Hsuan-Sheng Chiu
Conversational speech recognition leveraging effective fusion methods for cross-utterance language modeling
Nov 05, 2021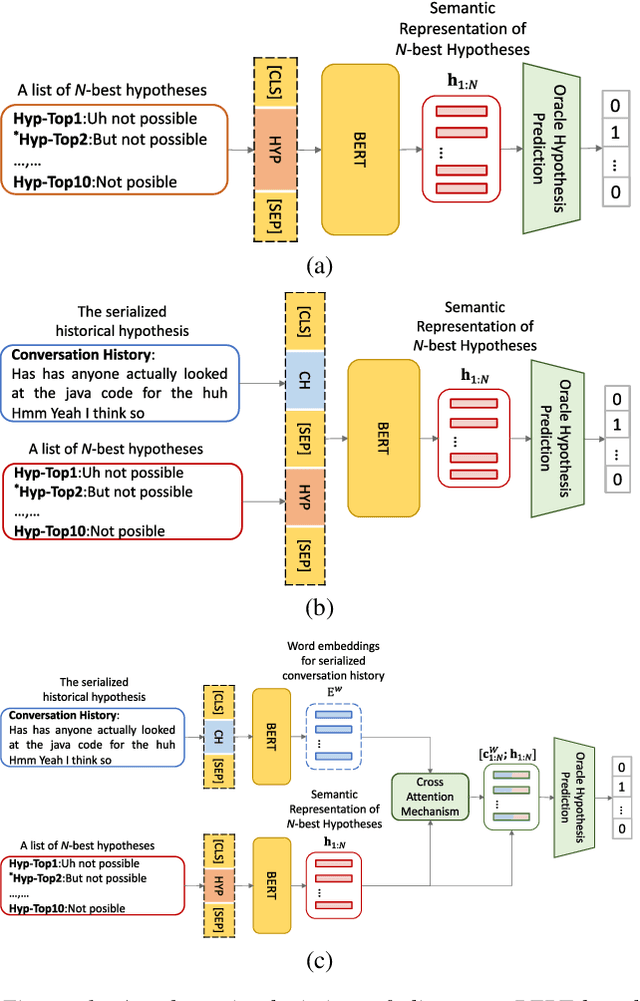
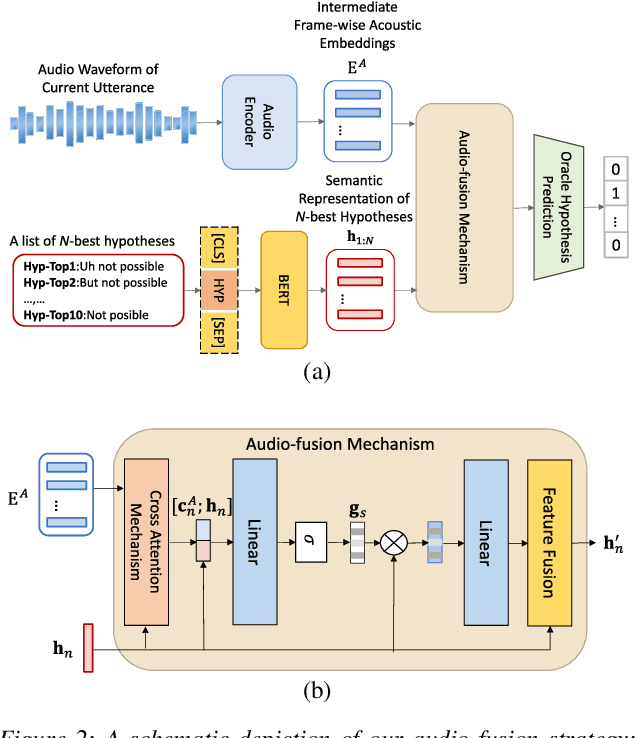

Abstract:Conversational speech normally is embodied with loose syntactic structures at the utterance level but simultaneously exhibits topical coherence relations across consecutive utterances. Prior work has shown that capturing longer context information with a recurrent neural network or long short-term memory language model (LM) may suffer from the recent bias while excluding the long-range context. In order to capture the long-term semantic interactions among words and across utterances, we put forward disparate conversation history fusion methods for language modeling in automatic speech recognition (ASR) of conversational speech. Furthermore, a novel audio-fusion mechanism is introduced, which manages to fuse and utilize the acoustic embeddings of a current utterance and the semantic content of its corresponding conversation history in a cooperative way. To flesh out our ideas, we frame the ASR N-best hypothesis rescoring task as a prediction problem, leveraging BERT, an iconic pre-trained LM, as the ingredient vehicle to facilitate selection of the oracle hypothesis from a given N-best hypothesis list. Empirical experiments conducted on the AMI benchmark dataset seem to demonstrate the feasibility and efficacy of our methods in relation to some current top-of-line methods.
Exploring Non-Autoregressive End-To-End Neural Modeling For English Mispronunciation Detection And Diagnosis
Nov 01, 2021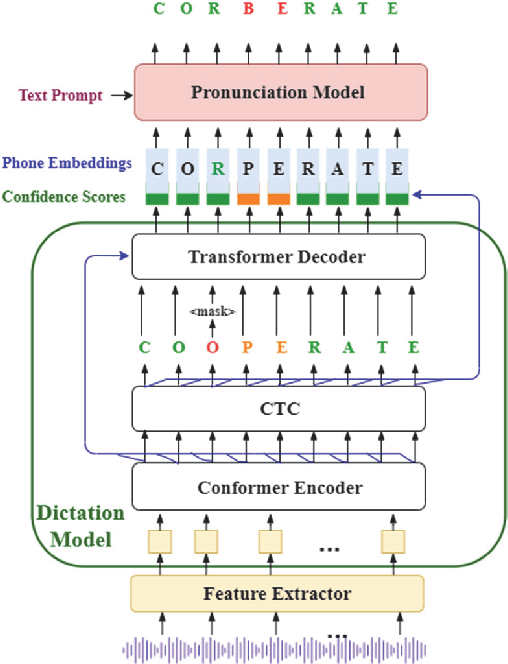
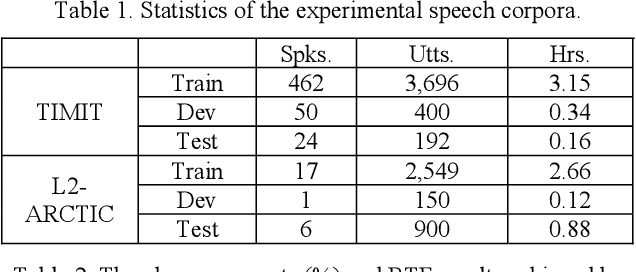
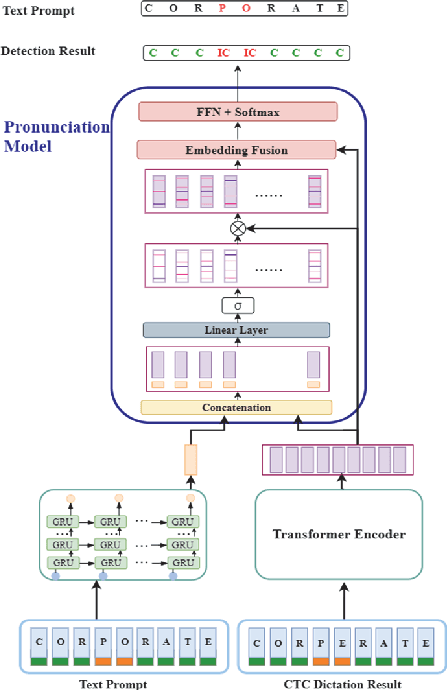
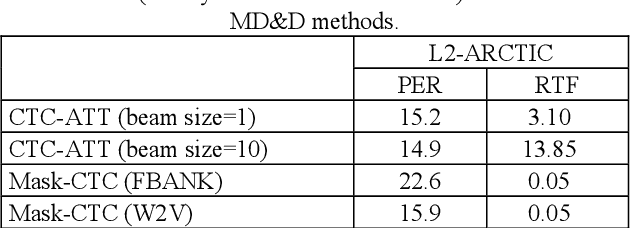
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) neural modeling has emerged as one predominant school of thought to develop computer-assisted language training (CAPT) systems, showing competitive performance to conventional pronunciation-scoring based methods. However, current E2E neural methods for CAPT are faced with at least two pivotal challenges. On one hand, most of the E2E methods operate in an autoregressive manner with left-to-right beam search to dictate the pronunciations of an L2 learners. This however leads to very slow inference speed, which inevitably hinders their practical use. On the other hand, E2E neural methods are normally data greedy and meanwhile an insufficient amount of nonnative training data would often reduce their efficacy on mispronunciation detection and diagnosis (MD&D). In response, we put forward a novel MD&D method that leverages non-autoregressive (NAR) E2E neural modeling to dramatically speed up the inference time while maintaining performance in line with the conventional E2E neural methods. In addition, we design and develop a pronunciation modeling network stacked on top of the NAR E2E models of our method to further boost the effectiveness of MD&D. Empirical experiments conducted on the L2-ARCTIC English dataset seems to validate the feasibility of our method, in comparison to some top-of-the-line E2E models and an iconic pronunciation-scoring based method built on a DNN-HMM acoustic model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge