Heinrich Schulz
Bottom-Up Instance Segmentation of Catheters for Chest X-Rays
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:Chest X-ray (CXR) is frequently employed in emergency departments and intensive care units to verify the proper placement of central lines and tubes and to rule out related complications. The automation of the X-ray reading process can be a valuable support tool for non-specialist technicians and minimize reporting delays due to non-availability of experts. While existing solutions for automated catheter segmentation and malposition detection show promising results, the disentanglement of individual catheters remains an open challenge, especially in complex cases where multiple devices appear superimposed in the X-ray projection. Moreover, conventional top-down instance segmentation methods are ineffective on such thin and long devices, that often extend through the entire image. In this paper, we propose a deep learning approach based on associative embeddings for catheter instance segmentation, able to overcome those limitations and effectively handle device intersections.
Defending against Reconstruction Attacks through Differentially Private Federated Learning for Classification of Heterogeneous Chest X-Ray Data
May 06, 2022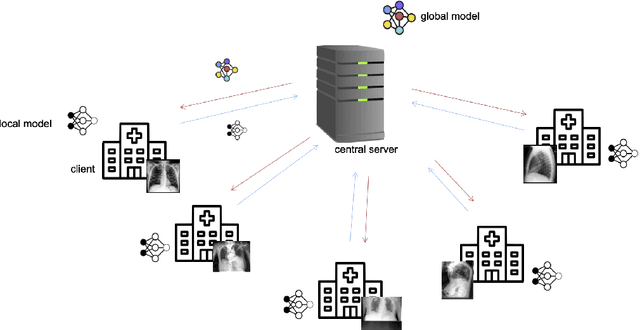
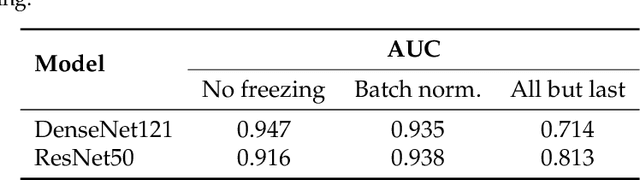
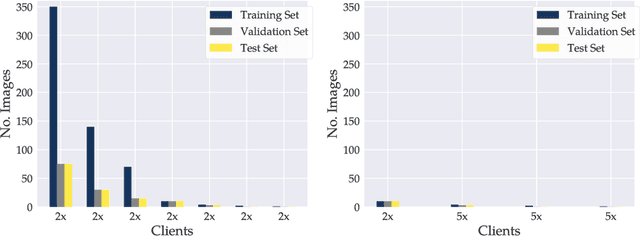
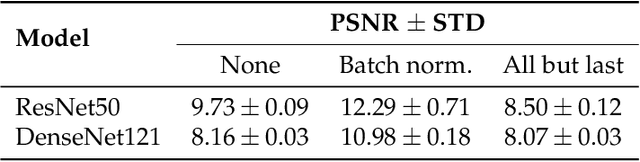
Abstract:Privacy regulations and the physical distribution of heterogeneous data are often primary concerns for the development of deep learning models in a medical context. This paper evaluates the feasibility of differentially private federated learning for chest X-ray classification as a defense against privacy attacks on DenseNet121 and ResNet50 network architectures. We simulated a federated environment by distributing images from the public CheXpert and Mendeley chest X-ray datasets unevenly among 36 clients. Both non-private baseline models achieved an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.94 on the binary classification task of detecting the presence of a medical finding. We demonstrate that both model architectures are vulnerable to privacy violation by applying image reconstruction attacks to local model updates from individual clients. The attack was particularly successful during later training stages. To mitigate the risk of privacy breach, we integrated R\'enyi differential privacy with a Gaussian noise mechanism into local model training. We evaluate model performance and attack vulnerability for privacy budgets $\epsilon \in$ {1, 3, 6, 10}. The DenseNet121 achieved the best utility-privacy trade-off with an AUC of 0.94 for $\epsilon$ = 6. Model performance deteriorated slightly for individual clients compared to the non-private baseline. The ResNet50 only reached an AUC of 0.76 in the same privacy setting. Its performance was inferior to that of the DenseNet121 for all considered privacy constraints, suggesting that the DenseNet121 architecture is more robust to differentially private training.
Tubular Shape Aware Data Generation for Semantic Segmentation in Medical Imaging
Oct 02, 2020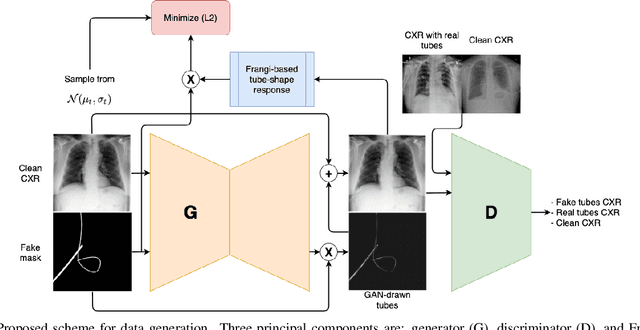
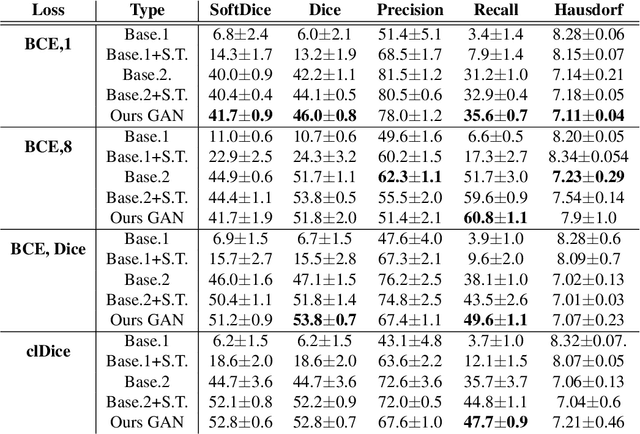
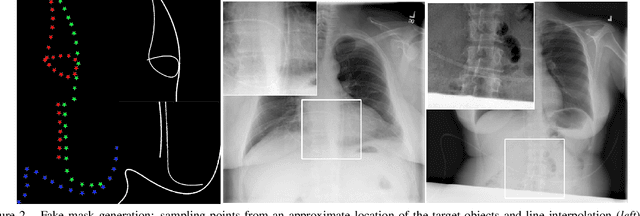
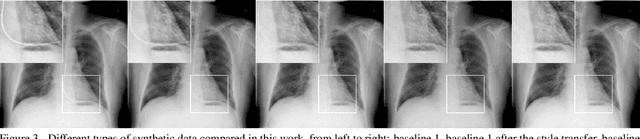
Abstract:Chest X-ray is one of the most widespread examinations of the human body. In interventional radiology, its use is frequently associated with the need to visualize various tube-like objects, such as puncture needles, guiding sheaths, wires, and catheters. Detection and precise localization of these tube-like objects in the X-ray images is, therefore, of utmost value, catalyzing the development of accurate target-specific segmentation algorithms. Similar to the other medical imaging tasks, the manual pixel-wise annotation of the tubes is a resource-consuming process. In this work, we aim to alleviate the lack of the annotated images by using artificial data. Specifically, we present an approach for synthetic data generation of the tube-shaped objects, with a generative adversarial network being regularized with a prior-shape constraint. Our method eliminates the need for paired image--mask data and requires only a weakly-labeled dataset (10--20 images) to reach the accuracy of the fully-supervised models. We report the applicability of the approach for the task of segmenting tubes and catheters in the X-ray images, whereas the results should also hold for the other imaging modalities.
Anomaly Detection with Deep Perceptual Autoencoders
Jun 23, 2020



Abstract:Anomaly detection is the problem of recognizing abnormal inputs based on the seen examples of normal data. Despite recent advances of deep learning in recognizing image anomalies, these methods still prove incapable of handling complex medical images, such as barely visible abnormalities in chest X-rays and metastases in lymph nodes. To address this problem, we introduce a new powerful method of image anomaly detection. It relies on the classical autoencoder approach with a re-designed training pipeline to handle high-resolution, complex images and a robust way of computing an image abnormality score. We revisit the very problem statement of fully unsupervised anomaly detection, where no abnormal examples at all are provided during the model setup. We propose to relax this unrealistic assumption by using a very small number of anomalies of confined variability merely to initiate the search of hyperparameters of the model. We evaluate our solution on natural image datasets with a known benchmark, as well as on two medical datasets containing radiology and digital pathology images. The proposed approach suggests a new strong baseline for image anomaly detection and outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in complex medical image analysis tasks.
Continual Learning for Domain Adaptation in Chest X-ray Classification
Jan 16, 2020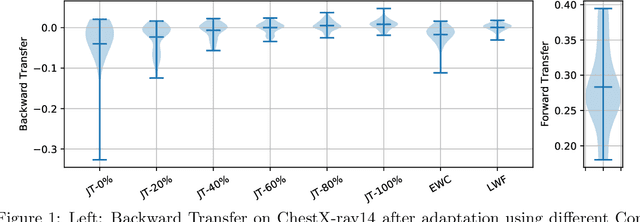
Abstract:Over the last years, Deep Learning has been successfully applied to a broad range of medical applications. Especially in the context of chest X-ray classification, results have been reported which are on par, or even superior to experienced radiologists. Despite this success in controlled experimental environments, it has been noted that the ability of Deep Learning models to generalize to data from a new domain (with potentially different tasks) is often limited. In order to address this challenge, we investigate techniques from the field of Continual Learning (CL) including Joint Training (JT), Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) and Learning Without Forgetting (LWF). Using the ChestX-ray14 and the MIMIC-CXR datasets, we demonstrate empirically that these methods provide promising options to improve the performance of Deep Learning models on a target domain and to mitigate effectively catastrophic forgetting for the source domain. To this end, the best overall performance was obtained using JT, while for LWF competitive results could be achieved - even without accessing data from the source domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge