Hsin-Wei Wang
Enhancing Code-Switching ASR Leveraging Non-Peaky CTC Loss and Deep Language Posterior Injection
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Code-switching-where multilingual speakers alternately switch between languages during conversations-still poses significant challenges to end-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems due to phenomena of both acoustic and semantic confusion. This issue arises because ASR systems struggle to handle the rapid alternation of languages effectively, which often leads to significant performance degradation. Our main contributions are at least threefold: First, we incorporate language identification (LID) information into several intermediate layers of the encoder, aiming to enrich output embeddings with more detailed language information. Secondly, through the novel application of language boundary alignment loss, the subsequent ASR modules are enabled to more effectively utilize the knowledge of internal language posteriors. Third, we explore the feasibility of using language posteriors to facilitate deep interaction between shared encoder and language-specific encoders. Through comprehensive experiments on the SEAME corpus, we have verified that our proposed method outperforms the prior-art method, disentangle based mixture-of-experts (D-MoE), further enhancing the acuity of the encoder to languages.
An Effective Context-Balanced Adaptation Approach for Long-Tailed Speech Recognition
Sep 10, 2024


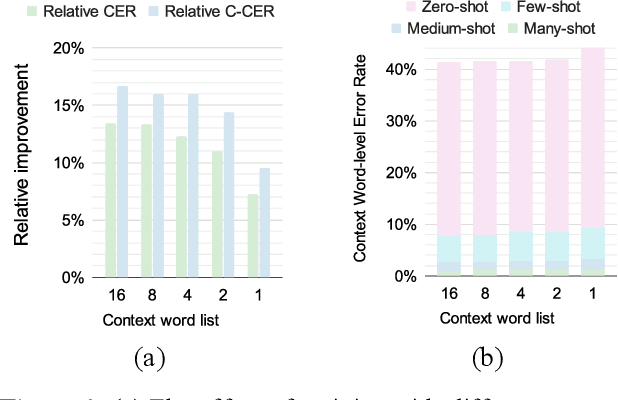
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) models have become standard practice for various commercial applications. However, in real-world scenarios, the long-tailed nature of word distribution often leads E2E ASR models to perform well on common words but fall short in recognizing uncommon ones. Recently, the notion of a contextual adapter (CA) was proposed to infuse external knowledge represented by a context word list into E2E ASR models. Although CA can improve recognition performance on rare words, two crucial data imbalance problems remain. First, when using low-frequency words as context words during training, since these words rarely occur in the utterance, CA becomes prone to overfit on attending to the <no-context> token due to higher-frequency words not being present in the context list. Second, the long-tailed distribution within the context list itself still causes the model to perform poorly on low-frequency context words. In light of this, we explore in-depth the impact of altering the context list to have words with different frequency distributions on model performance, and meanwhile extend CA with a simple yet effective context-balanced learning objective. A series of experiments conducted on the AISHELL-1 benchmark dataset suggests that using all vocabulary words from the training corpus as the context list and pairing them with our balanced objective yields the best performance, demonstrating a significant reduction in character error rate (CER) by up to 1.21% and a more pronounced 9.44% reduction in the error rate of zero-shot words.
ConPCO: Preserving Phoneme Characteristics for Automatic Pronunciation Assessment Leveraging Contrastive Ordinal Regularization
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Automatic pronunciation assessment (APA) manages to evaluate the pronunciation proficiency of a second language (L2) learner in a target language. Existing efforts typically draw on regression models for proficiency score prediction, where the models are trained to estimate target values without explicitly accounting for phoneme-awareness in the feature space. In this paper, we propose a contrastive phonemic ordinal regularizer (ConPCO) tailored for regression-based APA models to generate more phoneme-discriminative features while considering the ordinal relationships among the regression targets. The proposed ConPCO first aligns the phoneme representations of an APA model and textual embeddings of phonetic transcriptions via contrastive learning. Afterward, the phoneme characteristics are retained by regulating the distances between inter- and intra-phoneme categories in the feature space while allowing for the ordinal relationships among the output targets. We further design and develop a hierarchical APA model to evaluate the effectiveness of our method. Extensive experiments conducted on the speechocean762 benchmark dataset suggest the feasibility and efficacy of our approach in relation to some cutting-edge baselines.
DANCER: Entity Description Augmented Named Entity Corrector for Automatic Speech Recognition
Apr 11, 2024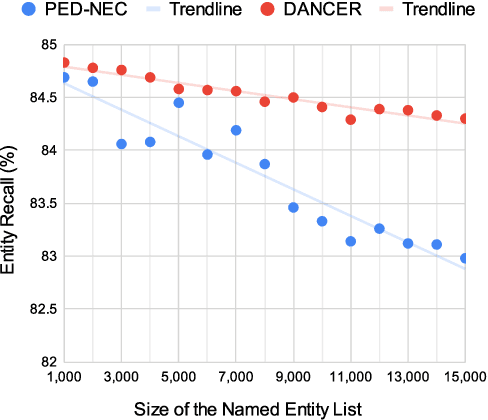
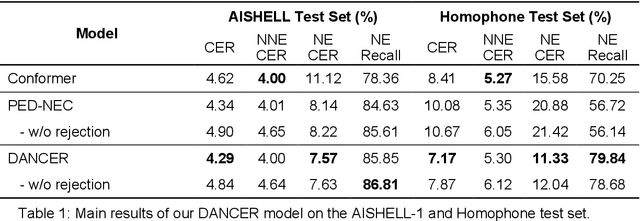
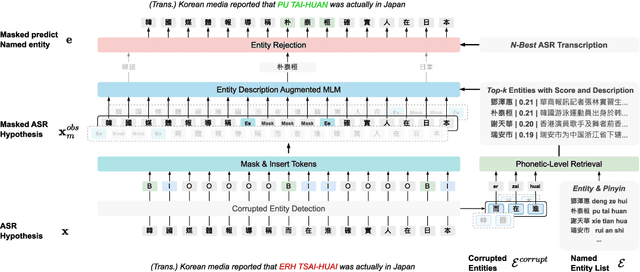
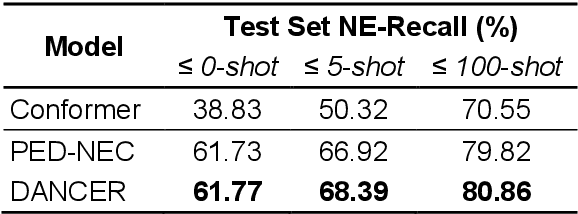
Abstract:End-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E ASR) systems often suffer from mistranscription of domain-specific phrases, such as named entities, sometimes leading to catastrophic failures in downstream tasks. A family of fast and lightweight named entity correction (NEC) models for ASR have recently been proposed, which normally build on phonetic-level edit distance algorithms and have shown impressive NEC performance. However, as the named entity (NE) list grows, the problems of phonetic confusion in the NE list are exacerbated; for example, homophone ambiguities increase substantially. In view of this, we proposed a novel Description Augmented Named entity CorrEctoR (dubbed DANCER), which leverages entity descriptions to provide additional information to facilitate mitigation of phonetic confusion for NEC on ASR transcription. To this end, an efficient entity description augmented masked language model (EDA-MLM) comprised of a dense retrieval model is introduced, enabling MLM to adapt swiftly to domain-specific entities for the NEC task. A series of experiments conducted on the AISHELL-1 and Homophone datasets confirm the effectiveness of our modeling approach. DANCER outperforms a strong baseline, the phonetic edit-distance-based NEC model (PED-NEC), by a character error rate (CER) reduction of about 7% relatively on AISHELL-1 for named entities. More notably, when tested on Homophone that contain named entities of high phonetic confusion, DANCER offers a more pronounced CER reduction of 46% relatively over PED-NEC for named entities.
An Effective Mixture-Of-Experts Approach For Code-Switching Speech Recognition Leveraging Encoder Disentanglement
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:With the massive developments of end-to-end (E2E) neural networks, recent years have witnessed unprecedented breakthroughs in automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, the codeswitching phenomenon remains a major obstacle that hinders ASR from perfection, as the lack of labeled data and the variations between languages often lead to degradation of ASR performance. In this paper, we focus exclusively on improving the acoustic encoder of E2E ASR to tackle the challenge caused by the codeswitching phenomenon. Our main contributions are threefold: First, we introduce a novel disentanglement loss to enable the lower-layer of the encoder to capture inter-lingual acoustic information while mitigating linguistic confusion at the higher-layer of the encoder. Second, through comprehensive experiments, we verify that our proposed method outperforms the prior-art methods using pretrained dual-encoders, meanwhile having access only to the codeswitching corpus and consuming half of the parameterization. Third, the apparent differentiation of the encoders' output features also corroborates the complementarity between the disentanglement loss and the mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture.
Leveraging Language ID to Calculate Intermediate CTC Loss for Enhanced Code-Switching Speech Recognition
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:In recent years, end-to-end speech recognition has emerged as a technology that integrates the acoustic, pronunciation dictionary, and language model components of the traditional Automatic Speech Recognition model. It is possible to achieve human-like recognition without the need to build a pronunciation dictionary in advance. However, due to the relative scarcity of training data on code-switching, the performance of ASR models tends to degrade drastically when encountering this phenomenon. Most past studies have simplified the learning complexity of the model by splitting the code-switching task into multiple tasks dealing with a single language and then learning the domain-specific knowledge of each language separately. Therefore, in this paper, we attempt to introduce language identification information into the middle layer of the ASR model's encoder. We aim to generate acoustic features that imply language distinctions in a more implicit way, reducing the model's confusion when dealing with language switching.
Preserving Phonemic Distinctions for Ordinal Regression: A Novel Loss Function for Automatic Pronunciation Assessment
Oct 04, 2023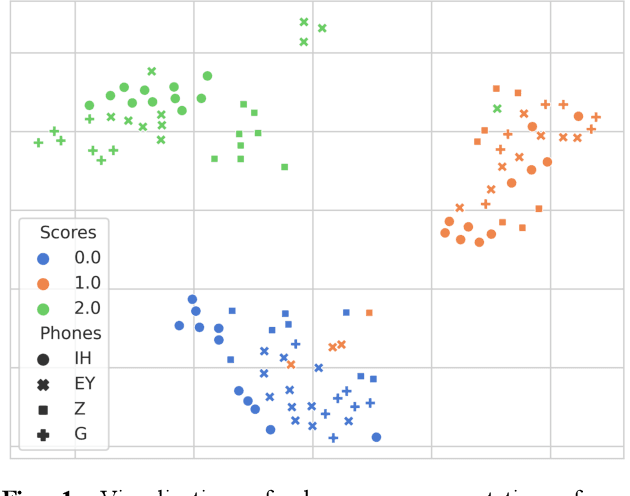
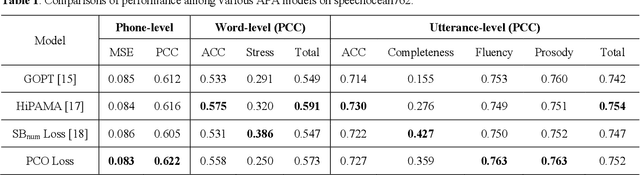
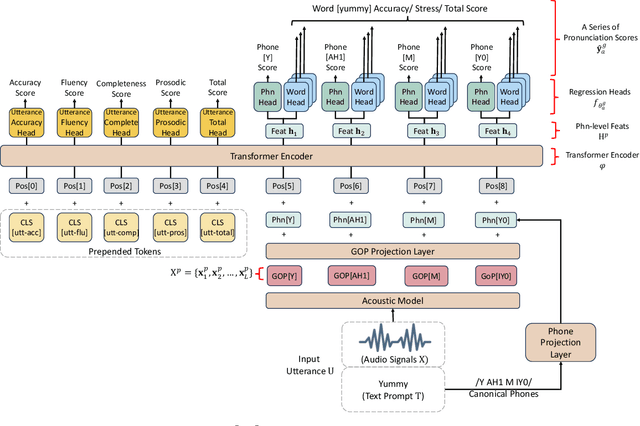
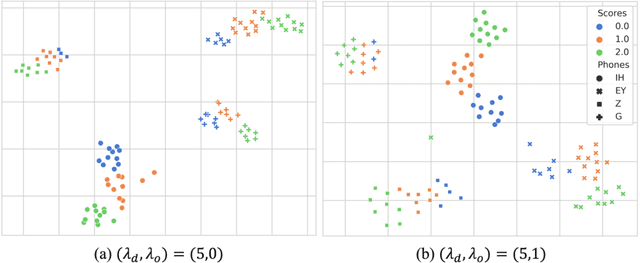
Abstract:Automatic pronunciation assessment (APA) manages to quantify the pronunciation proficiency of a second language (L2) learner in a language. Prevailing approaches to APA normally leverage neural models trained with a regression loss function, such as the mean-squared error (MSE) loss, for proficiency level prediction. Despite most regression models can effectively capture the ordinality of proficiency levels in the feature space, they are confronted with a primary obstacle that different phoneme categories with the same proficiency level are inevitably forced to be close to each other, retaining less phoneme-discriminative information. On account of this, we devise a phonemic contrast ordinal (PCO) loss for training regression-based APA models, which aims to preserve better phonemic distinctions between phoneme categories meanwhile considering ordinal relationships of the regression target output. Specifically, we introduce a phoneme-distinct regularizer into the MSE loss, which encourages feature representations of different phoneme categories to be far apart while simultaneously pulling closer the representations belonging to the same phoneme category by means of weighted distances. An extensive set of experiments carried out on the speechocean762 benchmark dataset suggest the feasibility and effectiveness of our model in relation to some existing state-of-the-art models.
AVATAR: Robust Voice Search Engine Leveraging Autoregressive Document Retrieval and Contrastive Learning
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Voice, as input, has progressively become popular on mobiles and seems to transcend almost entirely text input. Through voice, the voice search (VS) system can provide a more natural way to meet user's information needs. However, errors from the automatic speech recognition (ASR) system can be catastrophic to the VS system. Building on the recent advanced lightweight autoregressive retrieval model, which has the potential to be deployed on mobiles, leading to a more secure and personal VS assistant. This paper presents a novel study of VS leveraging autoregressive retrieval and tackles the crucial problems facing VS, viz. the performance drop caused by ASR noise, via data augmentations and contrastive learning, showing how explicit and implicit modeling the noise patterns can alleviate the problems. A series of experiments conducted on the Open-Domain Question Answering (ODSQA) confirm our approach's effectiveness and robustness in relation to some strong baseline systems.
Conversational speech recognition leveraging effective fusion methods for cross-utterance language modeling
Nov 05, 2021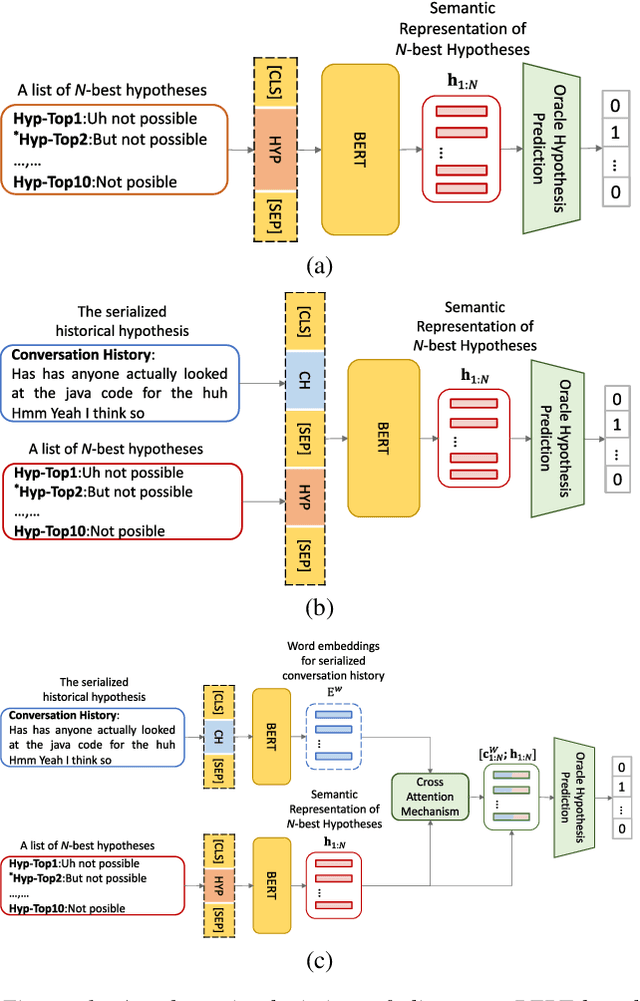
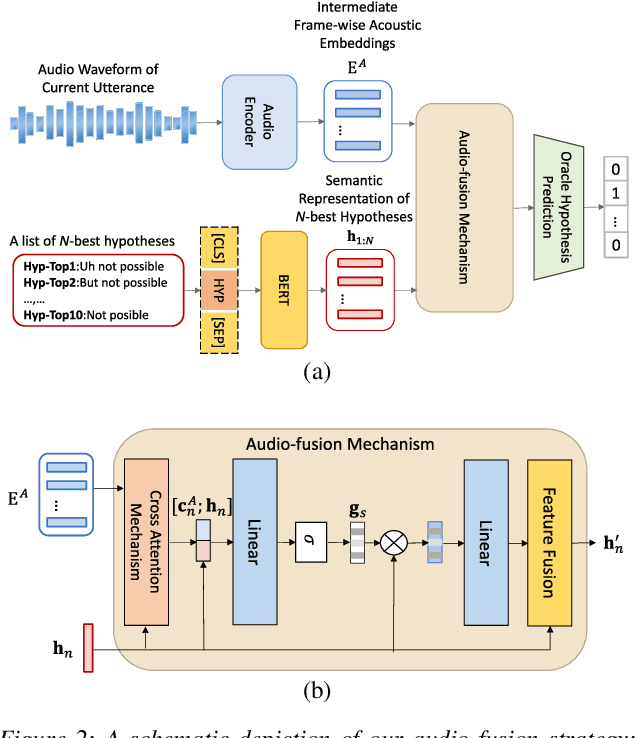

Abstract:Conversational speech normally is embodied with loose syntactic structures at the utterance level but simultaneously exhibits topical coherence relations across consecutive utterances. Prior work has shown that capturing longer context information with a recurrent neural network or long short-term memory language model (LM) may suffer from the recent bias while excluding the long-range context. In order to capture the long-term semantic interactions among words and across utterances, we put forward disparate conversation history fusion methods for language modeling in automatic speech recognition (ASR) of conversational speech. Furthermore, a novel audio-fusion mechanism is introduced, which manages to fuse and utilize the acoustic embeddings of a current utterance and the semantic content of its corresponding conversation history in a cooperative way. To flesh out our ideas, we frame the ASR N-best hypothesis rescoring task as a prediction problem, leveraging BERT, an iconic pre-trained LM, as the ingredient vehicle to facilitate selection of the oracle hypothesis from a given N-best hypothesis list. Empirical experiments conducted on the AMI benchmark dataset seem to demonstrate the feasibility and efficacy of our methods in relation to some current top-of-line methods.
Exploring Non-Autoregressive End-To-End Neural Modeling For English Mispronunciation Detection And Diagnosis
Nov 01, 2021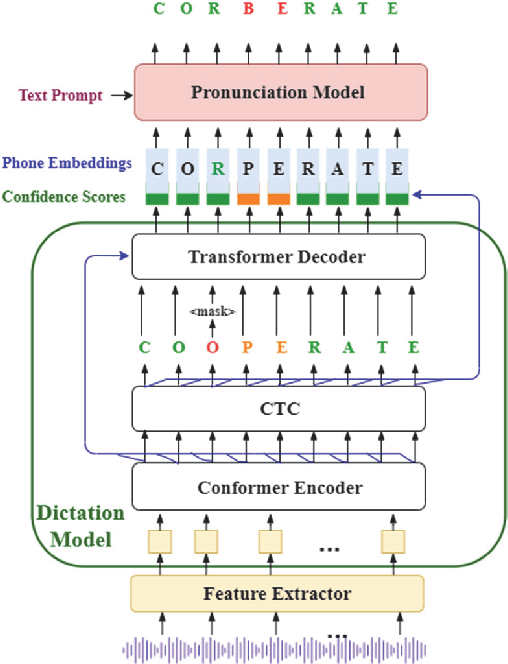
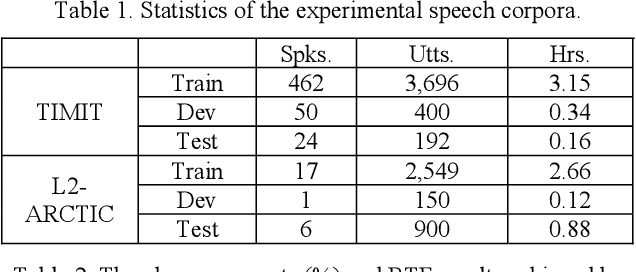
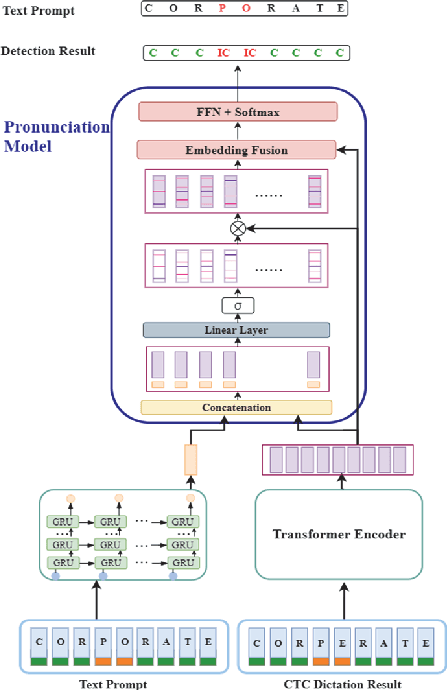
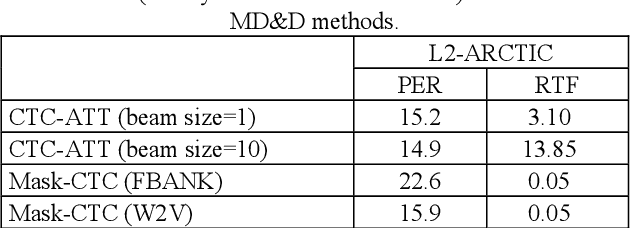
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) neural modeling has emerged as one predominant school of thought to develop computer-assisted language training (CAPT) systems, showing competitive performance to conventional pronunciation-scoring based methods. However, current E2E neural methods for CAPT are faced with at least two pivotal challenges. On one hand, most of the E2E methods operate in an autoregressive manner with left-to-right beam search to dictate the pronunciations of an L2 learners. This however leads to very slow inference speed, which inevitably hinders their practical use. On the other hand, E2E neural methods are normally data greedy and meanwhile an insufficient amount of nonnative training data would often reduce their efficacy on mispronunciation detection and diagnosis (MD&D). In response, we put forward a novel MD&D method that leverages non-autoregressive (NAR) E2E neural modeling to dramatically speed up the inference time while maintaining performance in line with the conventional E2E neural methods. In addition, we design and develop a pronunciation modeling network stacked on top of the NAR E2E models of our method to further boost the effectiveness of MD&D. Empirical experiments conducted on the L2-ARCTIC English dataset seems to validate the feasibility of our method, in comparison to some top-of-the-line E2E models and an iconic pronunciation-scoring based method built on a DNN-HMM acoustic model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge