRICOT on a dataset of diverse organization tasks and demonstrate its effectiveness in real-world scenarios, showing significant improvements in both preference satisfaction and plan feasibility. The project website is at https://portal-cornell.github.io/apricot/
MOSAIC: A Modular System for Assistive and Interactive Cooking
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:We present MOSAIC, a modular architecture for home robots to perform complex collaborative tasks, such as cooking with everyday users. MOSAIC tightly collaborates with humans, interacts with users using natural language, coordinates multiple robots, and manages an open vocabulary of everyday objects. At its core, MOSAIC employs modularity: it leverages multiple large-scale pre-trained models for general tasks like language and image recognition, while using streamlined modules designed for task-specific control. We extensively evaluate MOSAIC on 60 end-to-end trials where two robots collaborate with a human user to cook a combination of 6 recipes. We also extensively test individual modules with 180 episodes of visuomotor picking, 60 episodes of human motion forecasting, and 46 online user evaluations of the task planner. We show that MOSAIC is able to efficiently collaborate with humans by running the overall system end-to-end with a real human user, completing 68.3% (41/60) collaborative cooking trials of 6 different recipes with a subtask completion rate of 91.6%. Finally, we discuss the limitations of the current system and exciting open challenges in this domain. The project's website is at https://portal-cornell.github.io/MOSAIC/
Demo2Code: From Summarizing Demonstrations to Synthesizing Code via Extended Chain-of-Thought
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Language instructions and demonstrations are two natural ways for users to teach robots personalized tasks. Recent progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) has shown impressive performance in translating language instructions into code for robotic tasks. However, translating demonstrations into task code continues to be a challenge due to the length and complexity of both demonstrations and code, making learning a direct mapping intractable. This paper presents Demo2Code, a novel framework that generates robot task code from demonstrations via an extended chain-of-thought and defines a common latent specification to connect the two. Our framework employs a robust two-stage process: (1) a recursive summarization technique that condenses demonstrations into concise specifications, and (2) a code synthesis approach that expands each function recursively from the generated specifications. We conduct extensive evaluation on various robot task benchmarks, including a novel game benchmark Robotouille, designed to simulate diverse cooking tasks in a kitchen environment. The project's website is available at https://portal-cornell.github.io/demo2code-webpage
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge